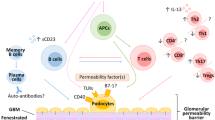
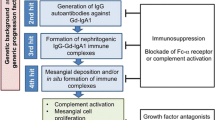
Abstract
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy (IgAN) is the most common primary glomerulonephritis worldwide. Up to 40% of IgAN patients develop end-stage kidney disease after 15–20 years. Despite the poor prognosis associated with this multifactorial disease, no clear treatment strategy has been identified, primarily due to the lack of understanding of its pathogenesis. Clinical observations indicate that aberrant IgAN immune systems, rather than intrinsic renal abnormalities, may be involved in its pathogenesis. Moreover, nephritogenic IgA and its related immune complexes are considered to be produced not only in the mucosa, but also in systemic immune sites, such as the bone marrow; however, there are numerous challenges to understanding this dynamic and complex immune axis in humans. Thus, several investigators have used experimental animal models. Although there are inter-strain differences in IgA molecules and immune responses between humans and rodents, animal models remain a powerful tool for investigating IgAN’s pathogenesis, and the subsequent development of effective treatments. Here, we introduced some classical models of IgAN with or without genetic manipulation and recent translational approaches with some promising models. This includes humanized mouse models expressing human IgA1 and human IgA Fc receptor (CD89) that develops spontaneously the disease. Pre-clinical studies targeting IgA1 are discussed. Together, animal models are very useful tools to study pathophysiology and to validate new therapeutic approaches for IgAN.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waldherr R, Rambausek M, Duncker WD, Ritz E (1989) Frequency of mesangial IgA deposits in a non-selected autopsy series. Nephrol Dial Transplant 4:943–946
Suganuma T (1994) Glomerular IgA deposits in an autopsy study. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi 36:813–822
Suzuki K, Honda K, Tanabe K, Toma H, Nihei H, Yamaguchi Y (2003) Incidence of latent mesangial IgA deposition in renal allograft donors in Japan. Kidney Int 63:2286–2294
Rifai A, Small PA, Teague PO, Ayoub EM (1979) Experimental IgA nephropathy. J Exp Med 150:1161–1173
Rifai A, Millard K (1985) Glomerular deposition of immune complexes prepared with monomeric or polymeric IgA. Clin Exp Immunol 60:363–368
Chen A, Wong SS, Rifai A (1988) Glomerular immune deposits in experimental IgA nephropathy: a continuum of circulating and in situ formed immune complexes. Am J Pathol 130:216–222
Isaacs K, Miller F, Lane B (1981) Experimental model for IgA nephropathy. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 20:419–426
Isaacs K, Miller F (1982) Role of antigen size and charge in immune complex glomerulonephritis. I. Active induction of disease with dextran and its derivatives. Lab Investig 47:198–205
Suzuki Y, Tomino Y (2007) The mucosa-bone-marrow axis in IgA nephropathy. Contrib Nephrol 157:70–79
Emancipator SN, Gallo GR, Lamm ME (1983) Experimental IgA nephropathy induced by oral immunization. J Exp Med 157:572–582
Coppo R, Basolo B, Rollino C, Roccatello D, Martina G, Amore A, Bongiorno G, Piccoli G (1986) Mediterranean diet and primary IgA nephropathy. Clin Nephrol 26:72–82
Kumar V, Sieniawska M, Beutner EH, Chorzelski TP (1988) Are immunological markers of gluten-sensitive enteropathy detectable in IgA nephropathy? Lancet 2:1307
Fornasieri A, Sinico RA, Maldifassi P, Bernasconi P, Vegni M, D’Amico G (1987) IgA-antigliadin antibodies in IgA mesangial nephropathy (Berger's disease). Br Med J 295:78–80
