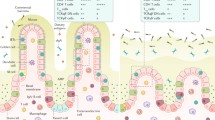
Abstract
Celiac disease is a T cell-mediated immune disorder induced by dietary gluten that is characterized by the development of an inflammatory anti-gluten CD4 T cell response, anti-gluten antibodies, and autoantibodies against tissue transglutaminase 2 and the activation of intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) leading to the destruction of the intestinal epithelium. Intraepithelial lymphocytes represent a heterogeneous population of T cells composed mainly of cytotoxic CD8 T cells residing within the epithelial layer, whose main role is to maintain the integrity of the epithelium by eliminating infected cells and promoting epithelial repair. Dysregulated activation of IELs is a hallmark of CD and is critically involved in epithelial cell destruction and the subsequent development of villous atrophy. In this review, we compare and contrast the phenotype and function of human and mouse small intestinal IELs under physiological conditions. Furthermore, we discuss how conditions of epithelial distress associated with overexpression of IL-15 and non-classical MHC class I molecules induce cytotoxic IELs to become licensed killer cells that upregulate activating NKG2D and CD94/NKG2C natural killer receptors, acquiring lymphokine killer activity. Pathways leading to dysregulated IEL activation could eventually be targeted to prevent villous atrophy and treat patients who respond poorly to gluten-free diet.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beagley KW, Fujihashi K, Lagoo AS, Lagoo-Deenadaylan S, Black CA, Murray AM, Sharmanov AT, Yamamoto M, McGhee JR, Elson CO et al (1995) Differences in intraepithelial lymphocyte T cell subsets isolated from murine small versus large intestine. J Immunol 154:5611–5619
Lundqvist C, Baranov V, Hammarstrom S, Athlin L, Hammarstrom ML (1995) Intra-epithelial lymphocytes. Evidence for regional specialization and extrathymic T cell maturation in the human gut epithelium. Int Immunol 7:1473–1487
Ebert EC (1998) Interleukin 15 is a potent stimulant of intraepithelial lymphocytes. Gastroenterology 115:1439–1445
Guy-Grand D, Cuenod-Jabri B, Malassis-Seris M, Selz F, Vassalli P (1996) Complexity of the mouse gut T cell immune system: identification of two distinct natural killer T cell intraepithelial lineages. Eur J Immunol 26:2248–2256
Roberts AI, Lee L, Schwarz E, Groh V, Spies T, Ebert EC, Jabri B (2001) NKG2D receptors induced by IL-15 costimulate CD28-negative effector CTL in the tissue microenvironment. J Immunol 167:5527–5530
Jabri B, Ebert E (2007) Human CD8+ intraepithelial lymphocytes: a unique model to study the regulation of effector cytotoxic T lymphocytes in tissue. Immunol Rev 215:202–214
Mysorekar IU, Lorenz RG, Gordon JI (2002) A gnotobiotic transgenic mouse model for studying interactions between small intestinal enterocytes and intraepithelial lymphocytes. J Biol Chem 277:37811–37819
Ferguson A (1977) Intraepithelial lymphocytes of the small intestine. Gut 18:921–937
Wurbel MA, Philippe JM, Nguyen C, Victorero G, Freeman T, Wooding P, Miazek A, Mattei MG, Malissen M, Jordan BR, Malissen B, Carrier A, Naquet P (2000) The chemokine TECK is expressed by thymic and intestinal epithelial cells and attracts double- and single-positive thymocytes expressing the TECK receptor CCR9. Eur J Immunol 30:262–271
Zabel BA, Agace WW, Campbell JJ, Heath HM, Parent D, Roberts AI, Ebert EC, Kassam N, Qin S, Zovko M, LaRosa GJ, Yang LL, Soler D, Butcher EC, Ponath PD, Parker CM, Andrew DP (1999) Human G protein-coupled receptor GPR-9-6/CC chemokine receptor 9 is selectively expressed on intestinal homing T lymphocytes, mucosal lymphocytes, and thymocytes and is required for thymus-expressed chemokine-mediated chemotaxis. J Exp Med 190:1241–1256
Cepek KL, Shaw SK, Parker CM, Russell GJ, Morrow JS, Rimm DL, Brenner MB (1994) Adhesion between epithelial cells and T lymphocytes mediated by E-cadherin and the alpha E beta 7 integrin. Nature 372:190–193
Cerf-Bensussan N, Jarry A, Brousse N, Lisowska-Grospierre B, Guy-Grand D, Griscelli C (1987) A monoclonal antibody (HML-1) defining a novel membrane molecule present on human intestinal lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol 17:1279–1285
