Abstract
Purpose
miRNAs are implicated in drug resistance of multiple cancers including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), highlighting the potential of miRNAs as chemoresistance regulators in cancer treatment. This study aims to explore the relationship between miR-181c and chemoresistance of NSCLC cells.
Methods
qRT-PCR was conducted to examine the expression of miR-181c in NSCLC tissues, and parental and cisplatin (DDP)-resistant NSCLC cells. MTT assay and flow cytometry were performed to detect the survival rate and apoptosis in NSCLC cells. Luciferase reporter assay was performed to confirm the potential target of miR-181c. Xenograft tumor experiment was applied to confirm the effect of miR-181c on DDP sensitivity of DDP-resistant NSCLC cells in vivo.
Results
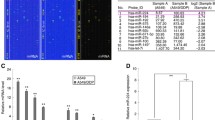
miR-181c was upregulated in NSCLC tissues, and parental and DDP-resistant NSCLC cells. miR-181c downregulation or WIF1 overexpression increased DDP sensitivity of DDP-resistant NSCLC cells by decreasing survival rate and promoting DDP-induced apoptosis. miR-181c was demonstrated to be able to bind to WIF1 and negatively regulate the expression of WIF1. WIF1 knockdown abolished anti-miR-181c-induced DDP sensitivity. Moreover, anti-miR-181c suppressed the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by regulating WIF1. XAV939 treatment reversed miR-181c-induced increase in IC50 value and miR-181c-triggered decrease in apoptosis. Finally, anti-miR-181c improved DDP sensitivity of DDP-resistant NSCLC cells in vivo.
Conclusion
miR-181c contributed to DDP resistance in NSCLC cells through activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by targeting WIF1, providing a potential therapeutic application for the treatment of patients with DDP-resistant NSCLC in the future.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- OD:
-
Optical density
- miRNAs:
-
MicroRNAs
- SDS–PAGE:
-
Odium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- HRP:
-
Horseradish peroxidase
- SPF:
-
Specific pathogen-free
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 66:7–30. doi:10.3322/caac.21332
Boyer MJ, Gu L, Wang X, Kelsey CR, Yoo DS, Onaitis MW, Dunphy FR, Crawford J, Ready NE, Salama JK (2016) Toxicity of definitive and post-operative radiation following ipilimumab in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung cancer 98:76–78. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.05.014
Meng W, Ye Z, Cui R, Perry J, Dedousihuebner V, Huebner A, Wang Y, Li B, Volinia S, Nakanishi H (2013) MicroRNA-31 predicts the presence of lymph node metastases and survival in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 19:5423–5433. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0320
Jin Z, Guan L, Song Y, Xiang GM, Chen SX, Gao B (2016) MicroRNA-138 regulates chemoresistance in human non-small cell lung cancer via epithelial mesenchymal transition. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 20:1080–1086
Lin WU, Xingxiang PU, Wang Q, Cao J, Fang XU, Li XU, Kang LI (2016) miR-96 induces cisplatin chemoresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells by downregulating SAMD9. Oncol Lett 11:945–952. doi:10.3892/ol.2015.4000
Ohashi R, Takahashi F, Cui R, Yoshioka M, Gu T, Sasaki S, Tominaga S, Nishio K, Tanabe KK, Takahashi K (2007) Interaction between CD44 and hyaluronate induces chemoresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cell. Cancer Lett 252:225–234. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2006.12.025
Yang H, Wang W, Zhang Y, Zhao J, Lin E, Gao J, He J (2011) The role of NF-E2-related factor 2 in predicting chemoresistance and prognosis in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 12:166–171. doi:10.1016/j.cllc.2011.03.012
Shen DW, Pouliot LM, Hall MD, Gottesman MM (2012) Cisplatin resistance: a cellular self-defense mechanism resulting from multiple epigenetic and genetic changes. Pharmacol Rev 64:706–721. doi:10.1124/pr.111.005637
