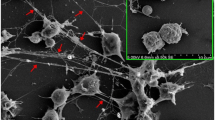
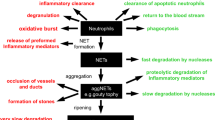
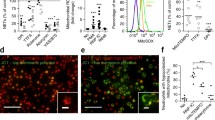
Abstract
Autoantibodies to DNA and histones (chromatin) are the defining antigen specificity in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and related musculoskeletal disorders but the mechanisms responsible for their induction remain mysterious. That situation rapidly changed once neutrophil extracellular chromatin traps (NETs) were discovered and observed to play a conserved role in innate immune responses to a broad variety of microbial pathogens. At the center of an infectious process, neutrophils exert various antimicrobial defenses, including the release of nuclear chromatin into the extracellular space. The externalized NETs, a complex meshwork of nuclear chromatin and antimicrobial proteins, serve to immobilize and degrade microbial pathogens. Here, we critically evaluate the evidence supporting NETs versus apoptotic bodies as a source for nuclear antigens in autoimmunity. We also discuss the possibility that NET chromatin forms an essential component of immune deposits in the pathogenesis of glomerulonephritis in SLE and other autoimmune immune complex diseases.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park H, Bourla AB, Kastner DL, Colbert RA, Siegel RM (2012) Lighting the fires within: the cell biology of autoinflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Immunol 12(8):570–580. doi:10.1038/nri3261
Thomas R (2010) The balancing act of autoimmunity: central and peripheral tolerance versus infection control. Int Rev Immunol 29(2):211–233. doi:10.3109/08830180903434219
Nowling TK, Gilkeson GS (2011) Mechanisms of tissue injury in lupus nephritis. Arthritis Res Ther 13(6):250. doi:10.1186/ar3528
McQueen F (2012) A B cell explanation for autoimmune disease: the forbidden clone returns. Postgrad Med J 88(1038):226–233. doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2011-130364
Pisetsky DS (2012) Antinuclear antibodies in rheumatic disease: a proposal for a function-based classification. Scand J Immunol 76(3):223–228. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3083.2012.02728.x
Hoffman IE, Peene I, Meheus L, Huizinga TW, Cebecauer L, Isenberg D, De Bosschere K, Hulstaert F, Veys EM, De Keyser F (2004) Specific antinuclear antibodies are associated with clinical features in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 63(9):1155–1158. doi:10.1136/ard.2003.013417
Isenberg D, Rahman A (2006) Systemic lupus erythematosus—2005 annus mirabilis? Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 2(3):145–152. doi:10.1038/ncprheum0116
Hahn BH (1998) Antibodies to DNA. N Engl J Med 338(19):1359–1368. doi:10.1056/NEJM199805073381906
Brunner HI, Huggins J, Klein-Gitelman MS (2011) Pediatric SLE—towards a comprehensive management plan. Nat Rev Rheumatol 7(4):225–233. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2011.15
Liu Z, Davidson A (2012) Taming lupus-a new understanding of pathogenesis is leading to clinical advances. Nat Med 18(6):871–882. doi:10.1038/nm.2752
Gabriel SE (2001) The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 27(2):269–281
Falgarone G, Jaen O, Boissier MC (2005) Role for innate immunity in rheumatoid arthritis. Joint Bone Spine 72(1):17–25. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2004.05.013
Nandakumar KS, Holmdahl R (2006) Antibody-induced arthritis: disease mechanisms and genes involved at the effector phase of arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 8(6):223. doi:10.1186/ar2089
Balint GP, Balint PV (2004) Felty’s syndrome. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 18(5):631–645. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2004.05.002
Shlomchik MJ, Marshak-Rothstein A, Wolfowicz CB, Rothstein TL, Weigert MG (1987) The role of clonal selection and somatic mutation in autoimmunity. Nature 328(6133):805–811. doi:10.1038/328805a0
Schellekens GA, de Jong BA, van den Hoogen FH, van de Putte LB, van Venrooij WJ (1998) Citrulline is an essential constituent of antigenic determinants recognized by rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies. J Clin Invest 101(1):273–281. doi:10.1172/JCI1316
Bicker KL, Thompson PR (2013) The protein arginine deiminases: structure, function, inhibition, and disease. Biopolymers 99(2):155–163. doi:10.1002/bip.22127
Rohrbach AS, Slade DJ, Thompson PR, Mowen KA (2012) Activation of PAD4 in NET formation. Front Immunol 3:360. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2012.00360
Hermansson M, Artemenko K, Ossipova E, Eriksson H, Lengqvist J, Makrygiannakis D, Catrina AI, Nicholas AP, Klareskog L, Savitski M, Zubarev RA, Jakobsson PJ (2010) MS analysis of rheumatoid arthritic synovial tissue identifies specific citrullination sites on fibrinogen. Proteomics Clin Appl 4(5):511–518. doi:10.1002/prca.200900088
Suzuki A, Yamada R, Chang X, Tokuhiro S, Sawada T, Suzuki M, Nagasaki M, Nakayama-Hamada M, Kawaida R, Ono M, Ohtsuki M, Furukawa H, Yoshino S, Yukioka M, Tohma S, Matsubara T, Wakitani S, Teshima R, Nishioka Y, Sekine A, Iida A, Takahashi A, Tsunoda T, Nakamura Y, Yamamoto K (2003) Functional haplotypes of PADI4, encoding citrullinating enzyme peptidylarginine deiminase 4, are associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet 34(4):395–402. doi:10.1038/ng1206