Kilshaw PJ, Murant SJ (1990) A new surface antigen on intraepithelial lymphocytes in the intestine. Eur J Immunol 20:2201–2207
Schon MP, Arya A, Murphy EA, Adams CM, Strauch UG, Agace WW, Marsal J, Donohue JP, Her H, Beier DR, Olson S, Lefrancois L, Brenner MB, Grusby MJ, Parker CM (1999) Mucosal T lymphocyte numbers are selectively reduced in integrin alpha E (CD103)-deficient mice. J Immunol 162:6641–6649
Probert CS, Saubermann LJ, Balk S, Blumberg RS (2007) Repertoire of the alpha beta T-cell receptor in the intestine. Immunol Rev 215:215–225
Blumberg RS, Yockey CE, Gross GG, Ebert EC, Balk SP (1993) Human intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes are derived from a limited number of T cell clones that utilize multiple V beta T cell receptor genes. J Immunol 150:5144–5153
Van Kerckhove C, Russell GJ, Deusch K, Reich K, Bhan AK, DerSimonian H, Brenner MB (1992) Oligoclonality of human intestinal intraepithelial T cells. J Exp Med 175:57–63
Jabri B, Selby JM, Negulescu H, Lee L, Roberts AI, Beavis A, Lopez-Botet M, Ebert EC, Winchester RJ (2002) TCR specificity dictates CD94/NKG2A expression by human CTL. Immunity 17:487–499
Bruce D, Cantorna MT (2011) Intrinsic requirement for the vitamin D receptor in the development of CD8alphaalpha-expressing T cells. J Immunol 186:2819–2825
Li Y, Innocentin S, Withers DR, Roberts NA, Gallagher AR, Grigorieva EF, Wilhelm C, Veldhoen M (2011) Exogenous stimuli maintain intraepithelial lymphocytes via aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation. Cell 147:629–640
Jarry A, Cerf-Bensussan N, Brousse N, Selz F, Guy-Grand D (1990) Subsets of CD3+ (T cell receptor alpha/beta or gamma/delta) and CD3- lymphocytes isolated from normal human gut epithelium display phenotypical features different from their counterparts in peripheral blood. Eur J Immunol 20:1097–1103
Guy-Grand D, Cerf-Bensussan N, Malissen B, Malassis-Seris M, Briottet C, Vassalli P (1991) Two gut intraepithelial CD8+ lymphocyte populations with different T cell receptors: a role for the gut epithelium in T cell differentiation. J Exp Med 173:471–481
Pereira P, Gerber D, Huang SY, Tonegawa S (1995) Ontogenic development and tissue distribution of V gamma 1-expressing gamma/delta T lymphocytes in normal mice. J Exp Med 182:1921–1930
Takagaki Y, DeCloux A, Bonneville M, Tonegawa S (1989) Diversity of gamma delta T-cell receptors on murine intestinal intra-epithelial lymphocytes. Nature 339:712–714
Chowers Y, Holtmeier W, Harwood J, Morzycka-Wroblewska E, Kagnoff MF (1994) The V delta 1 T cell receptor repertoire in human small intestine and colon. J Exp Med 180:183–190
Deusch K, Luling F, Reich K, Classen M, Wagner H, Pfeffer K (1991) A major fraction of human intraepithelial lymphocytes simultaneously expresses the gamma/delta T cell receptor, the CD8 accessory molecule and preferentially uses the V delta 1 gene segment. Eur J Immunol 21:1053–1059
Halstensen TS, Scott H, Brandtzaeg P (1989) Intraepithelial T cells of the TcR gamma/delta + CD8- and V delta 1/J delta 1+ phenotypes are increased in coeliac disease. Scand J Immunol 30:665–672
Guy-Grand D, Rocha B, Mintz P, Malassis-Seris M, Selz F, Malissen B, Vassalli P (1994) Different use of T cell receptor transducing modules in two populations of gut intraepithelial lymphocytes are related to distinct pathways of T cell differentiation. J Exp Med 180:673–679
Cheroutre H, Lambolez F, Mucida D (2011) The light and dark sides of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Nat Rev Immunol 11:445–456
Leishman AJ, Naidenko OV, Attinger A, Koning F, Lena CJ, Xiong Y, Chang HC, Reinherz E, Kronenberg M, Cheroutre H (2001) T cell responses modulated through interaction between CD8alphaalpha and the nonclassical MHC class I molecule, TL. Science 294:1936–1939
Hayday A, Theodoridis E, Ramsburg E, Shires J (2001) Intraepithelial lymphocytes: exploring the Third Way in immunology. Nat Immunol 2:997–1003
Das G, Janeway CA Jr (1999) Development of CD8alpha/alpha and CD8alpha/beta T cells in major histocompatibility complex class I-deficient mice. J Exp Med 190:881–884