Rostoker G, Laurent J, André C, Cholin S, Lagrue G (1988) High levels of IgA antigliadin antibodies in patients who have IgA mesangial glomerulonephritis but not coeliac disease. Lancet 356-357
Coppo R, Mazzucco G, Martina G, Roccatello D, Amore A, Novara R, Bargoni A, Piccoli G, Sena LM (1989) Gluten-induced experimental IgA glomerulopathy. Lab Investig 60:499–506
Yan D, Rumbeiha WK, Pestka JJ (1998) Experimental murine IgA nephropathy following passive administration of vomitoxin-induced IgA monoclonal antibodies. Food Chem Toxicol 36:1095–1106
Pestka JJ (2003) Deoxynivalenol-induced IgA production and IgA nephropathy-aberrant mucosal immune response with systemic repercussions. Toxicol Lett 140-141:287–295
Shi Y, Pestka JJ (2006) Attenuation of mycotoxin-induced IgA nephropathy by eicosapentaenoic acid in the mouse: dose response and relation to IL-6 expression. J Nutr Biochem 17:697–706
Hinoshita F, Suzuki Y, Yokoyama K, Hara S, Yamada A, Ogura Y, Hashimoto H, Tomura S, Marumo F, Ueno Y (1997) Experimental IgA nephropathy induced by a low-dose environmental mycotoxin, nivalenol. Nephron 75:469–478
Gesualdo L, Lamm ME, Emancipator SN (1990) Defective oral tolerance promotes nephritogenesis in experimental IgA nephropathy induced by oral immunization. J Immunol 145:3684–3691
Monteiro RC, Van De Winkel JGJ (2003) IgA Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 21:177–204
Diebel ME, Diebel LN, Liberati DM (2011) Gender dimorphism in the gut: mucosal protection by estrogen stimulation of IgA transcytosis. J Trauma 71:474–479
Koyama A, Kobayashi M, Yamaguchi N, Yamagata K, Takano K, Nakajima M, Irie F, Goto M, Igarashi M, Iitsuka T, Aoki Y, Sakurai H, Sakurayama N, Fukao K (1995) Glomerulonephritis associated with MRSA infection: a possible role of bacterial superantigen. Kidney Int 47:207–216
Satoskar AA, Nadasdy G, Plaza JA, Sedmak D, Shidham G, Hebert L (2006) Nadasdy T:Staphylococcus infection-associated glomerulonephritis mimicking IgA nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 1:1179–1186
Sharmin S, Shimizu Y, Hagiwara M, Hirayama K, Koyama A (2004) Staphylococcus aureus antigens induce IgA-type glomerulonephritis in Balb/c mice. J Nephrol 17:504–511
Suzuki S, Nakatomi Y, Sato H, Tsukada H, Arakawa M (1994) Haemophilus parainfluenzae antigen and antibody in renal biopsy samples and serum of patients with IgA nephropathy. Lancet 343:12–16
Yamamoto C, Suzuki S, Kimura H, Yoshida H, Gejyo F (2002) Experimental nephropathy induced by Haemophilus parainfluenzae antigens. Nephron 90:320–327
Porter DD, Larsen AE, Porter HG (1980) Aleutian disease of mink. Adv Immunol 29:261–286
Portis JL, Coe JE (1979) Deposition of IgA in renal glomeruli of mink affected with Aleutian disease. Am J Pathol 96:227–236
Jessen RH, Emancipator SN, Jacobs GH (1992) Experimental IgA-IgG nephropathy induced by a viral respiratory pathogen. Dependence on antigen form and immune status. Lab Investig 67:379–386
Imai H, Nakamoto Y, Asakura K, Miki K, Yasuda T, Miura A (1985) Spontaneous glomerular IgA deposition in ddY mice: an animal model of IgA nephritis. Kidney Int 27:756–761
Muso E, Yoshida H, Takeuchi E, Yashiro M, Matsushima H, Oyama A, Suyama K, Kawamura T, Kamata T, Miyawaki S, Izui S, Sasayama S (1996) Enhanced production of glomerular extracellular matrix in a new mouse strain of high serum IgA ddY mice. Kidney Int 50:1946–1957
Suzuki H, Suzuki Y, Yamanaka T, Hirose S, Nishimura H, Toei J, Horikoshi S, Tomino Y (2005) Genome-wide association study in IgA nephropathy model identifies susceptibility locus on murine chromosome 10, in a region syntenic to human IGAN1 on chromosome 6q22-23. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:1289–1299