Nakashima K, Hagiwara T, Ishigami A, Nagata S, Asaga H, Kuramoto M, Senshu T, Yamada M (1999) Molecular characterization of peptidylarginine deiminase in HL-60 cells induced by retinoic acid and 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3). J Biol Chem 274(39):27786–27792
Dwivedi N, Upadhyay J, Neeli I, Khan S, Pattanaik D, Myers L, Kirou KA, Hellmich B, Knuckley B, Thompson PR, Crow MK, Mikuls TR, Csernok E, Radic M (2012) Felty’s syndrome autoantibodies bind to deiminated histones and neutrophil extracellular chromatin traps. Arthritis Rheum 64(4):982–992. doi:10.1002/art.33432
Holman HR, Kunkel HG (1957) Affinity between the lupus erythematosus serum factor and cell nuclei and nucleoprotein. Science 126(3265):162–163
Ceppellini R, Polli E, Celada F (1957) A DNA-reacting factor in serum of a patient with lupus erythematosus diffusus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 96(3):572–574
Miescher P (1957) The antigenic constituents of the neutrophilic leukocyte with special reference to the L. E. phenomenon. Vox Sang 2(3):145–158
Koffler D, Schur PH, Kunkel HG (1967) Immunological studies concerning the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med 126(4):607–624
Leadbetter EA, Rifkin IR, Hohlbaum AM, Beaudette BC, Shlomchik MJ, Marshak-Rothstein A (2002) Chromatin-IgG complexes activate B cells by dual engagement of IgM and toll-like receptors. Nature 416(6881):603–607. doi:10.1038/416603a
Fukui R, Saitoh S, Kanno A, Onji M, Shibata T, Ito A, Matsumoto M, Akira S, Yoshida N, Miyake K (2011) Unc93B1 Restricts systemic lethal inflammation by orchestrating toll-like receptor 7 and 9 trafficking. Immunity 35(1):69–81. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2011.05.010
Pisitkun P, Deane JA, Difilippantonio MJ, Tarasenko T, Satterthwaite AB, Bolland S (2006) Autoreactive B cell responses to RNA-related antigens due to TLR7 gene duplication. Science 312(5780):1669–1672. doi:10.1126/science.1124978
Subramanian S, Tus K, Li QZ, Wang A, Tian XH, Zhou J, Liang C, Bartov G, McDaniel LD, Zhou XJ, Schultz RA, Wakeland EK (2006) A Tlr7 translocation accelerates systemic autoimmunity in murine lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(26):9970–9975. doi:10.1073/pnas.0603912103
Santiago-Raber ML, Kikuchi S, Borel P, Uematsu S, Akira S, Kotzin BL, Izui S (2008) Evidence for genes in addition to Tlr7 in the Yaa translocation linked with acceleration of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 181(2):1556–1562
Nickerson KM, Christensen SR, Shupe J, Kashgarian M, Kim D, Elkon K, Shlomchik MJ (2010) TLR9 regulates TLR7- and MyD88-dependent autoantibody production and disease in a murine model of lupus. J Immunol 184(4):1840–1848. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0902592
Foote J, Milstein C (1991) Kinetic maturation of an immune response. Nature 352(6335):530–532. doi:10.1038/352530a0
Murakami A, Takahashi Y, Nishimura M, Shimizu T, Azuma T (2010) The amino acid residue at position 95 and the third CDR region in the H chain determine the ceiling affinity and the maturation pathway of an anti-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)acetyl antibody. Mol Immunol 48(1–3):48–58. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2010.09.013
Shlomchik MJ, Aucoin AH, Pisetsky DS, Weigert MG (1987) Structure and function of anti-DNA autoantibodies derived from a single autoimmune mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84(24):9150–9154
Marion TN, Bothwell AL, Briles DE, Janeway CA Jr (1989) IgG anti-DNA autoantibodies within an individual autoimmune mouse are the products of clonal selection. J Immunol 142(12):4269–4274
Radic MZ, Weigert M (1994) Genetic and structural evidence for antigen selection of anti-DNA antibodies. Annu Rev Immunol 12:487–520. doi:10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.002415
Marion TN, Tillman DM, Jou NT, Hill RJ (1992) Selection of immunoglobulin variable regions in autoimmunity to DNA. Immunol Rev 128:123–149
Tillman DM, Jou NT, Hill RJ, Marion TN (1992) Both IgM and IgG anti-DNA antibodies are the products of clonally selective B cell stimulation in (NZB × NZW)F1 mice. J Exp Med 176(3):761–779
Radic MZ, Mackle J, Erikson J, Mol C, Anderson WF, Weigert M (1993) Residues that mediate DNA binding of autoimmune antibodies. J Immunol 150(11):4966–4977
Wellmann U, Letz M, Herrmann M, Angermuller S, Kalden JR, Winkler TH (2005) The evolution of human anti-double-stranded DNA autoantibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(26):9258–9263. doi:10.1073/pnas.0500132102
Madaio MP, Hodder S, Schwartz RS, Stollar BD (1984) Responsiveness of autoimmune and normal mice to nucleic acid antigens. J Immunol 132(2):872–876
Desai DD, Marion TN (2000) Induction of anti-DNA antibody with DNA-peptide complexes. Int Immunol 12(11):1569–1578
Konstantinidis DG, Pushkaran S, Johnson JF, Cancelas JA, Manganaris S, Harris CE, Williams DA, Zheng Y, Kalfa TA (2012) Signaling and cytoskeletal requirements in erythroblast enucleation. Blood 119(25):6118–6127. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-09-379263
Nagata S (2005) DNA degradation in development and programmed cell death. Annu Rev Immunol 23:853–875. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.23.021704.115811
Radic M, Marion T, Monestier M (2004) Nucleosomes are exposed at the cell surface in apoptosis. J Immunol 172(11):6692–6700
