Abstract
Purpose
The pancreatic cancer has extremely low overall 5-year survival, and gemcitabine is the only approved single agent for pancreatic cancer treatment.
Methods
In the present study, we investigated the potential effect of perifosine, a novel Akt inhibitor on gemcitabine-induced anti-pancreatic cancer effect both in vivo and in vitro.
Results
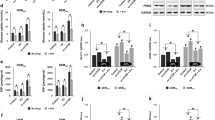
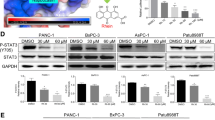
We showed that sub-cytotoxic low concentration of perifosine dramatically enhanced gemcitabine-induced cytotoxicity in cultured pancreatic cancer cells. Perifosine inhibited Akt–mammalian target of rapamycin and Erk–mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in pancreatic cancer cells. Meanwhile, perifosine suppressed the hedgehog signaling, as it inhibited glioma-associated oncogenes (Gli) 1 activation and decreased its target protein patched 1 (PTCH1) expression. Our data demonstrated that perifosine blocked p70S6K1 (S6K1) activation, thus disrupting S6K1–Gli1 association and subsequent Gli1 activation. The reduction of S6K1 or Gli1 expression by target siRNAs inhibited PTCH1 expression and enhanced gemcitabine-induced cytotoxicity in pancreatic cancer cells. Significantly, perifosine dramatically enhanced gemcitabine-mediated antitumor effect in a PANC-1 xenograft severe combined immunodeficiency mice model.
Conclusions
In summary, we conclude that perifosine sensitizes gemcitabine-mediated anti-pancreatic cancer efficiency through regulating multiple signaling pathways.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Gli:
-
Glioma-associated oncogenes
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- Hh:
-
Hedgehog
- CCK-8:
-
Cell counting kit-8
- SMO:
-
Smoothened
- Sufu:
-
Suppressor of fused
- PTCH1:
-
Patched 1
References
Stathis A, Moore MJ (2010) Advanced pancreatic carcinoma: current treatment and future challenges. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 7(3):163–172
Schneider G, Siveke JT, Eckel F, Schmid RM (2005) Pancreatic cancer: basic and clinical aspects. Gastroenterology 128(6):1606–1625
Gudjonsson B (2009) Pancreatic cancer: survival, errors and evidence. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 21(12):1379–1382
Wray CJ, Ahmad SA, Matthews JB, Lowy AM (2005) Surgery for pancreatic cancer: recent controversies and current practice. Gastroenterology 128(6):1626–1641
Lockhart AC, Rothenberg ML, Berlin JD (2005) Treatment for pancreatic cancer: current therapy and continued progress. Gastroenterology 128(6):1642–1654
Oettle H, Post S, Neuhaus P, Gellert K, Langrehr J, Ridwelski K, Schramm H, Fahlke J, Zuelke C, Burkart C, Gutberlet K, Kettner E, Schmalenberg H, Weigang-Koehler K, Bechstein WO, Niedergethmann M, Schmidt-Wolf I, Roll L, Doerken B, Riess H (2007) Adjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine vs observation in patients undergoing curative-intent resection of pancreatic cancer: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 297(3):267–277
Rivera F, Lopez-Tarruella S, Vega-Villegas ME, Salcedo M (2009) Treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer: from gemcitabine single agent to combinations and targeted therapy. Cancer Treat Rev 35(4):335–339
Westphal S, Kalthoff H (2003) Apoptosis: targets in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer 2:6
Gills JJ, Dennis PA (2009) Perifosine: update on a novel Akt inhibitor. Curr Oncol Rep 11(2):102–110
Kondapaka SB, Singh SS, Dasmahapatra GP, Sausville EA, Roy KK (2003) Perifosine, a novel alkylphospholipid, inhibits protein kinase B activation. Mol Cancer Ther 2(11):1093–1103
Richardson PG, Wolf J, Jakubowiak A, Zonder J, Lonial S, Irwin D, Densmore J, Krishnan A, Raje N, Bar M, Martin T, Schlossman R, Ghobrial IM, Munshi N, Laubach J, Allerton J, Hideshima T, Colson K, Poradosu E, Gardner L, Sportelli P, Anderson KC (2011) Perifosine plus bortezomib and dexamethasone in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma previously treated with bortezomib: results of a multicenter phase I/II trial. J Clin Oncol 29(32):4243–4249