Park SH, Guy-Grand D, Lemonnier FA, Wang CR, Bendelac A, Jabri B (1999) Selection and expansion of CD8alpha/alpha(1) T cell receptor alpha/beta(1) intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes in the absence of both classical major histocompatibility complex class I and nonclassical CD1 molecules. J Exp Med 190:885–890
Regnault A, Cumano A, Vassalli P, Guy-Grand D, Kourilsky P (1994) Oligoclonal repertoire of the CD8 alpha alpha and the CD8 alpha beta TCR-alpha/beta murine intestinal intraepithelial T lymphocytes: evidence for the random emergence of T cells. J Exp Med 180:1345–1358
Gapin L, Cheroutre H, Kronenberg M (1999) Cutting edge: TCR alpha beta + CD8 alpha alpha + T cells are found in intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes of mice that lack classical MHC class I molecules. J Immunol 163:4100–4104
Rocha B, Vassalli P, Guy-Grand D (1991) The V beta repertoire of mouse gut homodimeric alpha CD8+ intraepithelial T cell receptor alpha/beta + lymphocytes reveals a major extrathymic pathway of T cell differentiation. J Exp Med 173:483–486
Guy-Grand D, DiSanto JP, Henchoz P, Malassis-Seris M, Vassalli P (1998) Small bowel enteropathy: role of intraepithelial lymphocytes and of cytokines (IL-12, IFN-gamma, TNF) in the induction of epithelial cell death and renewal. Eur J Immunol 28:730–744
Long EO, Burshtyn DN, Clark WP, Peruzzi M, Rajagopalan S, Rojo S, Wagtmann N, Winter CC (1997) Killer cell inhibitory receptors: diversity, specificity, and function. Immunol Rev 155:135–144
Eagle RA, Trowsdale J (2007) Promiscuity and the single receptor: NKG2D. Nat Rev Immunol 7:737–744
Vance RE, Kraft JR, Altman JD, Jensen PE, Raulet DH (1998) Mouse CD94/NKG2A is a natural killer cell receptor for the nonclassical major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecule Qa-1(b). J Exp Med 188:1841–1848
Balk SP, Ebert EC, Blumenthal RL, McDermott FV, Wucherpfennig KW, Landau SB, Blumberg RS (1991) Oligoclonal expansion and CD1 recognition by human intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Science 253:1411–1415
Gross GG, Schwartz VL, Stevens C, Ebert EC, Blumberg RS, Balk SP (1994) Distribution of dominant T cell receptor beta chains in human intestinal mucosa. J Exp Med 180:1337–1344
Eiras P, Roldan E, Camarero C, Olivares F, Bootello A, Roy G (1998) Flow cytometry description of a novel CD3-/CD7+ intraepithelial lymphocyte subset in human duodenal biopsies: potential diagnostic value in coeliac disease. Cytometry 34:95–102
Jabri B, de Serre NP, Cellier C, Evans K, Gache C, Carvalho C, Mougenot JF, Allez M, Jian R, Desreumaux P, Colombel JF, Matuchansky C, Cugnenc H, Lopez-Botet M, Vivier E, Moretta A, Roberts AI, Ebert EC, Guy-Grand D, Brousse N, Schmitz J, Cerf-Bensussan N (2000) Selective expansion of intraepithelial lymphocytes expressing the HLA-E-specific natural killer receptor CD94 in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 118:867–879
Bauer S, Groh V, Wu J, Steinle A, Phillips JH, Lanier LL, Spies T (1999) Activation of NK cells and T cells by NKG2D, a receptor for stress-inducible MICA. Science 285:727–729
Chalupny NJ, Sutherland CL, Lawrence WA, Rein-Weston A, Cosman D (2003) ULBP4 is a novel ligand for human NKG2D. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 305:129–135
Cosman D, Mullberg J, Sutherland CL, Chin W, Armitage R, Fanslow W, Kubin M, Chalupny NJ (2001) ULBPs, novel MHC class I-related molecules, bind to CMV glycoprotein UL16 and stimulate NK cytotoxicity through the NKG2D receptor. Immunity 14:123–133
Jabri B, Meresse B (2006) NKG2 receptor-mediated regulation of effector CTL functions in the human tissue microenvironment. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 298:139–156
Jamieson AM, Diefenbach A, McMahon CW, Xiong N, Carlyle JR, Raulet DH (2002) The role of the NKG2D immunoreceptor in immune cell activation and natural killing. Immunity 17:19–29
Wu J, Song Y, Bakker AB, Bauer S, Spies T, Lanier LL, Phillips JH (1999) An activating immunoreceptor complex formed by NKG2D and DAP10. Science 285:730–732
Diefenbach A, Tomasello E, Lucas M, Jamieson AM, Hsia JK, Vivier E, Raulet DH (2002) Selective associations with signaling proteins determine stimulatory versus costimulatory activity of NKG2D. Nat Immunol 3:1142–1149