Casciola-Rosen LA, Anhalt G, Rosen A (1994) Autoantigens targeted in systemic lupus erythematosus are clustered in two populations of surface structures on apoptotic keratinocytes. J Exp Med 179(4):1317–1330
van Bavel CC, Dieker J, Muller S, Briand JP, Monestier M, Berden JH, van der Vlag J (2009) Apoptosis-associated acetylation on histone H2B is an epitope for lupus autoantibodies. Mol Immunol 47(2–3):511–516. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2009.08.009
Radic MZ, Shah K, Zhang W, Lu Q, Lemke G, Hilliard GM (2006) Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein P2 is an autoantibody target in mice deficient for Mer, Axl, and Tyro3 receptor tyrosine kinases. J Immunol 176(1):68–74
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR (1972) Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26(4):239–257
Fadok VA, Bratton DL, Guthrie L, Henson PM (2001) Differential effects of apoptotic versus lysed cells on macrophage production of cytokines: role of proteases. J Immunol 166(11):6847–6854
Xu H, Li H, Suri-Payer E, Hardy RR, Weigert M (1998) Regulation of anti-DNA B cells in recombination-activating gene-deficient mice. J Exp Med 188(7):1247–1254
Kawane K, Fukuyama H, Yoshida H, Nagase H, Ohsawa Y, Uchiyama Y, Okada K, Iida T, Nagata S (2003) Impaired thymic development in mouse embryos deficient in apoptotic DNA degradation. Nat Immunol 4(2):138–144. doi:10.1038/ni881
Mevorach D, Zhou JL, Song X, Elkon KB (1998) Systemic exposure to irradiated apoptotic cells induces autoantibody production. J Exp Med 188(2):387–392
Fransen JH, Berden JH, Koeter CM, Adema GJ, Van Der Vlag J, Hilbrands LB (2012) Effect of administration of apoptotic blebs on disease development in lupus mice. Autoimmunity 45(4):290–297. doi:10.3109/08916934.2012.664668
Botto M, Walport MJ (2002) C1q, autoimmunity and apoptosis. Immunobiology 205(4–5):395–406. doi:10.1078/0171-2985-00141
Nagata S, Hanayama R, Kawane K (2010) Autoimmunity and the clearance of dead cells. Cell 140(5):619–630. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.014
Wakeland EK, Liu K, Graham RR, Behrens TW (2001) Delineating the genetic basis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunity 15(3):397–408
Cline AM, Radic MZ (2004) Apoptosis, subcellular particles, and autoimmunity. Clin Immunol 112(2):175–182. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2004.02.017
Harper L, Ren Y, Savill J, Adu D, Savage CO (2000) Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies induce reactive oxygen-dependent dysregulation of primed neutrophil apoptosis and clearance by macrophages. Am J Pathol 157(1):211–220. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64532-4
Brinkmann V, Reichard U, Goosmann C, Fauler B, Uhlemann Y, Weiss DS, Weinrauch Y, Zychlinsky A (2004) Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 303(5663):1532–1535. doi:10.1126/science.1092385
Hirsch JG (1958) Bactericidal action of histone. J Exp Med 108(6):925–944
Kim HS, Yoon H, Minn I, Park CB, Lee WT, Zasloff M, Kim SC (2000) Pepsin-mediated processing of the cytoplasmic histone H2A to strong antimicrobial peptide buforin I. J Immunol 165(6):3268–3274
Brinkmann V, Zychlinsky A (2007) Beneficial suicide: why neutrophils die to make NETs. Nat Rev Microbiol 5(8):577–582. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1710
Neeli I, Dwivedi N, Khan S, Radic M (2009) Regulation of extracellular chromatin release from neutrophils. J Innate Immun 1(3):194–201. doi:10.1159/000206974
Garcia-Romo GS, Caielli S, Vega B, Connolly J, Allantaz F, Xu Z, Punaro M, Baisch J, Guiducci C, Coffman RL, Barrat FJ, Banchereau J, Pascual V (2011) Netting neutrophils are major inducers of type I IFN production in pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci Transl Med 3(73):73ra20. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3001201
Hakkim A, Fuchs TA, Martinez NE, Hess S, Prinz H, Zychlinsky A, Waldmann H (2011) Activation of the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway is required for neutrophil extracellular trap formation. Nat Chem Biol 7(2):75–77. doi:10.1038/nchembio.496
Steinberg BE, Grinstein S (2007) Unconventional roles of the NADPH oxidase: signaling, ion homeostasis, and cell death. Sci STKE 2007(379):pe11. doi:10.1126/stke.3792007pe11
Fuchs TA, Abed U, Goosmann C, Hurwitz R, Schulze I, Wahn V, Weinrauch Y, Brinkmann V, Zychlinsky A (2007) Novel cell death program leads to neutrophil extracellular traps. J Cell Biol 176(2):231–241. doi:10.1083/jcb.200606027
Brinkmann V, Zychlinsky A (2012) Neutrophil extracellular traps: is immunity the second function of chromatin? J Cell Biol 198(5):773–783. doi:10.1083/jcb.201203170
Bianchi M, Hakkim A, Brinkmann V, Siler U, Seger RA, Zychlinsky A, Reichenbach J (2009) Restoration of NET formation by gene therapy in CGD controls aspergillosis. Blood 114(13):2619–2622. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-05-221606
Papayannopoulos V, Staab D, Zychlinsky A (2011) Neutrophil elastase enhances sputum solubilization in cystic fibrosis patients receiving DNase therapy. PLoS One 6(12):e28526. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028526
Metzler KD, Fuchs TA, Nauseef WM, Reumaux D, Roesler J, Schulze I, Wahn V, Papayannopoulos V, Zychlinsky A (2011) Myeloperoxidase is required for neutrophil extracellular trap formation: implications for innate immunity. Blood 117(3):953–959. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-06-290171