Bendell JC, Nemunaitis J, Vukelja SJ, Hagenstad C, Campos LT, Hermann RC, Sportelli P, Gardner L, Richards DA (2011) Randomized placebo-controlled phase II trial of perifosine plus capecitabine as second- or third-line therapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 29(33):4394–4400
Ruiz i Altaba A, Sanchez P, Dahmane N (2002) Gli and hedgehog in cancer: tumours, embryos and stem cells. Nat Rev Cancer 2(5):361–372
Yauch RL, Gould SE, Scales SJ, Tang T, Tian H, Ahn CP, Marshall D, Fu L, Januario T, Kallop D, Nannini-Pepe M, Kotkow K, Marsters JC, Rubin LL, de Sauvage FJ (2008) A paracrine requirement for hedgehog signalling in cancer. Nature 455(7211):406–410
Thayer SP, di Magliano MP, Heiser PW, Nielsen CM, Roberts DJ, Lauwers GY, Qi YP, Gysin S, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Yajnik V, Antoniu B, McMahon M, Warshaw AL, Hebrok M (2003) Hedgehog is an early and late mediator of pancreatic cancer tumorigenesis. Nature 425(6960):851–856
Pasca di Magliano M, Hebrok M (2003) Hedgehog signalling in cancer formation and maintenance. Nat Rev Cancer 3(12):903–911
Taipale J, Beachy PA (2001) The hedgehog and Wnt signalling pathways in cancer. Nature 411(6835):349–354
Feldmann G, Dhara S, Fendrich V, Bedja D, Beaty R, Mullendore M, Karikari C, Alvarez H, Iacobuzio-Donahue C, Jimeno A, Gabrielson KL, Matsui W, Maitra A (2007) Blockade of hedgehog signaling inhibits pancreatic cancer invasion and metastases: a new paradigm for combination therapy in solid cancers. Cancer Res 67(5):2187–2196
Rubin LL, de Sauvage FJ (2006) Targeting the hedgehog pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5(12):1026–1033
Wang Y, Ding Q, Yen CJ, Xia W, Izzo JG, Lang JY, Li CW, Hsu JL, Miller SA, Wang X, Lee DF, Hsu JM, Huo L, Labaff AM, Liu D, Huang TH, Lai CC, Tsai FJ, Chang WC, Chen CH, Wu TT, Buttar NS, Wang KK, Wu Y, Wang H, Ajani J, Hung MC (2012) The crosstalk of mTOR/S6K1 and hedgehog pathways. Cancer Cell 21(3):374–387
Stecca B, Mas C, Clement V, Zbinden M, Correa R, Piguet V, Beermann F, Ruiz IAA (2007) Melanomas require HEDGEHOG–GLI signaling regulated by interactions between GLI1 and the RAS-MEK/AKT pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(14):5895–5900
Seto M, Ohta M, Asaoka Y, Ikenoue T, Tada M, Miyabayashi K, Mohri D, Tanaka Y, Ijichi H, Tateishi K, Kanai F, Kawabe T, Omata M (2009) Regulation of the hedgehog signaling by the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in gastric cancer. Mol Carcinog 48(8):703–712
Wan X, Harkavy B, Shen N, Grohar P, Helman LJ (2007) Rapamycin induces feedback activation of Akt signaling through an IGF-1R-dependent mechanism. Oncogene 26(13):1932–1940
Sanchez P, Hernandez AM, Stecca B, Kahler AJ, DeGueme AM, Barrett A, Beyna M, Datta MW, Datta S, Ruiz i Altaba A (2004) Inhibition of prostate cancer proliferation by interference with SONIC HEDGEHOG–GLI1 signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(34):12561–12566
Parsons CM, Muilenburg D, Bowles TL, Virudachalam S, Bold RJ (2010) The role of Akt activation in the response to chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Res 30(9):3279–3289
Shin-Kang S, Ramsauer VP, Lightner J, Chakraborty K, Stone W, Campbell S, Reddy SA, Krishnan K (2011) Tocotrienols inhibit AKT and ERK activation and suppress pancreatic cancer cell proliferation by suppressing the ErbB2 pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 51(6):1164–1174
Garrido-Laguna I, Tan AC, Uson M, Angenendt M, Ma WW, Villaroel MC, Zhao M, Rajeshkumar NV, Jimeno A, Donehower R, Iacobuzio-Donahue C, Barrett M, Rudek MA, Rubio-Viqueira B, Laheru D, Hidalgo M (2010) Integrated preclinical and clinical development of mTOR inhibitors in pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer 103(5):649–655