Braud VM, Allan DS, O'Callaghan CA, Soderstrom K, D'Andrea A, Ogg GS, Lazetic S, Young NT, Bell JI, Phillips JH, Lanier LL, McMichael AJ (1998) HLA-E binds to natural killer cell receptors CD94/NKG2A, B and C. Nature 391:795–799
Lee N, Llano M, Carretero M, Ishitani A, Navarro F, Lopez-Botet M, Geraghty DE (1998) HLA-E is a major ligand for the natural killer inhibitory receptor CD94/NKG2A. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:5199–5204
Lopez-Botet M, Llano M, Navarro F, Bellon T (2000) NK cell recognition of non-classical HLA class I molecules. Semin Immunol 12:109–119
Lanier LL, Corliss B, Wu J, Phillips JH (1998) Association of DAP12 with activating CD94/NKG2C NK cell receptors. Immunity 8:693–701
Meresse B, Curran SA, Ciszewski C, Orbelyan G, Setty M, Bhagat G, Lee L, Tretiakova M, Semrad C, Kistner E, Winchester RJ, Braud V, Lanier LL, Geraghty DE, Green PH, Guandalini S, Jabri B (2006) Reprogramming of CTLs into natural killer-like cells in celiac disease. J Exp Med 203:1343–1355
Aldemir H, Prod'homme V, Dumaurier MJ, Retiere C, Poupon G, Cazareth J, Bihl F, Braud VM (2005) Cutting edge: lectin-like transcript 1 is a ligand for the CD161 receptor. J Immunol 175:7791–7795
Rosen DB, Bettadapura J, Alsharifi M, Mathew PA, Warren HS, Lanier LL (2005) Cutting edge: lectin-like transcript-1 is a ligand for the inhibitory human NKR-P1A receptor. J Immunol 175:7796–7799
Inagaki-Ohara K, Sakamoto Y, Dohi T, Smith AL (2011) gammadelta T cells play a protective role during infection with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis by promoting goblet cell function in the small intestine. Immunology 134:448–458
Roberts SJ, Smith AL, West AB, Wen L, Findly RC, Owen MJ, Hayday AC (1996) T-cell alpha beta + and gamma delta + deficient mice display abnormal but distinct phenotypes toward a natural, widespread infection of the intestinal epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:11774–11779
Lepage AC, Buzoni-Gatel D, Bout DT, Kasper LH (1998) Gut-derived intraepithelial lymphocytes induce long term immunity against Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol 161:4902–4908
Chardes T, Buzoni-Gatel D, Lepage A, Bernard F, Bout D (1994) Toxoplasma gondii oral infection induces specific cytotoxic CD8 alpha/beta + Thy-1+ gut intraepithelial lymphocytes, lytic for parasite-infected enterocytes. J Immunol 153:4596–4603
Moretto M, Weiss LM, Khan IA (2004) Induction of a rapid and strong antigen-specific intraepithelial lymphocyte response during oral Encephalitozoon cuniculi infection. J Immunol 172:4402–4409
Lefrancois L, Goodman T (1989) In vivo modulation of cytolytic activity and Thy-1 expression in TCR-gamma delta + intraepithelial lymphocytes. Science 243:1716–1718
Dalton JE, Cruickshank SM, Egan CE, Mears R, Newton DJ, Andrew EM, Lawrence B, Howell G, Else KJ, Gubbels MJ, Striepen B, Smith JE, White SJ, Carding SR (2006) Intraepithelial gammadelta + lymphocytes maintain the integrity of intestinal epithelial tight junctions in response to infection. Gastroenterology 131:818–829
Epple HJ, Allers K, Troger H, Kuhl A, Erben U, Fromm M, Zeitz M, Loddenkemper C, Schulzke JD, Schneider T (2010) Acute HIV infection induces mucosal infiltration with CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, epithelial apoptosis, and a mucosal barrier defect. Gastroenterology 139:1289–1300
Raffatellu M, Santos RL, Verhoeven DE, George MD, Wilson RP, Winter SE, Godinez I, Sankaran S, Paixao TA, Gordon MA, Kolls JK, Dandekar S, Baumler AJ (2008) Simian immunodeficiency virus-induced mucosal interleukin-17 deficiency promotes Salmonella dissemination from the gut. Nat Med 14:421–428
Hue S, Mention JJ, Monteiro RC, Zhang S, Cellier C, Schmitz J, Verkarre V, Fodil N, Bahram S, Cerf-Bensussan N, Caillat-Zucman S (2004) A direct role for NKG2D/MICA interaction in villous atrophy during celiac disease. Immunity 21:367–377
Meresse B, Chen Z, Ciszewski C, Tretiakova M, Bhagat G, Krausz TN, Raulet DH, Lanier LL, Groh V, Spies T, Ebert EC, Green PH, Jabri B (2004) Coordinated induction by IL15 of a TCR-independent NKG2D signaling pathway converts CTL into lymphokine-activated killer cells in celiac disease. Immunity 21:357–366