Li P, Li M, Lindberg MR, Kennett MJ, Xiong N, Wang Y (2010) PAD4 Is essential for antibacterial innate immunity mediated by neutrophil extracellular traps. J Exp Med 207(9):1853–1862. doi:10.1084/jem.20100239
Hemmers S, Teijaro JR, Arandjelovic S, Mowen KA (2011) PAD4-Mediated neutrophil extracellular trap formation is not required for immunity against influenza infection. PLoS One 6(7):e22043. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022043
Neeli I, Khan SN, Radic M (2008) Histone deimination as a response to inflammatory stimuli in neutrophils. J Immunol 180(3):1895–1902
Vitkov L, Klappacher M, Hannig M, Krautgartner WD (2010) Neutrophil fate in gingival crevicular fluid. Ultrastruct Pathol 34(1):25–30. doi:10.3109/01913120903419989
Brill A, Fuchs TA, Savchenko AS, Thomas GM, Martinod K, De Meyer SF, Bhandari AA, Wagner DD (2012) Neutrophil extracellular traps promote deep vein thrombosis in mice. J Thromb Haemost 10(1):136–144. doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04544.x
McKee AS, Munks MW, MacLeod MK, Fleenor CJ, Van Rooijen N, Kappler JW, Marrack P (2009) Alum induces innate immune responses through macrophage and mast cell sensors, but these sensors are not required for alum to act as an adjuvant for specific immunity. J Immunol 183(7):4403–4414. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0900164
Li P, Wang D, Yao H, Doret P, Hao G, Shen Q, Qiu H, Zhang X, Wang Y, Chen G (2010) Coordination of PAD4 and HDAC2 in the regulation of p53-target gene expression. Oncogene 29(21):3153–3162. doi:10.1038/onc.2010.51
Leshner M, Wang S, Lewis C, Zheng H, Chen XA, Santy L, Wang Y (2012) PAD4 Mediated histone hypercitrullination induces heterochromatin decondensation and chromatin unfolding to form neutrophil extracellular trap-like structures. Front Immunol 3:307. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2012.00307
Kessenbrock K, Krumbholz M, Schonermarck U, Back W, Gross WL, Werb Z, Grone HJ, Brinkmann V, Jenne DE (2009) Netting neutrophils in autoimmune small-vessel vasculitis. Nat Med 15(6):623–625. doi:10.1038/nm.1959
Sangaletti S, Tripodo C, Chiodoni C, Guarnotta C, Cappetti B, Casalini P, Piconese S, Parenza M, Guiducci C, Vitali C, Colombo MP (2012) Neutrophil extracellular traps mediate transfer of cytoplasmic neutrophil antigens to myeloid dendritic cells toward ANCA induction and associated autoimmunity. Blood 120(15):3007–3018. doi:10.1182/blood-2012-03-416156
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Gasim AH (2011) Pathogenesis of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody vasculitis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 20(3):263–270. doi:10.1097/MNH.0b013e3283456731
Gupta AK, Joshi MB, Philippova M, Erne P, Hasler P, Hahn S, Resink TJ (2010) Activated endothelial cells induce neutrophil extracellular traps and are susceptible to NETosis-mediated cell death. FEBS Lett 584(14):3193–3197. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2010.06.006
Courtney PA, Crockard AD, Williamson K, Irvine AE, Kennedy RJ, Bell AL (1999) Increased apoptotic peripheral blood neutrophils in systemic lupus erythematosus: relations with disease activity, antibodies to double stranded DNA, and neutropenia. Ann Rheum Dis 58(5):309–314
Hashimoto Y, Nakano K, Yoshinoya S, Tanimoto K, Itoh K (1992) Endothelial cell destruction by polymorphonuclear leukocytes incubated with sera from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Scand J Rheumatol 21(5):209–214
Jonsson H, Sturfelt G (1990) A novel assay for neutrophil clustering activity of human sera: relation to disease activity and neutropenia in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 49(1):46–50
Lande R, Ganguly D, Facchinetti V, Frasca L, Conrad C, Gregorio J, Meller S, Chamilos G, Sebasigari R, Riccieri V, Bassett R, Amuro H, Fukuhara S, Ito T, Liu YJ, Gilliet M (2011) Neutrophils activate plasmacytoid dendritic cells by releasing self-DNA-peptide complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Sci Transl Med 3(73):73ra19. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3001180
Villanueva E, Yalavarthi S, Berthier CC, Hodgin JB, Khandpur R, Lin AM, Rubin CJ, Zhao W, Olsen SH, Klinker M, Shealy D, Denny MF, Plumas J, Chaperot L, Kretzler M, Bruce AT, Kaplan MJ (2011) Netting neutrophils induce endothelial damage, infiltrate tissues, and expose immunostimulatory molecules in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 187(1):538–552. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1100450
Hakkim A, Furnrohr BG, Amann K, Laube B, Abed UA, Brinkmann V, Herrmann M, Voll RE, Zychlinsky A (2010) Impairment of neutrophil extracellular trap degradation is associated with lupus nephritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(21):9813–9818. doi:10.1073/pnas.0909927107
Zykova SN, Tveita AA, Rekvig OP (2010) Renal Dnase1 enzyme activity and protein expression is selectively shut down in murine and human membranoproliferative lupus nephritis. PLoS One 5(8). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0012096
Leffler J, Martin M, Gullstrand B, Tyden H, Lood C, Truedsson L, Bengtsson AA, Blom AM (2012) Neutrophil extracellular traps that are not degraded in systemic lupus erythematosus activate complement exacerbating the disease. J Immunol 188(7):3522–3531. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1102404