Roy SK, Srivastava RK, Shankar S (2010) Inhibition of PI3 K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways causes activation of FOXO transcription factor, leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in pancreatic cancer. J Mol Signal 5:10
Costello E, Neoptolemos JP (2011) Pancreatic cancer in 2010: new insights for early intervention and detection. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8(2):71–73
Heinemann V, Boeck S, Hinke A, Labianca R, Louvet C (2008) Meta-analysis of randomized trials: evaluation of benefit from gemcitabine-based combination chemotherapy applied in advanced pancreatic cancer. BMC Cancer 8:82
Moore MJ, Goldstein D, Hamm J, Figer A, Hecht JR, Gallinger S, Au HJ, Murawa P, Walde D, Wolff RA, Campos D, Lim R, Ding K, Clark G, Voskoglou-Nomikos T, Ptasynski M, Parulekar W (2007) Erlotinib plus gemcitabine compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: a phase III trial of the national cancer institute of Canada clinical trials group. J Clin Oncol 25(15):1960–1966
Hennessy BT, Smith DL, Ram PT, Lu Y, Mills GB (2005) Exploiting the PI3 K/AKT pathway for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4(12):988–1004
Tanno S, Mitsuuchi Y, Altomare DA, Xiao GH, Testa JR (2001) AKT activation up-regulates insulin-like growth factor I receptor expression and promotes invasiveness of human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 61(2):589–593
Azzariti A, Porcelli L, Gatti G, Nicolin A, Paradiso A (2008) Synergic antiproliferative and antiangiogenic effects of EGFR and mTOR inhibitors on pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol 75(5):1035–1044
Wolpin BM, Hezel AF, Abrams T, Blaszkowsky LS, Meyerhardt JA, Chan JA, Enzinger PC, Allen B, Clark JW, Ryan DP, Fuchs CS (2009) Oral mTOR inhibitor everolimus in patients with gemcitabine-refractory metastatic pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol 27(2):193–198
Elrod HA, Lin YD, Yue P, Wang X, Lonial S, Khuri FR, Sun SY (2007) The alkylphospholipid perifosine induces apoptosis of human lung cancer cells requiring inhibition of Akt and activation of the extrinsic apoptotic pathway. Mol Cancer Ther 6(7):2029–2038
Ji C, Yang YL, Yang Z, Tu Y, Cheng L, Chen B, Xia JP, Sun WL, Su ZL, He L, Bi ZG (2012) Perifosine sensitizes UVB-induced apoptosis in skin cells: new implication of skin cancer prevention? Cell Signal 24(9):1781–1789
Coni S, Infante P, Gulino A (2013) Control of stem cells and cancer stem cells by hedgehog signaling: pharmacologic clues from pathway dissection. Biochem Pharmacol 85(5):623–628
Metcalfe C, de Sauvage FJ (2011) Hedgehog fights back: mechanisms of acquired resistance against Smoothened antagonists. Cancer Res 71(15):5057–5061
Buonamici S, Williams J, Morrissey M, Wang A, Guo R, Vattay A, Hsiao K, Yuan J, Green J, Ospina B, Yu Q, Ostrom L, Fordjour P, Anderson DL, Monahan JE, Kelleher JF, Peukert S, Pan S, Wu X, Maira SM, GarciaEcheverria C, Briggs KJ, Watkins DN, Yao YM, Lengauer C, Warmuth M, Sellers WR, Dorsch M (2010) Interfering with resistance to smoothened antagonists by inhibition of the PI3 K pathway in medulloblastoma. Sci Transl Med 2 (51): 51ra70
Guertin DA, Sabatini DM (2007) Defining the role of mTOR in cancer. Cancer Cell 12(1):9–22
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the talent plan of Science and Technology Bureau of Zhejiang Province (2012R10043). The founders have no roles in study design; in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the article for publication.
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interests are stated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Ying Xin, Xiang-di Shen and Long Cheng are Co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xin, Y., Shen, Xd., Cheng, L. et al. Perifosine inhibits S6K1–Gli1 signaling and enhances gemcitabine-induced anti-pancreatic cancer efficiency. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 73, 711–719 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2397-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2397-9