Kim VN (2005) MicroRNA biogenesis: coordinated cropping and dicing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:376–385. doi:10.1038/nrm1644
Kouwenhove MV, Kedde M, Agami R (2011) MicroRNA regulation by RNA-binding proteins and its implications for cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 11:644–656. doi:10.1038/nrc3107
Blower PE, Chung JH, Verducci JS, Lin S, Park JK, Dai Z, Liu CG, Schmittgen TD, Reinhold WC, Croce CM (2008) MicroRNAs modulate the chemosensitivity of tumor cells. Mol Cancer Ther 7:1–9. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0573
Su W, Mo Y, Wu F, Guo K, Li J, Luo Y, Ye H, Guo H, Li D, Yang Z (2016) miR-135b reverses chemoresistance of non-small cell lung cancer cells by downregulation of FZD1. Biomed Pharmacother 84:123–129. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.027
Chen X, Jiang Y, Huang Z, Li D, Chen X, Cao M, Meng Q, Pang H, Sun L, Zhao Y (2016) miRNA-378 reverses chemoresistance to cisplatin in lung adenocarcinoma cells by targeting secreted clusterin. Sci Rep 6:19455. doi:10.1038/srep19455
Ren P, Gong F, Zhang Y, Jiang J, Zhang H (2016) MicroRNA-92a promotes growth, metastasis, and chemoresistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting PTEN. Tumor Biol 37:3215–3225. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-4150-3
Zhang WL, Zhang JH (2015) miR-181c promotes proliferation via suppressing PTEN expression in inflammatory breast cancer. Int J Oncol 46:2011–2020. doi:10.3892/ijo.2015.2896
Ruan J, Lou S, Dai Q, Mao D, Ji J, Sun X (2015) Tumor suppressor miR-181c attenuates proliferation, invasion, and self-renewal abilities in glioblastoma. Neuroreport 26:66–73. doi:10.1097/WNR.0000000000000302
Yao L, Li W, Li F, Gao X, Wei X, Liu Z (2015) MiR181c inhibits ovarian cancer metastasis and progression by targeting PRKCD expression. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:15198–15205
Yang Y, Ma ZH, Li XG, Zhang WF, Wan J, Du LJ, Li GJ, Yang GK, Lu P (2016) Iodine-125 irradiation inhibits invasion of gastric cancer cells by reactivating microRNA-181c expression. Oncol Lett 12:2789
Jing L, Yang S, Ning S, Yuan W, Yu J, Qiu H, He X (2016) Overexpression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR leads to chemoresistance by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in human ovarian cancer. Tumor Biol 37:2057–2065. doi:10.1007/s13277-015-3998-6
Kim ES, Lee JJ, He G, Chow CW, Fujimoto J, Kalhor N, Swisher SG, Wistuba II, Stewart DJ, Siddik ZH (2012) Tissue platinum concentration and tumor response in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 30:3345–3352. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.40.8120
Gong Z, Yang J, Li J, Yang L, Le Y, Wang S, Lin HK (2014) Novel insights into the role of microRNA in lung cancer resistance to treatment and targeted therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targ 14:241–258
Sun X, Sit A, Feinberg MW (2014) Role of miR-181 family in regulating vascular inflammation and immunity. Trends Cardiovasc Med 24:105–112. doi:10.1016/j.tcm.2013.09.002
She X, Yu Z, Cui Y, Lei Q, Wang Z, Xu G, Luo Z, Li G, Wu M (2014) miR-181 subunits enhance the chemosensitivity of temozolomide by Rap1B-mediated cytoskeleton remodeling in glioblastoma cells. Med Oncol 31:1–10. doi:10.1007/s12032-014-0892-9
Li H, Zhang P, Sun X, Sun Y, Shi C, Liu H, Liu X (2015) MicroRNA-181a regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting PTEN in drug-resistant lung adenocarcinoma cells. Int J Oncol 47:1379–1392. doi:10.3892/ijo.2015.3144
Chen Y, Li T (2014) MicroRNA-181a enhances the chemoresistance of human cervical squamous cell carcinoma to cisplatin by targeting PRKCD. Exp Cell Res 320:12–20. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.10.014