Urban CF, Ermert D, Schmid M, Abu-Abed U, Goosmann C, Nacken W, Brinkmann V, Jungblut PR, Zychlinsky A (2009) Neutrophil extracellular traps contain calprotectin, a cytosolic protein complex involved in host defense against candida albicans. PLoS Pathog 5(10):e1000639. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000639
Wang Y, Li M, Stadler S, Correll S, Li P, Wang D, Hayama R, Leonelli L, Han H, Grigoryev SA, Allis CD, Coonrod SA (2009) Histone hypercitrullination mediates chromatin decondensation and neutrophil extracellular trap formation. J Cell Biol 184(2):205–213. doi:10.1083/jcb.200806072
Oliver SS, Denu JM (2011) Dynamic interplay between histone H3 modifications and protein interpreters: emerging evidence for a “histone language”. ChemBioChem 12(2):299–307. doi:10.1002/cbic.201000474
Heinecke JW (1999) Mass spectrometric quantification of amino acid oxidation products in proteins: insights into pathways that promote LDL oxidation in the human artery wall. FASEB J 13(10):1113–1120
Nakashima K, Hagiwara T, Yamada M (2002) Nuclear localization of peptidylarginine deiminase V and histone deimination in granulocytes. J Biol Chem 277(51):49562–49568. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208795200
Dwivedi N, Radic M (2012) Neutrophil activation and B-cell stimulation in the pathogenesis of Felty’s syndrome. Pol Arch Med Wewn 122(7–8):374–379
Lande R, Gregorio J, Facchinetti V, Chatterjee B, Wang YH, Homey B, Cao W, Wang YH, Su B, Nestle FO, Zal T, Mellman I, Schroder JM, Liu YJ, Gilliet M (2007) Plasmacytoid dendritic cells sense self-DNA coupled with antimicrobial peptide. Nature 449(7162):564–569. doi:10.1038/nature06116
Andrews BS, Eisenberg RA, Theofilopoulos AN, Izui S, Wilson CB, McConahey PJ, Murphy ED, Roths JB, Dixon FJ (1978) Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med 148:1198–1215
Channing AA, Kasuga T, Horowitz RE, Dubois EL, Demopoulos HB (1965) An ultrastructural study of spontaneous lupus nephritis in the NZB-BL-NZW mouse. Am J Pathol 47(4):677–694
Farquhar MG, Vernier RL, Good RA (1957) An electron microscope study of the glomerulus in nephrosis, glomerulonephritis, and lupus erythematosus. J Exp Med 106(5):649–660
Kalaaji M, Mortensen E, Jorgensen L, Olsen R, Rekvig OP (2006) Nephritogenic lupus antibodies recognize glomerular basement membrane-associated chromatin fragments released from apoptotic intraglomerular cells. Am J Pathol 168(6):1779–1792. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2006.051329
Knight JS, Kaplan MJ (2012) Lupus neutrophils: ‘NET’ gain in understanding lupus pathogenesis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 24(5):441–450. doi:10.1097/BOR.0b013e3283546703
Chen K, Nishi H, Travers R, Tsuboi N, Martinod K, Wagner DD, Stan R, Croce K, Mayadas TN (2012) Endocytosis of soluble immune complexes leads to their clearance by FcgammaRIIIB but induces neutrophil extracellular traps via FcgammaRIIA in vivo. Blood 120(22):4421–4431. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-12-401133
Pisitkun P, Ha HL, Wang H, Claudio E, Tivy CC, Zhou H, Mayadas TN, Illei GG, Siebenlist U (2012) Interleukin-17 cytokines are critical in development of fatal lupus glomerulonephritis. Immunity 37(6):1104–1115. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2012.08.014
Isenberg DA (1997) Autoantibodies: markers of disease or pathogenic? Ann N Y Acad Sci 823:256–262
Manson JJ, Ma A, Rogers P, Mason LJ, Berden JH, van der Vlag J, D’Cruz DP, Isenberg DA, Rahman A (2009) Relationship between anti-dsDNA, anti-nucleosome and anti-alpha-actinin antibodies and markers of renal disease in patients with lupus nephritis: a prospective longitudinal study. Arthritis Res Ther 11(5):R154. doi:10.1186/ar2831
Wu T, Xie C, Wang HW, Zhou XJ, Schwartz N, Calixto S, Mackay M, Aranow C, Putterman C, Mohan C (2007) Elevated urinary VCAM-1, P-selectin, soluble TNF receptor-1, and CXC chemokine ligand 16 in multiple murine lupus strains and human lupus nephritis. J Immunol 179(10):7166–7175
Narain S, Richards HB, Satoh M, Sarmiento M, Davidson R, Shuster J, Sobel E, Hahn P, Reeves WH (2004) Diagnostic accuracy for lupus and other systemic autoimmune diseases in the community setting. Arch Intern Med 164(22):2435–2441. doi:10.1001/archinte.164.22.2435
Isenberg DA, Manson JJ, Ehrenstein MR, Rahman A (2007) Fifty years of anti-ds DNA antibodies: are we approaching journey’s end? Rheumatology (Oxford) 46(7):1052–1056. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kem112
Madaio MP (2003) Lupus autoantibodies 101: one size does not fit all; however, specificity influences pathogenicity. Clin Exp Immunol 131(3):396–397
Dixon FJ, Oldstone MB, Tonietti G (1971) Pathogenesis of immune complex glomerulonephritis of new zealand mice. J Exp Med 134(3):65–71
Morioka T, Woitas R, Fujigaki Y, Batsford SR, Vogt A (1994) Histone mediates glomerular deposition of small size DNA anti-DNA complex. Kidney Int 45(4):991–997. doi:10.1038/ki.1994.134
Kramers C, Hylkema MN, van Bruggen MC, van de Lagemaat R, Dijkman HB, Assmann KJ, Smeenk RJ, Berden JH (1994) Anti-nucleosome antibodies complexed to nucleosomal antigens show anti-DNA reactivity and bind to rat glomerular basement membrane in vivo. J Clin Invest 94(2):568–577. doi:10.1172/JCI117371