Okazaki K, Suzuki Y, Otsuji M, Suzuki H, Kihara M, Kajiyama T, Hashimoto A, Nishimura H, Brown R, Hall S, Novak J, Izui S, Hirose S, Tomino Y (2012) Establishment of a novel ddY mouse model with early onset IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:1364–1374
van den Wall Bake AW, Daha MR, van Es LA (1989) Immunopathogenetic aspects of IgA nephropathy. Nephrologie 10:141–145
de Fijter JW, Eijgenraam JW, Braam CA, Holmgren J, Daha MR, van Es LA, van den Wall Bake AW (1996) Deficient IgA1 immune response to nasal cholera toxin subunit B in primary IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 50:952–961
Suzuki Y, Suzuki H, Sato D, Kajiyama T, Okazaki K, Hashimoto A, Kihara M, Yamaji K, Satake K, Nakata J, Aizawa M, Novak J, Tomino Y (2011) Reevaluation of the mucosa-bone marrow axis in IgA nephropathy with animal models. Adv Otorhinolaryngol 72:64–67
Suzuki H, Suzuki Y, Narita I, Aizawa M, Kihara M, Yamanaka T, Kanou T, Tsukaguchi H, Novak J, Horikoshi S, Tomino Y (2008) Toll-like receptor 9 affects severity of IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:2384–2395
Kajiyama T, Suzuki Y, Kihara M, Suzuki H, Horikoshi S, Tomino Y (2011) Different pathological roles of toll-like receptor 9 on mucosal B cells and dendritic cells in murine IgA nephropathy. Clin Dev Immunol 2011:819646
Kano T, Suzuki H, Makita Y, Fukao Y, Suzuki Y (in press) Nasal-associated lymphoid tissue is the major induction site for nephritogenic IgA in murine IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 2021
Sato D, Suzuki Y, Kano T, Suzuki H, Matsuoka J, Yokoi H, Horikoshi S, Ikeda K, Tomino Y (2012) Tonsillar TLR9 expression and efficacy of tonsillectomy with steroid pulse therapy in IgA nephropathy patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:1090–1097
Hirano K, Matsuzaki K, Yasuda T, Nishikawa M, Yasuda Y, Koike K, Maruyama S, Yokoo T, Matsuo S, Kawamura T, Suzuki Y (2019) Association between tonsillectomy and outcomes in patients with immunoglobulin A nephropathy. JAMA Netw Open 2:e194772
Suzuki Y, Nakata J, Suzuki H, Sato D, Kano T, Yanagawa H, Matsuzaki K, Horikoshi S, Novak J, Tomino Y (2014) Changes in nephritogenic serum galactose-deficient IgA1 in IgA nephropathy following tonsillectomy and steroid therapy. PLoS One 9:e89707
Suzuki H, Suzuki Y, Aizawa M, Yamanaka T, Kihara M, Pang H, Horikoshi S, Tomino Y (2007) Th1 polarization in murine IgA nephropathy directed by bone marrow-derived cells. Kidney Int 72:319–327
Aizawa M, Suzuki Y, Suzuki H, Pang H, Kihara M, Nakata J, Yamaji K, Horikoshi S, Tomino Y (2014) Uncoupling of glomerular IgA deposition and disease progression in alymphoplasia mice with IgA nephropathy. PLoS One 9:e95365
Nakata J, Suzuki Y, Suzuki H, Sato D, Kano T, Horikoshi S, Novak J, Tomino Y (2013) Experimental evidence of cell dissemination playing a role in pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy in multiple lymphoid organs. Nephrol Dial Transplant 28:320–326
Gharavi AG, Kiryluk K, Choi M, Li Y, Hou P, Xie J, Sanna-Cherchi S, Men CJ, Julian BA, Wyatt RJ, Novak J, He JC, Wang H, Lv J, Zhu L, Wang W, Wang Z, Yasuno K, Gunel M, Mane S, Umlauf S, Tikhonova I, Beerman I, Savoldi S, Magistroni R, Ghiggeri GM, Bodria M, Lugani F, Ravani P, Ponticelli C, Allegri L, Boscutti G, Frasca G, Amore A, Peruzzi L, Coppo R, Izzi C, Viola BF, Prati E, Salvadori M, Mignani R, Gesualdo L, Bertinetto F, Mesiano P, Amoroso A, Scolari F, Chen N, Zhang H, Lifton RP (2011) Genome-wide association study identifies dusceptibility loci for IgA nephropathy. Nat Genet 43:321–327