Li P, Lu X, Wang Y, Sun L, Qian C, Yan W, Liu N, You Y, Fu Z (2010) MiR-181b suppresses proliferation of and reduces chemoresistance to temozolomide in U87 glioma stem cells. J Biomed Res 24:436–443. doi:10.1016/S1674-8301(10)60058-9
Wang J, Ke S, Chen FR, Chen ZP (2013) miR-181b modulates glioma cell sensitivity to temozolomide by targeting MEK1. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 72:14158. doi:10.1007/s00280-013-2180-3
Cinegaglia NC, Andrade SC, Tokar T, Pinheiro M, Severino FE, Oliveira RA, Hasimoto EN, Cataneo DC, Cataneo AJ, Defaveri J (2016) Integrative transcriptome analysis identifies deregulated microRNA-transcription factor networks in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 7:28920–28934. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.8713
Yamazaki N, Koga Y, Taniguchi H, Kojima M, Kanemitsu Y, Saito N, Matsumura Y (2017) High expression of miR-181c as a predictive marker of recurrence in stage II colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 8:6970–6983. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.14344
Chen M, Wang M, Xu S, Guo X, Jiang J (2011) Upregulation of miR-181c contributes to chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer by inactivating the Hippo signaling pathway. Oncotarget 6:44466–44479. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.6298
Mosakhani N, Mustjoki S, Knuutila S (2013) Down-regulation of miR-181c in imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia. Mol Cytogenet 6:27. doi:10.1186/1755-8166-6-27
Zhao L, Li Y, Song X, Zhou H, Li N, Yuan M, Li J (2014) Upregulation of miR-181c inhibits chemoresistance by targeting ST8SIA4 in chronic myelocytic leukemia. Oncotarget 7:60074–60086. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11054
Cadigan KM (2008) Wnt-β-catenin signaling. Curr Biol 18:R943-947. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2008.08.017
Clevers H, Nusse R (2012) Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Disease. Cell 149:1192–1250. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.012
Stewart DJ, Chang DW, Ye Y, Spitz M, Lu C, Shu X, Wampfler JA, Marks RS, Garces YI, Yang P (2014) Wnt signaling pathway pharmacogenetics in non-small cell lung cancer. Pharmacogenomics J 14:509–522. doi:10.1038/tpj.2014.21
Stewart DJ (2014) Wnt signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 106:djt356. doi:10.1093/jnci/djt356
Wissmann C, Wild PJ, Kaiser S, Roepcke S, Stoehr R, Woenckhaus M, Kristiansen G, Hsieh JC, Hofstaedter F, Hartmann A (2003) WIF1, a component of the Wnt pathway, is down-regulated in prostate, breast, lung, and bladder cancer. J Pathol 201:204–212. doi:10.1002/path.1449
Li L, Liu HC, Wang C, Liu X, Hu FC, Xie N, Lü L, Chen X, Huang HZ (2016) Overexpression of β-catenin induces cisplatin resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed Res Int 2016:5378567. doi:10.1155/2016/5378567
Zhang C, Zhang Z, Zhang S, Wang W, Hu P (2017) Targeting of Wnt/β-catenin by anthelmintic drug pyrvinium enhances sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to chemotherapy. Med Sci Monit 23:266–275
Gao W, Ying L, Qin R, Liu D, Feng Q (2016) Silence of fibronectin 1 increases cisplatin sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 476:35–41. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.05.081
MacDonald BT, Tamai K, He X (2009) Wnt/β-catenin signaling: components, mechanisms, and diseases. Dev Cell 17:9–26. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2009.06.016
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Science and Technology Project of Henan Province (172102310158).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Hu, B., Wang, Z. et al. miR-181c contributes to cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting Wnt inhibition factor 1. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 80, 973–984 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-017-3435-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-017-3435-1