van Bruggen MC, Walgreen B, Rijke TP, Tamboer W, Kramers K, Smeenk RJ, Monestier M, Fournie GJ, Berden JH (1997) Antigen specificity of anti-nuclear antibodies complexed to nucleosomes determines glomerular basement membrane binding in vivo. Eur J Immunol 27(6):1564–1569. doi:10.1002/eji.1830270636
Fenton KA, Tommeras B, Marion TN, Rekvig OP (2010) Pure anti-dsDNA mAbs need chromatin structures to promote glomerular mesangial deposits in BALB/c mice. Autoimmunity 43(2):179–188. doi:10.3109/08916930903305633
Kalaaji M, Fenton KA, Mortensen ES, Olsen R, Sturfelt G, Alm P, Rekvig OP (2007) Glomerular apoptotic nucleosomes are central target structures for nephritogenic antibodies in human SLE nephritis. Kidney Int 71(7):664–672. doi:10.1038/sj.ki.5002133
Mjelle JE, Kalaaji M, Rekvig OP (2009) Exposure of chromatin and not high affinity for dsDNA determines the nephritogenic impact of anti-dsDNA antibodies in (NZBxNZW)F1 mice. Autoimmunity 42(2):104–111. doi:10.1080/08916930802375729
Mjelle JE, Rekvig OP, Fenton KA (2007) Nucleosomes possess a high affinity for glomerular laminin and collagen IV and bind nephritogenic antibodies in murine lupus-like nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis 66(12):1661–1668. doi:10.1136/ard.2007.070482
Mjelle JE, Rekvig OP, Van Der Vlag J, Fenton KA (2011) Nephritogenic antibodies bind in glomeruli through interaction with exposed chromatin fragments and not with renal cross-reactive antigens. Autoimmunity 44(5):373–383. doi:10.3109/08916934.2010.541170
Termaat RM, Assmann KJ, Dijkman HB, van Gompel F, Smeenk RJ, Berden JH (1992) Anti-DNA antibodies can bind to the glomerulus via two distinct mechanisms. Kidney Int 42(6):1363–1371
Faaber P, Rijke TP, van de Putte LB, Capel PJ, Berden JH (1986) Cross-reactivity of human and murine anti-DNA antibodies with heparan sulfate. The major glycosaminoglycan in glomerular basement membranes. J Clin Invest 77(6):1824–1830. doi:10.1172/JCI112508
Madaio MP, Carlson J, Cataldo J, Ucci A, Migliorini P, Pankewycz O (1987) Murine monoclonal anti-DNA antibodies bind directly to glomerular antigens and form immune deposits. J Immunol 138(9):2883–2889
Raz E, Ben-Bassat H, Davidi T, Shlomai Z, Eilat D (1993) Cross-reactions of anti-DNA autoantibodies with cell surface proteins. Eur J Immunol 23(2):383–390. doi:10.1002/eji.1830230213
Vlahakos DV, Foster MH, Adams S, Katz M, Ucci AA, Barrett KJ, Datta SK, Madaio MP (1992) Anti-DNA antibodies form immune deposits at distinct glomerular and vascular sites. Kidney Int 41(6):1690–1700. doi:10.1038/ki.1992.242
D’Andrea DM, Coupaye-Gerard B, Kleyman TR, Foster MH, Madaio MP (1996) Lupus autoantibodies interact directly with distinct glomerular and vascular cell surface antigens. Kidney Int 49(5):1214–1221. doi:10.1038/ki.1996.176
Sabbaga J, Line SR, Potocnjak P, Madaio MP (1989) A murine nephritogenic monoclonal anti-DNA autoantibody binds directly to mouse laminin, the major non-collagenous protein component of the glomerular basement membrane. Eur J Immunol 19(1):137–143. doi:10.1002/eji.1830190122
Chan TM, Frampton G, Staines NA, Hobby P, Perry GJ, Cameron JS (1992) Different mechanisms by which anti-DNA MoAbs bind to human endothelial cells and glomerular mesangial cells. Clin Exp Immunol 88(1):68–74
Deocharan B, Qing X, Lichauco J, Putterman C (2002) Alpha-actinin is a cross-reactive renal target for pathogenic anti-DNA antibodies. J Immunol 168(6):3072–3078
Hasselaar P, Derksen RH, Blokzijl L, de Groot PG (1990) Crossreactivity of antibodies directed against cardiolipin, DNA, endothelial cells and blood platelets. Thromb Haemost 63(2):169–173
Moscato S, Pratesi F, Bongiorni F, Scavuzzo MC, Chimenti D, Bombardieri S, Migliorini P (2002) Endothelial cell binding by systemic lupus antibodies: functional properties and relationship with anti-DNA activity. J Autoimmun 18(3):231–238
Qing X, Zavadil J, Crosby MB, Hogarth MP, Hahn BH, Mohan C, Gilkeson GS, Bottinger EP, Putterman C (2006) Nephritogenic anti-DNA antibodies regulate gene expression in MRL/lpr mouse glomerular mesangial cells. Arthritis Rheum 54(7):2198–2210. doi:10.1002/art.21934
Yung S, Cheung KF, Zhang Q, Chan TM (2010) Anti-dsDNA antibodies bind to mesangial annexin II in lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(11):1912–1927. doi:10.1681/ASN.2009080805
Ben Chetrit E, Dunsky EH, Wollner S, Eilat D (1985) In vivo clearance and tissue uptake of an anti-DNA monoclonal antibody and its complexes with DNA. Clin Exp Immunol 60(1):159–168
Emlen W, Mannik M (1982) Clearance of circulating DNA-anti-DNA immune complexes in mice. J Exp Med 155(4):1210–1215
Gauthier VJ, Mannik M, Striker GE (1982) Effect of cationized antibodies in performed immune complexes on deposition and persistence in renal glomeruli. J Exp Med 156(3):766–777
Agodoa LY, Gauthier VJ, Mannik M (1985) Antibody localization in the glomerular basement membrane may precede in situ immune deposit formation in rat glomeruli. J Immunol 134(2):880–884
Krishnan MR, Wang C, Marion TN (2012) Anti-DNA autoantibodies initiate experimental lupus nephritis by binding directly to the glomerular basement membrane in mice. Kidney Int 82(2):184–192. doi:10.1038/ki.2011.484
Bergtold A, Gavhane A, D’Agati V, Madaio M, Clynes R (2006) FcR-bearing myeloid cells are responsible for triggering murine lupus nephritis. J Immunol 177(10):7287–7295