Rust C, Kooy Y, Pena S, Mearin ML, Kluin P, Koning F (1992) Phenotypical and functional characterization of small intestinal TcR gamma delta + T cells in coeliac disease. Scand J Immunol 35:459–468
Chen Y, Chou K, Fuchs E, Havran WL, Boismenu R (2002) Protection of the intestinal mucosa by intraepithelial gamma delta T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:14338–14343
Inagaki-Ohara K, Dewi FN, Hisaeda H, Smith AL, Jimi F, Miyahira M, Abdel-Aleem AS, Horii Y, Nawa Y (2006) Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes sustain the epithelial barrier function against Eimeria vermiformis infection. Infect Immun 74:5292–5301
Ismail AS, Behrendt CL, Hooper LV (2009) Reciprocal interactions between commensal bacteria and gamma delta intraepithelial lymphocytes during mucosal injury. J Immunol 182:3047–3054
Boismenu R, Havran WL (1994) Modulation of epithelial cell growth by intraepithelial gamma delta T cells. Science 266:1253–1255
Komano H, Fujiura Y, Kawaguchi M, Matsumoto S, Hashimoto Y, Obana S, Mombaerts P, Tonegawa S, Yamamoto H, Itohara S et al (1995) Homeostatic regulation of intestinal epithelia by intraepithelial gamma delta T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:6147–6151
Yang H, Antony PA, Wildhaber BE, Teitelbaum DH (2004) Intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte gamma delta-T cell-derived keratinocyte growth factor modulates epithelial growth in the mouse. J Immunol 172:4151–4158
Kamanaka M, Kim ST, Wan YY, Sutterwala FS, Lara-Tejero M, Galan JE, Harhaj E, Flavell RA (2006) Expression of interleukin-10 in intestinal lymphocytes detected by an interleukin-10 reporter knockin tiger mouse. Immunity 25:941–952
Mengel J, Cardillo F, Aroeira LS, Williams O, Russo M, Vaz NM (1995) Anti-gamma delta T cell antibody blocks the induction and maintenance of oral tolerance to ovalbumin in mice. Immunol Lett 48:97–102
Fujihashi K, Dohi T, Kweon MN, McGhee JR, Koga T, Cooper MD, Tonegawa S, Kiyono H (1999) Gammadelta T cells regulate mucosally induced tolerance in a dose-dependent fashion. Int Immunol 11:1907–1916
Bhagat G, Naiyer AJ, Shah JG, Harper J, Jabri B, Wang TC, Green PH, Manavalan JS (2008) Small intestinal CD8 + TCRgammadelta + NKG2A + intraepithelial lymphocytes have attributes of regulatory cells in patients with celiac disease. J Clin Invest 118:281–293
Cheroutre H, Lambolez F (2008) Doubting the TCR coreceptor function of CD8alphaalpha. Immunity 28:149–159
Corazza GR, Villanacci V (2005) Coeliac disease. J Clin Pathol 58:573–574
Veress B, Franzen L, Bodin L, Borch K (2004) Duodenal intraepithelial lymphocyte-count revisited. Scand J Gastroenterol 39:138–144
Goldstein NS (2004) Proximal small-bowel mucosal villous intraepithelial lymphocytes. Histopathology 44:199–205
Vecchi M, Crosti L, Berti E, Agape D, Cerri A, De Franchis R (1992) Increased jejunal intraepithelial lymphocytes bearing gamma/delta T-cell receptor in dermatitis herpetiformis. Gastroenterology 102:1499–1505
Walker MM, Murray JA (2011) An update in the diagnosis of coeliac disease. Histopathology 59:166–179
Husby S, Koletzko S, Korponay-Szabo IR, Mearin ML, Phillips A, Shamir R, Troncone R, Giersiepen K, Branski D, Catassi C, Lelgeman M, Maki M, Ribes-Koninckx C, Ventura A, Zimmer KP (2012) European Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition guidelines for the diagnosis of coeliac disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 54:136–160
Spencer J, Isaacson PG, Diss TC, MacDonald TT (1989) Expression of disulfide-linked and non-disulfide-linked forms of the T cell receptor gamma/delta heterodimer in human intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol 19:1335–1338
Calleja S, Vivas S, Santiuste M, Arias L, Hernando M, Nistal E, Casqueiro J, Ruiz de Morales JG (2011) Dynamics of non-conventional intraepithelial lymphocytes-NK, NKT, and gammadelta T-in celiac disease: relationship with age, diet, and histopathology. Dig Dis Sci 56:2042–2049
Halstensen TS, Brandtzaeg P (1995) TCR gamma/delta + and CD8+TCR alpha/beta + intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL) express proliferation marker (Ki-67) in the coeliac lesion. Adv Exp Med Biol 371B:1333–1338