Kiryluk K, Li Y, Scolari F, Sanna-Cherchi S, Choi M, Verbitsky M, Fasel D, Lata S, Prakash S, Shapiro S, Fischman C, Snyder HJ, Appel G, Izzi C, Viola BF, Dallera N, Del Vecchio L, Barlassina C, Salvi E, Bertinetto FE, Amoroso A, Savoldi S, Rocchietti M, Amore A, Peruzzi L, Coppo R, Salvadori M, Ravani P, Magistroni R, Ghiggeri GM, Caridi G, Bodria M, Lugani F, Allegri L, Delsante M, Maiorana M, Magnano A, Frasca G, Boer E, Boscutti G, Ponticelli C, Mignani R, Marcantoni C, Di Landro D, Santoro D, Pani A, Polci R, Feriozzi S, Chicca S, Galliani M, Gigante M, Gesualdo L, Zamboli P, Battaglia GG, Garozzo M, Maixnerová D, Tesar V, Eitner F, Rauen T, Floege J, Kovacs T, Nagy J, Mucha K, Pączek L, Zaniew M, Mizerska-Wasiak M, Roszkowska-Blaim M, Pawlaczyk K, Gale D, Barratt J, Thibaudin L, Berthoux F, Canaud G, Boland A, Metzger M, Panzer U, Suzuki H, Goto S, Narita I, Caliskan Y, Xie J, Hou P, Chen N, Zhang H, Wyatt RJ, Novak J, Julian BA, Feehally J, Stengel B, Cusi D, Lifton RP, Gharavi AG (2014) Discovery of new risk loci for IgA nephropathy implicates genes involved in immunity against intestinal pathogens. Nat Genet 46:1187–1196
Yu XQ, Li M, Zhang H, Low HQ, Wei X, Wang JQ, Sun LD, Sim KS, Li Y, Foo JN, Wang W, Li ZJ, Yin XY, Tang XQ, Fan L, Chen J, Li RS, Wan JX, Liu ZS, Lou TQ, Zhu L, Huang XJ, Zhang XJ, Liu ZH, Liu JJ (2011) A genome-wide association study in Han Chinese identifies multiple susceptibility loci for IgA nephropathy. Nat Genet 44:178–182
Kim YG, Alvarez M, Suzuki H, Hirose S, Izui S, Tomino Y, Bertrand H, Suzuki Y (2015) Pathogenic role of a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) in murine IgA nephropathy. PLoS One 10:e0137044
Myette JR, Kano T, Suzuki H, Sloan SE, Szretter KJ, Ramakrishnan B, Adari H, Deotale KD, Engler F, Shriver Z, Wollacott AM, Suzuki Y, Pereira BJG (2019) A Proliferation Inducing Ligand (APRIL) targeted antibody is a safe and effective treatment of murine IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 96:104–116
Muto M, Manfroi B, Suzuki H, Joh K, Nagai M, Wakui S, Righini C, Maiguma M, Izui S, Tomino Y, Huard B, Suzuki Y (2017) Toll-like receptor 9 stimulation induces aberrant expression of a proliferation-inducing ligand by tonsillar germinal center B cell in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 28:1227–1238
Makita Y, Suzuki H, Kano T, Takahata A, Julian BA, Novak J, Suzuki Y (2020) TLR9 activation induces aberrant IgA glycosylation via APRIL-and IL-6-mediated pathways in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int 97:340–349
Suzuki H, Fan R, Zhang Z, Brown R, Hall S, Julian BA, Chatham WW, Suzuki Y, Wyatt RJ, Moldoveanu Z, Lee JY, Robinson J, Tomana M, Tomino Y, Mestecky J, Novak J (2009) Aberrantly glycosylated IgA1 in IgA nephropathy patients is recognized by IgG antibodies with restricted heterogeneity. J Clin Invest 119:1668–1677
Suzuki Y, Matsuzaki K, Suzuki H, Okazaki K, Yanagawa H, Ieiri N, Sato M, Sato T, Taguma Y, Matsuoka J, Horikoshi S, Novak J, Hotta O, Tomino Y (2014) Serum levels of galactose deficient IgA1 and related immune complex are associated with disease activity of IgA nephropathy. Clin Exp Nephrol 18:770–777
Yanagawa H, Suzuki H, Suzuki Y, Kiryluk K, Gharavi AG, Matsuoka K, Makita Y, Julian BA, Novak J, Tomino Y (2014) A panel of serum biomarkers differentiates IgA nephropathy from other renal diseases. PLoS One 9:e98081
