Abstract
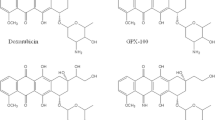
Purpose: The methoxymorpholinyl doxorubicin analogue PNU 152243 was brought into clinical studies because of preclinical observations of its non-cross-resistance in mdr tumor cells, dose-limiting neutropenia, lack of cardiotoxicity, and antitumor activity after oral administration. Methods: PNU 152243 was given orally every 4 weeks to 21 adults with a variety of solid tumors at doses ranging from 59 to 940 μg/m2. Antiemetic prophylaxis with 5-HT3 antagonists and steroids, given i.v. on day 1 and orally on days 2–8, was required beginning with the dose of 118 μg/m2. The plasma pharmacokinetics of PNU 152243 were determined by an HPLC method with fluorescence detection. The in vitro myelotoxic effects on granulocyte macrophage-colony forming cells (GM-CFC) of the plasma from 11 patients, obtained 4 and 6 h after treatment at all dose levels, were also assessed. Results: Neutropenia was the main hematologic toxic effect and the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) for myelotoxicity was 940 μg/m2, with neutropenia grade 3–4 in two of three patients. Dose-dependent nausea and vomiting were dose-limiting and the MTD for gastrointestinal toxicity was fixed at 820 μg/m2, with grade 4 vomiting in one of two patients. Other frequent toxic effects were diarrhea and fatigue. Peak levels of PNU 152243 were achieved 4 h after dosing. Dose-dependent Cmax and AUCExp, and significant interpatient variability of the main pharmacokinetic parameters were found. Very low levels of the 13-dihydrometabolite PNU 155051 were detected only at the highest doses. The hematotoxicity tests showed a <70% colony growth inhibition with no correlation between the growth inhibition effect and the degree of myelotoxicity in the same patient. Plasma concentrations of PNU 152243 were 1000 times lower than the concentration inhibiting the growth of 70% of colonies. No objective tumor responses were seen. Conclusions: Owing to the occurrence of severe and prolonged nausea and vomiting, the clinical development of oral PNU 152243 was discontinued. The higher-than-expected neutropenia and its lack of relationship with plasma levels of PNU 152243 and its 13-dihydroderivative PNU 155051 might be related to the formation of potent cytotoxic metabolites present in human plasma at undetectable concentrations and with prolonged half-life, as suggested by hematotoxicity tests performed with plasma from patients in GM-CFC assays.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 February 1999 / Accepted: 9 April 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sessa, C., Zucchetti, M., Ghielmini, M. et al. Phase I clinical and pharmacological study of oral methoxymorpholinyl doxorubicin (PNU 152243). Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 44, 403–410 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002800050996
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002800050996