Abstract
Background
[18F]fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)-PET is being evaluated as a tool for the early detection of response to various targeted agents in solid tumors. The aim of this study was to evaluate the predictive value of PET response after 2 days of erlotinib in unselected pretrated patients with stage IV NSCLC.
Patients and methods
FDG-PET/CT scans were conducted at baseline and after 2 days of erlotinib, with a CT evaluation performed at baseline and after 45–60 days of therapy. PET responses were evaluated by quantitative changes on SUVmax tumor/non-tumor ratio and classified according to EORTC criteria. PET responses were compared with RECIST responses and related to progression-free (PFS) and overall (OS) survival. Erlotinib effects on glucose uptake were also studied in a panel of NSCLC cell lines.
Results
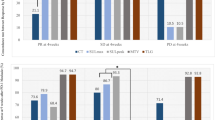
Fifty-three patients were enrolled. At 2 days of erlotinib, 20 (38 %) patients showed partial metabolic response (PMR), 25 (47 %) had stable metabolic disease (SMD) and 8 (15 %) had progressive metabolic disease (PMD). All patients with PMD had confirmed RECIST progression at 45–60 days. Patients with early PMR and SMD had significantly longer PFS (p < 0.001 and p = 0.001, respectively) and OS (p = 0.001 for both) than PMD patients.
Conclusions
FDG-PET assessment after 2 days of erlotinib could be useful to identify early resistent patients and to predict survival in unselected NSCLC pretreated population.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shepherd FA, Rodriguez Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, Tan EH, Hirsh V, Thongprasert S, Campos D, Maoleekoonpiroj S, Smylie M, Martins R, van Kooten M, Dediu M, Findlay B, Tu D, Johnston D, Bezjak A, Clark G, Santabárbara P, Seymour L; National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group (2005) Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 353:123–132
Mok TS, Wu Y-L, Thongprasert S, Yang CH, Chu DT, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y, Nishiwaki Y, Ohe Y, Yang JJ, Chewaskulyong B, Jiang H, Duffield EL, Watkins CL, Armour AA, Fukuoka M (2009) Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 361:947–957
Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, Palmero R, Garcia-Gomez R, Pallares C, Sanchez JM, Porta R, Cobo M, Garrido P, Longo F, Moran T, Insa A, De Marinis F, Corre R, Bover I, Illiano A, Dansin E, de Castro J, Milella M, Reguart N, Altavilla G, Jimenez U, Provencio M, Moreno MA, Terrasa J, Muñoz-Langa J, Valdivia J, Isla D, Domine M, Molinier O, Mazieres J, Baize N, Garcia-Campelo R, Robinet G, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Lopez-Vivanco G, Gebbia V, Ferrera-Delgado L, Bombaron P, Bernabe R, Bearz A, Artal A, Cortesi E, Rolfo C, Sanchez-Ronco M, Drozdowskyj A, Queralt C, de Aguirre I, Ramirez JL, Sanchez JJ, Molina MA, Taron M, Paz-Ares L; Spanish Lung Cancer Group in collaboration with Groupe Français de Pneumo-Cancérologie and Associazione Italiana Oncologia Toracica (2012) Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 13:239–246
Tsao MS, Sakurada A, Cutz JC, Zhu CQ, Kamel-Reid S, Squire J, Lorimer I, Zhang T, Liu N, Daneshmand M, Marrano P, da Cunha Santos G, Lagarde A, Richardson F, Seymour L, Whitehead M, Ding K, Pater J, Shepherd FA (2005) Erlotinib in lung cancer—molecular and clinical predictors of outcome. N Engl J Med 353:133–144
Cappuzzo F, Ciuleanu T, Stelmakh L, Cicenas S, Szczésna A, Juhász E, Esteban E, Molinier O, Brugger W, Melezínek I, Klingelschmitt G, Klughammer B, Giaccone G (2010) SATURN investigators, Erlotinib as maintenance treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase III study. Lancet Oncol 11:521–529