Placzek WJ, Yanagawa H, Makita Y, Renfrow MB, Julian BA, Rizk DV, Suzuki Y, Novak J, Suzuki H (2018) Serum galactose-deficient-IgA1 and IgG autoantibodies correlate in patients with IgA nephropathy. PLoS One 13:e0190967
Suzuki Y, Suzuki H, Makita Y, Takahata A, Takahashi K, Muto M, Sasaki Y, Kelimu A, Matsuzaki K, Yanagawa H, Okazaki K, Tomino Y (2014) Diagnosis and activity assessment of IgA nephropathy: current perspectives on non-invasive testing with aberrantly glycosylated IgA-related biomarkers. Int J Nephrol Renov Dis 7:409–414
Arai S, Kitada K, Yamazaki T, Takai R, Zhang X, Tsugawa Y, Sugisawa R, Matsumoto A, Mori M, Yoshihara Y, Doi K, Maehara N, Kusunoki S, Takahata A, Noiri E, Suzuki Y, Yahagi N, Nishiyama A, Gunaratnam L, Takano T, Miyazaki T (2016) AIM/CD5L enhances intraluminal debris clearance and ameliorates acute kidney injury. Nat Med 22:183–193
Takahata A, Arai S, Hiramoto E, Kitada K, Kato R, Makita Y, Suzuki H, Nakata J, Araki K, Miyazaki T, Suzuki Y (2020) Crucial role of AIM/CD5L in the development of glomerular inflammation in IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 31:2013–2024
Sugisawa R, Hiramoto E, Matsuoka S, Iwai S, Takai R, Yamazaki T, Mori N, Okada Y, Takeda N, Yamamura K, Arai T, Arai S, Miyazaki T (2016) Impact of feline AIM on the susceptibility of cats to renal disease. Sci Rep 6:35251
Berger J, Hinglais N (1968) Intercapillary deposits of IgA-IgG. J Urol Nephrol (Paris) 74(9):694–695
Maruoka T, Nagata T, Kasahara M (2004) Identification of the rat IgA Fc receptor encoded in the leukocyte receptor complex. Immunogenetics. 55(10):712–716
van Egmond M, van Vuuren AJ, Morton HC, van Spriel AB, Shen L, Hofhuis FM, Saito T, Mayadas TN, Verbeek JS, van de Winkel JG (1999) Human immunoglobulin A receptor (FcalphaRI, CD89) function in transgenic mice requires both FcR gamma chain and CR3 (CD11b/CD18). Blood. 93(12):4387–4394
Launay P, Grossetete B, Arcos-Fajardo M, Gaudin E, Torres SP, Beaudoin L, Patey-Mariaud de Serre N, Lehuen A, Monteiro RC (2000) Fca receptor (CD89) mediates the development of Immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy (Berger’s Disease): evidence for pathogenic soluble receptor-IgA complexes in patients and CD89 transgenic mice. J Exp Med 191:1999–2009
Berthelot L, Papista C, Maciel TT, Biarnes-Pelicot M, Tissandie E, Wang PHM, Tamouza H, Jamin A, Bex-Coudrat J, Gestin A, Boumediene A, Arcos-Fajardo M, England P, Pillebout E, Walker F, Daugas E, Vrtosvnik F, Flamant M, Benhamou M, Cogné M, Moura IC, Monteiro RC (2012) Transglutaminase is essential for IgA nephropathy development acting through IgA receptors. J Exp Med 209(4):793–806
Kanamaru Y, Arcos-Fajardo M, Moura IC, Tsuge T, Cohen H, Essig M, Vrtovsnik F, Loirat C, Peuchmaur M, Beaudoin L, Launay P, Lehuen A, Blank U, Monteiro RC (2007) Fc alpha receptor I activation induces leukocyte recruitment and promotes aggravation of glomerulonephritis through the FcR gamma adaptor. Eur J Immunol 37:1116–1128
Duchez S, Amin R, Cogné N, Delpy L, Sirac C, Pascal V, Corthésy B, Cogné M (2010) Premature replacement of mu with alpha immunoglobulin chains impairs lymphopoiesis and mucosal homing but promotes plasma cell maturation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(7):3064–3069. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0912393107 Epub 2010 Jan 28
Moura IC, Centelles MN, Arcos-Fajardo M, Malheiros DM, Collawn JF, Cooper MD, Monteiro RC (2001) Identification of the transferrin receptor as a novel immunoglobulin A1 receptor and its enhanced expression on mesangial cells in IgA nephropathy. J Exp Med 194:417–425