Clynes R, Dumitru C, Ravetch JV (1998) Uncoupling of immune complex formation and kidney damage in autoimmune glomerulonephritis. Science 279(5353):1052–1054. doi:10.1126/science.279.5353.1052
Qing X, Pitashny M, Thomas DB, Barrat FJ, Hogarth MP, Putterman C (2008) Pathogenic anti-DNA antibodies modulate gene expression in mesangial cells: involvement of HMGB1 in anti-DNA antibody-induced renal injury. Immunol Lett 121(1):61–73. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2008.08.007
Uciechowski P, Schwarz M, Gessner JE, Schmidt RE, Resch K, Radeke HH (1998) IFN-gamma induces the high-affinity Fc receptor I for IgG (CD64) on human glomerular mesangial cells. Eur J Immunol 28(9):2928–2935
Lopez-Armada MJ, Gomez-Guerrero C, Egido J (1996) Receptors for immune complexes activate gene expression and synthesis of matrix proteins in cultured rat and human mesangial cells: role of TGF-beta. J Immunol 157(5):2136–2142
Morcos M, Hansch GM, Schonermark M, Ellwanger S, Harle M, Heckl-Ostreicher B (1994) Human glomerular mesangial cells express CD16 and may be stimulated via this receptor. Kidney Int 46(6):1627–1634
Radeke HH, Janssen-Graalfs I, Sowa EN, Chouchakova N, Skokowa J, Loscher F, Schmidt RE, Heeringa P, Gessner JE (2002) Opposite regulation of type II and III receptors for immunoglobulin G in mouse glomerular mesangial cells and in the induction of anti-glomerular basement membrane (GBM) nephritis. J Biol Chem 277(30):27535–27544. doi:10.1074/jbc.M200419200
Kovalenko P, Fujinaka H, Yoshida Y, Kawamura H, Qu Z, El-Shemi AG, Li H, Matsuki A, Bilim V, Yaoita E, Abo T, Uchiyama M, Yamamoto T (2004) Fc receptor-mediated accumulation of macrophages in crescentic glomerulonephritis induced by anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody administration in WKY rats. Int Immunol 16(5):625–634. doi:10.1093/intimm/dxh058
Tarzi RM, Davies KA, Robson MG, Fossati-Jimack L, Saito T, Walport MJ, Cook HT (2002) Nephrotoxic nephritis is mediated by fcgamma receptors on circulating leukocytes and not intrinsic renal cells. Kidney Int 62(6):2087–2096. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00687.x
Taylor KE, Chung SA, Graham RR, Ortmann WA, Lee AT, Langefeld CD, Jacob CO, Kamboh MI, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Tsao BP, Moser KL, Gaffney PM, Harley JB, Petri M, Manzi S, Gregersen PK, Behrens TW, Criswell LA (2011) Risk alleles for systemic lupus erythematosus in a large case–control collection and associations with clinical subphenotypes. PLoS Genet 7(2):e1001311. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001311
Moser KL, Neas BR, Salmon JE, Yu H, Gray-McGuire C, Asundi N, Bruner GR, Fox J, Kelly J, Henshall S, Bacino D, Dietz M, Hogue R, Koelsch G, Nightingale L, Shaver T, Abdou NI, Albert DA, Carson C, Petri M, Treadwell EL, James JA, Harley JB (1998) Genome scan of human systemic lupus erythematosus: evidence for linkage on chromosome 1q in african-american pedigrees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(25):14869–14874
Agnello V, Koffler D, Kunkel HG (1973) Immune complex systems in the nephritis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Kidney Int 3(2):90–99
Godau J, Heller T, Hawlisch H, Trappe M, Howells E, Best J, Zwirner J, Verbeek JS, Hogarth PM, Gerard C, Van Rooijen N, Klos A, Gessner JE, Kohl J (2004) C5a initiates the inflammatory cascade in immune complex peritonitis. J Immunol 173(5):3437–3445
Wang Y, Hu Q, Madri JA, Rollins SA, Chodera A, Matis LA (1996) Amelioration of lupus-like autoimmune disease in NZB/WF1 mice after treatment with a blocking monoclonal antibody specific for complement component C5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(16):8563–8568
Shushakova N, Skokowa J, Schulman J, Baumann U, Zwirner J, Schmidt RE, Gessner JE (2002) C5a Anaphylatoxin is a major regulator of activating versus inhibitory FcgammaRs in immune complex-induced lung disease. J Clin Invest 110(12):1823–1830. doi:10.1172/JCI16577
Skokowa J, Ali SR, Felda O, Kumar V, Konrad S, Shushakova N, Schmidt RE, Piekorz RP, Nurnberg B, Spicher K, Birnbaumer L, Zwirner J, Claassens JW, Verbeek JS, van Rooijen N, Kohl J, Gessner JE (2005) Macrophages induce the inflammatory response in the pulmonary arthus reaction through G alpha i2 activation that controls C5aR and Fc receptor cooperation. J Immunol 174(5):3041–3050
Manderson AP, Botto M, Walport MJ (2004) The role of complement in the development of systemic lupus erythematosus. Annu Rev Immunol 22:431–456. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.22.012703.104549
Korb LC, Ahearn JM (1997) C1q Binds directly and specifically to surface blebs of apoptotic human keratinocytes: complement deficiency and systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. J Immunol 158(10):4525–4528
Mevorach D, Mascarenhas JO, Gershov D, Elkon KB (1998) Complement-dependent clearance of apoptotic cells by human macrophages. J Exp Med 188(12):2313–2320
Nauta AJ, Trouw LA, Daha MR, Tijsma O, Nieuwland R, Schwaeble WJ, Gingras AR, Mantovani A, Hack EC, Roos A (2002) Direct binding of C1q to apoptotic cells and cell blebs induces complement activation. Eur J Immunol 32(6):1726–1736. doi:10.1002/1521-4141(200206)32:6<1726::AID-IMMU1726>3.0.CO;2-R
McDonald B, Urrutia R, Yipp BG, Jenne CN, Kubes P (2012) Intravascular neutrophil extracellular traps capture bacteria from the bloodstream during sepsis. Cell Host Microbe 12(3):324–333. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2012.06.011