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Esenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, Verweij J, Van Glabbeke M, van Oosterom AT, Christian MC, Gwyther SG (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:205–216
Tuma R (2006) Sometimes size doesn’t matter: re-evaluating RECIST and tumor response rate endpoints. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:1272–1274
Vansteenkiste J, Fischer BM, Dooms C, Mortensen J (2004) Positron-emission tomography in prognostic and therapeutic assessment of lung cancer: systematic review. Lancet Oncol 5:531–540
Weber WA, Petersen V, Schmidt B, Tyndale-Hines L, Link T, Peschel C, Schwaiger M (2003) Positron emission tomography in non-small-cell lung cancer: prediction of response to chemotherapy by quantitative assessment of glucose use. J Clin Oncol 21:2651–2657
Lee DH, Kim SK, Lee DH, Lee SY, Park SH, Kim HY, Kang KW, Han JY, Kim HT, Lee JS (2009) Early prediction of response to first-line therapy using integrated 18F-FDG PET/CT for patients with advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 4:816–821
Stroobants S, Goeminne J, Seegers M, Dimitrijevic S, Dupont P, Nuyts J, Martens M, van den Borne B, Cole P, Sciot R, Dumez H, Silberman S, Mortelmans L, van Oosterom A (2003) 18FDG-Positron emission tomography for the early prediction of response in advanced soft tissue sarcoma treated with imatinib mesylate (Glivec). Eur J Cancer 39:2012–2020
Prior JO, Montemurro M, Orcurto MV, Michielin O, Luthi F, Benhattar J, Guillou L, Elsig V, Stupp R, Delaloye AB, Leyvraz S (2009) Early prediction of response to sunitinib after imatinib failure by 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. J Clin Oncol 27:439–445
Walter MA, Benz MR, Hildebrandt IJ, Laing RE, Hartung V, Damoiseaux RD, Bockisch A, Phelps ME, Czernin J, Weber WA (2011) Metabolic imaging allows early prediction of response to vandetinib. J Nucl Med 52:231–240
Whiteman EL, Cho H, Birnabaum MJ (2002) Role of Akt/protein kinase B in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab 13:444–451
Elstrom RL, Bauer DE, Buzzai M, Karnauskas R, Harris MH, Plas DR, Zhuang H, Cinalli RM, Alavi A, Rudin CM, Thompson CB (2004) Akt stimulates aerobic glycolysis in cancer cells. Cancer Res 64:3892–3899
Su H, Bodenstein C, Dumont RA, Seimbille Y, Dubinett S, Phelps ME, Herschman H, Czernin J, Weber W (2006) Monitoring tumor glucose utilization by positron emission tomography for the prediction of treatment response to epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res 12:5659–5667
Sunaga N, Oriuchi N, Kaira K, Yanagitani N, Tomizawa Y, Hisada T, Ishizuka T, Endo K, Mori M (2008) Usefulness of FDG-PET for early prediction of the response to gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 59:203–210
Young H, Baum R, Cremerius U, Herholz K, Hoekstra O, Lammertsma AA, Pruim J, Price P (1999) Measurement of clinical and subclinical tumour response using [18F]-fluorodeoxyglucose and positron emission tomography: review and 1999 EORTC recommendations. European organization for research and treatment of cancer (EORTC) PET study group. Eur J Cancer 35:1773–1782
Tiseo M, Rossi G, Capelletti M, Sartori G, Spiritelli E, Marchioni A, Bozzetti C, De Palma G, Lagrasta C, Campanini N, Camisa R, Boni L, Franciosi V, Rindi G, Ardizzoni A (2010) Predictors of gefitinib outcomes in advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): study of comprehensive panel of molecular markers. Lung Cancer 67:355–360
Cavazzoni A, Petronini PG, Galetti M, Roz L, Andriani F, Carbognani P, Rusca M, Fumarola C, Alfieri R, Sozzi G (2004) Dose-dependent effect of FHIT inducible expression in calu-1 lung cancer cell line. Oncogene 23:8439–8446