Haddad E, Moura IC, Arcos-Fajardo M, Macher M-A, Baudouin V, Alberti C, Loirat C, Monteiro RC, Peuchmaur M (2003) Enhanced expression of the CD71 mesangial IgA1 receptor in Berger’s disease and Henoch-Schönlein nephritis : association between CD71 expression and IgA deposits. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:327–337
Lebreton C, Ménard S, Abed J, Moura IC, Coppo R, Dugave C, Monteiro RC, Fricot A, Traore MG, Griffin M, Cellier C, Malamut G, Cerf-Bensussan N, Heyman M (2012) Interactions among secretory immunoglobulin A, CD71, and transglutaminase-2 affect permeability of intestinal epithelial cells to gliadin peptides. Gastroenterology. 143(3):698–707
Oruc Z, Oblet C, Boumediene A, Druilhe A, Pascal V, Le Rumeur E, Cuvillier A, El Hamel C, Lecardeur S, Leanderson T, Morelle W, Demengeot J, Aldigier JC, Cogné M (2016) IgA structure variations associate with immune stimulations and IgA mesangial deposition. J Am Soc Nephrol 27(9):2748–2761. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2015080911 Epub 2016 Jan 29
Wehbi B, Oblet C, Boyer F, Huard A, Druilhe A, Paraf F, Cogné E, Moreau J, El Makhour Y, Badran B, Van Egmond M, Cogné M, Aldigier JC (2019) Mesangial deposition can strongly involve innate-like IgA molecules lacking affinity maturation. J Am Soc Nephrol 30(7):1238–1249. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2018111089 Epub 2019 Jun 21
Coppo R, Amore A, Roccatello D (1992) Dietary antigens and primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 2(10 Suppl):S173–S180
Papista C, Lechner S, Ben Mkaddem S, LeStang MB, Abbad L, Bex-Coudrat J, Pillebout E, Chemouny JM, Jablonski M, Flamant M, Daugas E, Vrtovsnik F, Yiangou M, Berthelot L, Monteiro RC (2015) Gluten exacerbates IgA nephropathy in humanized mice through gliadin-CD89 interaction. Kidney Int 88(2):276–285. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2015.94 Epub 2015 Mar 25
Lechner SM, Abbad L, Boedec E, Papista C, Le Stang MB, Moal C, Maillard J, Jamin A, Bex-Coudrat J, Wang Y, Li A, Martini PG, Monteiro RC, Berthelot L (2016) IgA1 protease treatment reverses mesangial deposits and hematuria in a model of IgA nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 27(9):2622–2629. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2015080856
Segelmark M, Uhlin F, Sonesson E on behalf of the GOOD-IDES-01 study team. The immunoglobulin G degrading enzyme imlifidase for the treatment of anti-GBM disease – the GOOD-IDES-01 trial. Poster session at ASN in 2020
Fellström BC, Barratt J, Cook H, Coppo R, Feehally J, de Fijter JW, Floege J, Hetzel G, Jardine AG, Locatelli F, Maes BD, Mercer A, Ortiz F, Praga M, Sørensen SS, Tesar V, Del Vecchio L (2017) NEFIGAN Trial Investigators. Targeted-release budesonide versus placebo in patients with IgA nephropathy (NEFIGAN): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2b trial. Lancet. 389(10084):2117–2127. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30550-0 Epub 2017 Mar
De Angelis M, Montemurno E, Piccolo M, Vannini L, Lauriero G, Maranzano V, Gozzi G, Serrazanetti D, Dalfino G, Gobbetti M et al (2014) Microbiota and metabolome associated with immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN). PLoS One 9:e99006. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099006
Chemouny JM, Gleeson PJ, Abbad L, Lauriero G, Boedec E, Le Roux K, Monot C, Bredel M, Bex-Coudrat J, Sannier A, Daugas E, Vrtovsnik F, Gesualdo L, Leclerc M, Berthelot L, Ben Mkaddem S, Lepage P, Monteiro RC (2019) Modulation of the microbiota by oral antibiotics treats immunoglobulin A nephropathy in humanized mice. Nephrol Dial Transplant 34(7):1135–1144. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfy323