Troncone R, Greco L, Mayer M, Mazzarella G, Maiuri L, Congia M, Frau F, De Virgiliis S, Auricchio S (1996) In siblings of celiac children, rectal gluten challenge reveals gluten sensitization not restricted to celiac HLA. Gastroenterology 111:318–324
Savilahti E, Ormala T, Arato A, Hacsek G, Holm K, Klemola T, Nemeth A, Maki M, Reunala T (1997) Density of gamma/delta + T cells in the jejunal epithelium of patients with coeliac disease and dermatitis herpetiformis is increased with age. Clin Exp Immunol 109:464–467
Jarvinen TT, Kaukinen K, Laurila K, Kyronpalo S, Rasmussen M, Maki M, Korhonen H, Reunala T, Collin P (2003) Intraepithelial lymphocytes in celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol 98:1332–1337
Kutlu T, Brousse N, Rambaud C, Le Deist F, Schmitz J, Cerf-Bensussan N (1993) Numbers of T cell receptor (TCR) alpha beta + but not of TcR gamma delta + intraepithelial lymphocytes correlate with the grade of villous atrophy in coeliac patients on a long term normal diet. Gut 34:208–214
Trejdosiewicz LK, Calabrese A, Smart CJ, Oakes DJ, Howdle PD, Crabtree JE, Losowsky MS, Lancaster F, Boylston AW (1991) Gamma delta T cell receptor-positive cells of the human gastrointestinal mucosa: occurrence and V region gene expression in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis, coeliac disease and inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol 84:440–444
Iltanen S, Holm K, Partanen J, Laippala P, Maki M (1999) Increased density of jejunal gammadelta + T cells in patients having normal mucosa–marker of operative autoimmune mechanisms? Autoimmunity 29:179–187
Maki M, Holm K, Collin P, Savilahti E (1991) Increase in gamma/delta T cell receptor bearing lymphocytes in normal small bowel mucosa in latent coeliac disease. Gut 32:1412–1414
Holm K, Maki M, Savilahti E, Lipsanen V, Laippala P, Koskimies S (1992) Intraepithelial gamma delta T-cell-receptor lymphocytes and genetic susceptibility to coeliac disease. Lancet 339:1500–1503
Paparo F, Petrone E, Tosco A, Maglio M, Borrelli M, Salvati VM, Miele E, Greco L, Auricchio S, Troncone R (2005) Clinical, HLA, and small bowel immunohistochemical features of children with positive serum antiendomysium antibodies and architecturally normal small intestinal mucosa. Am J Gastroenterol 100:2294–2298
Holtmeier W, Rowell DL, Nyberg A, Kagnoff MF (1997) Distinct delta T cell receptor repertoires in monozygotic twins concordant for coeliac disease. Clin Exp Immunol 107:148–157
Schild H, Mavaddat N, Litzenberger C, Ehrich EW, Davis MM, Bluestone JA, Matis L, Draper RK, Chien YH (1994) The nature of major histocompatibility complex recognition by gamma delta T cells. Cell 76:29–37
Weintraub BC, Jackson MR, Hedrick SM (1994) Gamma delta T cells can recognize nonclassical MHC in the absence of conventional antigenic peptides. J Immunol 153:3051–3058
Holtmeier W, Witthoft T, Hennemann A, Winter HS, Kagnoff MF (1997) The TCR-delta repertoire in human intestine undergoes characteristic changes during fetal to adult development. J Immunol 158:5632–5641
Spada FM, Grant EP, Peters PJ, Sugita M, Melian A, Leslie DS, Lee HK, van Donselaar E, Hanson DA, Krensky AM, Majdic O, Porcelli SA, Morita CT, Brenner MB (2000) Self-recognition of CD1 by gamma/delta T cells: implications for innate immunity. J Exp Med 191:937–948
Groh V, Steinle A, Bauer S, Spies T (1998) Recognition of stress-induced MHC molecules by intestinal epithelial gammadelta T cells. Science 279:1737–1740
Xu B, Pizarro JC, Holmes MA, McBeth C, Groh V, Spies T, Strong RK (2011) Crystal structure of a gammadelta T-cell receptor specific for the human MHC class I homolog MICA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:2414–2419
Bandeira A, Itohara S, Bonneville M, Burlen-Defranoux O, Mota-Santos T, Coutinho A, Tonegawa S (1991) Extrathymic origin of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes bearing T-cell antigen receptor gamma delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:43–47
Kawaguchi M, Nanno M, Umesaki Y, Matsumoto S, Okada Y, Cai Z, Shimamura T, Matsuoka Y, Ohwaki M, Ishikawa H (1993) Cytolytic activity of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes in germ-free mice is strain dependent and determined by T cells expressing gamma delta T-cell antigen receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:8591–8594