von Bruhl ML, Stark K, Steinhart A, Chandraratne S, Konrad I, Lorenz M, Khandoga A, Tirniceriu A, Coletti R, Kollnberger M, Byrne RA, Laitinen I, Walch A, Brill A, Pfeiler S, Manukyan D, Braun S, Lange P, Riegger J, Ware J, Eckart A, Haidari S, Rudelius M, Schulz C, Echtler K, Brinkmann V, Schwaiger M, Preissner KT, Wagner DD, Mackman N, Engelmann B, Massberg S (2012) Monocytes, neutrophils, and platelets cooperate to initiate and propagate venous thrombosis in mice in vivo. J Exp Med 209(4):819–835. doi:10.1084/jem.20112322
Megens RT, Vijayan S, Lievens D, Doring Y, van Zandvoort MA, Grommes J, Weber C, Soehnlein O (2012) Presence of luminal neutrophil extracellular traps in atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost 107(3):597–598. doi:10.1160/TH11-09-0650
Dworski R, Simon HU, Hoskins A, Yousefi S (2011) Eosinophil and neutrophil extracellular DNA traps in human allergic asthmatic airways. J Allergy Clin Immunol 127(5):1260–1266. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2010.12.1103
Daigo K, Yamaguchi N, Kawamura T, Matsubara K, Jiang S, Ohashi R, Sudou Y, Kodama T, Naito M, Inoue K, Hamakubo T (2012) The proteomic profile of circulating pentraxin 3 (PTX3) complex in sepsis demonstrates the interaction with azurocidin 1 and other components of neutrophil extracellular traps. Mol Cell Proteomics 11(6):M111 015073. doi:10.1074/mcp.M111.015073
Schorn C, Janko C, Krenn V, Zhao Y, Munoz LE, Schett G, Herrmann M (2012) Bonding the foe—NETting neutrophils immobilize the pro-inflammatory monosodium urate crystals. Front Immunol 3:376. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2012.00376
Wermeling F, Chen Y, Pikkarainen T, Scheynius A, Winqvist O, Izui S, Ravetch JV, Tryggvason K, Karlsson MC (2007) Class a scavenger receptors regulate tolerance against apoptotic cells, and autoantibodies against these receptors are predictive of systemic lupus. J Exp Med 204(10):2259–2265. doi:10.1084/jem.20070600
Parvatiyar K, Zhang Z, Teles RM, Ouyang S, Jiang Y, Iyer SS, Zaver SA, Schenk M, Zeng S, Zhong W, Liu ZJ, Modlin RL, Liu YJ, Cheng G (2012) The helicase DDX41 recognizes the bacterial secondary messengers cyclic di-GMP and cyclic di-AMP to activate a type I interferon immune response. Nat Immunol 13(12):1155–1161. doi:10.1038/ni.2460
Nathan C (2006) Neutrophils and immunity: challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Immunol 6(3):173–182. doi:10.1038/nri1785
Abi Abdallah DS, Denkers EY (2012) Neutrophils cast extracellular traps in response to protozoan parasites. Front Immunol 3:382. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2012.00382
Guimaraes-Costa AB, Nascimento MT, Froment GS, Soares RP, Morgado FN, Conceicao-Silva F, Saraiva EM (2009) Leishmania amazonensis promastigotes induce and are killed by neutrophil extracellular traps. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(16):6748–6753. doi:10.1073/pnas.0900226106
Urban CF, Reichard U, Brinkmann V, Zychlinsky A (2006) Neutrophil extracellular traps capture and kill Candida albicans yeast and hyphal forms. Cell Microbiol 8(4):668–676. doi:10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00659.x
Kirchner T, Moller S, Klinger M, Solbach W, Laskay T, Behnen M (2012) The impact of various reactive oxygen species on the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps. Mediators Inflamm 2012:849136. doi:10.1155/2012/849136
Willis VC, Gizinski AM, Banda NK, Causey CP, Knuckley B, Cordova KN, Luo Y, Levitt B, Glogowska M, Chandra P, Kulik L, Robinson WH, Arend WP, Thompson PR, Holers VM (2011) N-alpha-benzoyl-N5-(2-chloro-1-iminoethyl)-l-ornithine amide, a protein arginine deiminase inhibitor, reduces the severity of murine collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol 186(7):4396–4404. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1001620
van Montfoort ML, Stephan F, Lauw MN, Hutten BA, Van Mierlo GJ, Solati S, Middeldorp S, Meijers JC, Zeerleder S (2013) Circulating nucleosomes and neutrophil activation as risk factors for deep vein thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33(1):147–151. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300498
Phillipson M, Kubes P (2011) The neutrophil in vascular inflammation. Nat Med 17(11):1381–1390. doi:10.1038/nm.2514
Knight JS, Carmona-Rivera C, Kaplan MJ (2012) Proteins derived from neutrophil extracellular traps may serve as self-antigens and mediate organ damage in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol 3:380. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2012.00380
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the research support from the Lupus Research Institute of New York, the National Institutes of Health grants AI26833 and RR301812, and the UTHSC Center of Excellence for Diseases of Connective Tissues. The authors gratefully acknowledge the expert assistance of Mr. Tim Higgins, Senior Illustrator.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is a contribution to the special issue on Neutrophils - Guest Editors: Paul Hasler and Sinuhe Hahn
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Radic, M., Marion, T.N. Neutrophil extracellular chromatin traps connect innate immune response to autoimmunity. Semin Immunopathol 35, 465–480 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-013-0376-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-013-0376-6