Lauriero G, Abbad L, Vacca M, Calasso M, Chemouny J, Berthelot L, Gesualdo L, De Angelis M, Monteiro RC. Fecal microbiota transplantation modulates renal phenotype in the humanized mouse model of IgA Nephropathy (article in revision)
Di Leo V, Gleeson PJ, Sallustio F, Bounaix C, Da Silva J, Loreto G, Mkaddem SB, Monteiro RC (2021) Rifaximin as a potential treatment for IgA nephropathy in a humanized mice model. J Pers Med 11:309
Zheng F, Kundu GC, Zhang Z, Ward J, DeMayo F, Mukherjee AB (1999) Uteroglobin is essential in preventing immunoglobulin A nephropathy in mice. Nat Med 5(9):1018–1025. https://doi.org/10.1038/12458
Coppo R, Chiesa M, Cirina P, Peruzzi L, Amore A, European IgACE Study Group (2002) In human IgA nephropathy uteroglobin does not play the role inferred from transgenic mice. Am J Kidney Dis 40(3):495–503
Wang J, Anders RA, Wu Q, Peng D, Cho JH, Sun Y, Karaliukas R, Kang HS, Turner JR, Fu YX (2004) Dysregulated LIGHT expression on T cells mediates intestinal inflammation and contributes to IgA nephropathy. J Clin Invest 113:826–835
Marquina R, Díez MA, López-Hoyos M, Buelta L, Kuroki A, Kikuchi S et al (2004) Inhibition of B cell death causes the development of an IgA nephropathy in (New Zealand white x C57BL/6)F(1)-bcl-2 transgenic mice. J Immunol 172(11):7177–7185
McCarthy DD, Kujawa J, Wilson C, Papandile A, Poreci U, Porfilio EA, Ward L, Lawson MAE, Macpherson AJ, McCoy KD, Pei Y, Novak L, Lee JY, Julian BA, Novak J, Ranger A, Gommerman JL, Browning JL (2011) Mice overexpressing BAFF develop a commensal flora-dependent, IgA-associated nephropathy. J Clin Invest 121:3991–4002
Nishie T, Miyaishi O, Azuma H, Kameyama A, Naruse C, Hashimoto N, Yokoyama H, Narimatsu H, Wada T, Asano M (2007) Development of immunoglobulin A nephropathy- like disease in beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase-I-deficient mice. Am J Pathol févr 170(2):447–456
Funding
A part of study with gddY mice was funded by a research grant from the Study Group on IgA Nephropathy, Grant-in-Aid for Progressive Renal Disease Research, Research on Intractable Disease from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan, and AMED under Grant Number JP21gm0010006; RCM acknowledges funding by ANR and Labex Inflamex (ANR-11-IDEX-0005-02) from French government, Inserm, and Fondation pour la recherche medicale (FRM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All experiments with a1KICD89Tg mice were performed in accordance with the French Council of Animal Care guidelines and national ethical guidelines of Paris-Nord Animal Care Committee (Comité d’Éthique Expérimentation Animale Bichat-Debré). The experimental protocol gddY mice for gd was approved by the Ethics Review Committee for Animal Experimentation of Juntendo University Faculty of Medicine.
Informed consent
Not needed for animal studies.
Conflict of interest
Some studies with gddY mice were in collaboration with Kyowa-Kirin Co ltd., Visterra Inc. Some studies of α1KICD89Tg mice were funded by Shire Co.
Additional information
This article is a contribution to the Special issue on: The IgA system, IgA nephropathy and IgA vasculitis - Guest Editors: Jürgen Floege & Jonathan Barratt
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monteiro, R.C., Suzuki, Y. Are there animal models of IgA nephropathy?. Semin Immunopathol 43, 639–648 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-021-00878-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-021-00878-5