Soderstrom K, Bucht A, Halapi E, Lundqvist C, Gronberg A, Nilsson E, Orsini DL, van de Wal Y, Koning F, Hammarstrom ML et al (1994) High expression of V gamma 8 is a shared feature of human gamma delta T cells in the epithelium of the gut and in the inflamed synovial tissue. J Immunol 152:6017–6027
DuBois RN, Lazenby AJ, Yardley JH, Hendrix TR, Bayless TM, Giardiello FM (1989) Lymphocytic enterocolitis in patients with 'refractory sprue'. JAMA 262:935–937
Loft DE, Marsh MN, Sandle GI, Crowe PT, Garner V, Gordon D, Baker R (1989) Studies of intestinal lymphoid tissue. XII. Epithelial lymphocyte and mucosal responses to rectal gluten challenge in celiac sprue. Gastroenterology 97:29–37
Maiuri L, Ciacci C, Vacca L, Ricciardelli I, Auricchio S, Quaratino S, Londei M (2001) IL-15 drives the specific migration of CD94+ and TCR-gammadelta + intraepithelial lymphocytes in organ cultures of treated celiac patients. Am J Gastroenterol 96:150–156
Inagaki-Ohara K, Nishimura H, Mitani A, Yoshikai Y (1997) Interleukin-15 preferentially promotes the growth of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes bearing gamma delta T cell receptor in mice. Eur J Immunol 27:2885–2891
Parker CM, Groh V, Band H, Porcelli SA, Morita C, Fabbi M, Glass D, Strominger JL, Brenner MB (1990) Evidence for extrathymic changes in the T cell receptor gamma/delta repertoire. J Exp Med 171:1597–1612
Mazzarella G, Stefanile R, Camarca A, Giliberti P, Cosentini E, Marano C, Iaquinto G, Giardullo N, Auricchio S, Sette A, Troncone R, Gianfrani C (2008) Gliadin activates HLA class I-restricted CD8+ T cells in celiac disease intestinal mucosa and induces the enterocyte apoptosis. Gastroenterology 134:1017–1027
Louka AS, Sollid LM (2003) HLA in coeliac disease: unravelling the complex genetics of a complex disorder. Tissue Antigens 61:105–117
Green PH, Jabri B (2003) Coeliac disease. Lancet 362:383–391
Jabri B, Sollid LM (2009) Tissue-mediated control of immunopathology in coeliac disease. Nat Rev Immunol 9:858–870
Abadie V, Sollid LM, Barreiro LB, Jabri B (2011) Integration of genetic and immunological insights into a model of celiac disease pathogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol 29:493–525
Maiuri L, Ciacci C, Ricciardelli I, Vacca L, Raia V, Auricchio S, Picard J, Osman M, Quaratino S, Londei M (2003) Association between innate response to gliadin and activation of pathogenic T cells in coeliac disease. Lancet 362:30–37
Terrazzano G, Sica M, Gianfrani C, Mazzarella G, Maurano F, De Giulio B, de Saint-Mezard S, Zanzi D, Maiuri L, Londei M, Jabri B, Troncone R, Auricchio S, Zappacosta S, Carbone E (2007) Gliadin regulates the NK-dendritic cell cross-talk by HLA-E surface stabilization. J Immunol 179:372–381
Rinke de Wit TF, Vloemans S, van den Elsen PJ, Haworth A, Stern PL (1990) Differential expression of the HLA class I multigene family by human embryonal carcinoma and choriocarcinoma cell lines. J Immunol 144:1080–1087
Forsberg G, Hernell O, Hammarstrom S, Hammarstrom ML (2007) Concomitant increase of IL-10 and pro-inflammatory cytokines in intraepithelial lymphocyte subsets in celiac disease. Int Immunol 19:993–1001
DePaolo RW, Abadie V, Tang F, Fehlner-Peach H, Hall JA, Wang W, Marietta EV, Kasarda DD, Waldmann TA, Murray JA, Semrad C, Kupfer SS, Belkaid Y, Guandalini S, Jabri B (2011) Co-adjuvant effects of retinoic acid and IL-15 induce inflammatory immunity to dietary antigens. Nature 471:220–224
Mention JJ, Ben Ahmed M, Begue B, Barbe U, Verkarre V, Asnafi V, Colombel JF, Cugnenc PH, Ruemmele FM, McIntyre E, Brousse N, Cellier C, Cerf-Bensussan N (2003) Interleukin 15: a key to disrupted intraepithelial lymphocyte homeostasis and lymphomagenesis in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 125:730–745
Benahmed M, Meresse B, Arnulf B, Barbe U, Mention JJ, Verkarre V, Allez M, Cellier C, Hermine O, Cerf-Bensussan N (2007) Inhibition of TGF-beta signaling by IL-15: a new role for IL-15 in the loss of immune homeostasis in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 132:994–1008
Song H, Hur DY, Kim KE, Park H, Kim T, Kim CW, Bang S, Cho DH (2006) IL-2/IL-18 prevent the down-modulation of NKG2D by TGF-beta in NK cells via the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathway. Cell Immunol 242:39–45
Tang F, Chen Z, Ciszewski C, Setty M, Solus J, Tretiakova M, Ebert E, Han J, Lin A, Guandalini S, Groh V, Spies T, Green P, Jabri B (2009) Cytosolic PLA2 is required for CTL-mediated immunopathology of celiac disease via NKG2D and IL-15. J Exp Med 206:707–719
Upshaw JL, Leibson PJ (2006) NKG2D-mediated activation of cytotoxic lymphocytes: unique signaling pathways and distinct functional outcomes. Semin Immunol 18:167–175
Zanzi D, Stefanile R, Santagata S, Iaffaldano L, Iaquinto G, Giardullo N, Lania G, Vigliano I, Vera AR, Ferrara K, Auricchio S, Troncone R, Mazzarella G (2011) IL-15 interferes with suppressive activity of intestinal regulatory T cells expanded in celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol 106:1308–1317
Peluso I, Fantini MC, Fina D, Caruso R, Boirivant M, MacDonald TT, Pallone F, Monteleone G (2007) IL-21 counteracts the regulatory T cell-mediated suppression of human CD4+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol 178:732–739
Fina D, Sarra M, Caruso R, Del Vecchio BG, Pallone F, MacDonald TT, Monteleone G (2008) Interleukin 21 contributes to the mucosal T helper cell type 1 response in coeliac disease. Gut 57:887–892
Zeng R, Spolski R, Finkelstein SE, Oh S, Kovanen PE, Hinrichs CS, Pise-Masison CA, Radonovich MF, Brady JN, Restifo NP, Berzofsky JA, Leonard WJ (2005) Synergy of IL-21 and IL-15 in regulating CD8+ T cell expansion and function. J Exp Med 201:139–148
Ebert EC (2009) Interleukin 21 up-regulates perforin-mediated cytotoxic activity of human intra-epithelial lymphocytes. Immunology 127:206–215
Sperandeo MP, Tosco A, Izzo V, Tucci F, Troncone R, Auricchio R, Romanos J, Trynka G, Auricchio S, Jabri B, Greco L (2011) Potential celiac patients: a model of celiac disease pathogenesis. PLoS One 6:e21281
Malamut G, El Machhour R, Montcuquet N, Martin-Lanneree S, Dusanter-Fourt I, Verkarre V, Mention JJ, Rahmi G, Kiyono H, Butz EA, Brousse N, Cellier C, Cerf-Bensussan N, Meresse B (2010) IL-15 triggers an antiapoptotic pathway in human intraepithelial lymphocytes that is a potential new target in celiac disease-associated inflammation and lymphomagenesis. J Clin Invest 120:2131–2143
Cellier C, Patey N, Mauvieux L, Jabri B, Delabesse E, Cervoni JP, Burtin ML, Guy-Grand D, Bouhnik Y, Modigliani R, Barbier JP, Macintyre E, Brousse N, Cerf-Bensussan N (1998) Abnormal intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes in refractory sprue. Gastroenterology 114:471–481
Daum S, Cellier C, Mulder CJ (2005) Refractory coeliac disease. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 19:413–424
Yokoyama S, Watanabe N, Sato N, Perera PY, Filkoski L, Tanaka T, Miyasaka M, Waldmann TA, Hiroi T, Perera LP (2009) Antibody-mediated blockade of IL-15 reverses the autoimmune intestinal damage in transgenic mice that overexpress IL-15 in enterocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:15849–15854
Zhou R, Wei H, Sun R, Zhang J, Tian Z (2007) NKG2D recognition mediates Toll-like receptor 3 signaling-induced breakdown of epithelial homeostasis in the small intestines of mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:7512–7515
Zhang Y, Moffatt MF, Cookson WO (2012) Genetic and genomic approaches to asthma: new insights for the origins. Curr Opin Pulm Med 18:6–13
Acknowledgments
We thank CD patients and their family members as well as the University of Chicago Celiac Disease Center for supporting our research. We thank B. Sally for critical reading of the manuscript.
This work was supported by the Digestive Diseases Research Core Center at the University of Chicago (DK42086), RO1 DK67180, and DK058727 (for B.J.) and a fellowship of the Italian Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (SIGENP) (for V.D.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This article is published as part of the Special Issue on Celiac Disease [34:5].
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abadie, V., Discepolo, V. & Jabri, B. Intraepithelial lymphocytes in celiac disease immunopathology. Semin Immunopathol 34, 551–566 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-012-0316-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-012-0316-x