Fumarola C, La Monica S, Alfieri RR, Borra E, Guidotti GG (2005) Cell size reduction induced by inhibition of the mTOR/S6 K-signaling pathway protects Jurkat cells from apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 12:1344–1357
Cavazzoni A, Galetti M, Fumarola C, Alfieri RR, Roz L, Andriani F, Carbognani P, Rusca M, Sozzi G, Petronini PG (2007) Effect of inducible FHIT and p53 expression in the Calu-1 lung cancer cell line. Cancer Lett 246:69–81
Younes M, Brown RW, Stephenson M, Gondo M, Cagle PT (1997) Overexpression of Glut1 and Glut3 in stage I nonsmall cell lung carcinoma is associated with poor survival. Cancer 80:1046–1051
Herrmann K, Benz MR, Krause BJ, Pomykala KL, Buck AK, Czernin J (2011) (18)F-FDG-PET/CT in evaluating response to therapy in solid tumors: where we are and where we can go. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 55:620–632
Zander T, Scheffler M, Nogova L, Kobe C, Engel-Riedel W, Hellmich M, Papachristou I, Toepelt K, Draube A, Heukamp L, Buettner R, Ko YD, Ullrich RT, Smit E, Boellaard R, Lammertsma AA, Hallek M, Jacobs AH, Schlesinger A, Schulte K, Querings S, Stoelben E, Neumaier B, Thomas RK, Dietlein M, Wolf J (2011) Early prediction of nonprogression in advanced non–small-cell lung cancer treated with erlotinib by using [18F]Fluorodeoxyglucose and [18F]Fluorothymidine positron emission tomography. J Clin Oncol 29:1701–1708
Mileshkin L, Hicks RJ, Hughes BG, Mitchell PL, Charu V, Gitlitz BJ, Macfarlane D, Solomon B, Amler LC, Yu W, Pirzkall A, Fine BM (2011) Changes in FDG- and FLT-PET imaging in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with erlotinib. Clin Cancer Res 17:3304–3315
Benz MR, Herrmann K, Walter F, Garon EB, Reckamp KL, Figlin R, Phelps ME, Weber WA, Czernin J, Allen-Auerbach MS (2011) [18]F-FDG PET/CT for monitoring treatment responses to the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor erlotinib. J Nucl Med 52:1684–1689
Takahashi R, Hirata H, Tachibana I, Shimosegawa E, Inoue A, Nagatomo I, Takeda Y, Kida H, Goya S, Kijima T, Yoshida M, Kumagai T, Kumanogoh A, Okumura M, Hatazawa J, Kawase I (2012) Early [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography at 2 days of gefitinib treatment predicts clinical outcome in patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung. Clin Cancer Res 18:220–228
O’Brien ME, Myerson JS, Coward JI, Puglisi M, Trani L, Wotherspoon A, Sharma B, Cook G, Ashley S, Gunapala R, Chua S, Popat S (2012) A phase II study of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET-CT in non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving erlotinib (Tarceva); objective and symptomatic responses at 6 and 12 weeks. Eur J Cancer 48:68–74
Bengtsson T, Hicks RJ, Peterson A, Port RE (2012) 18F-FDG PET as a surrogate biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer treated with erlotinib: newly identified lesions are more informative than standardized uptake value. J Nucl Med 53:530–537
Everitt S, Plumridge N, Herschtal A, Bressel M, Ball D, Callahan J, Kron T, Schneider-Kolsky M, Binns D, Hicks RJ, Mac Manus M (2013) The impact of time between staging PET/CT and definitive chemo-radiation on target volumes and survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Radiother Oncol 106:288–291
Chan CH, Li CF, Yang WL, Gao Y, Lee SW, Feng Z, Huang HY, Tsai KK, Flores LG, Shao Y, Hazle JD, Yu D, Wei W, Sarbassov D, Hung MC, Nakayama KI, Lin HK (2012) The Skp2-SCF E3 ligase regulates Akt ubiquitination, glycolysis, herceptin sensitivity, and tumorigenesis. Cell 149:1098–1111
Robey RB, Hay N (2009) Is Akt the “Warburg kinase”? Akt-energy metabolism interactions and oncogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol 19:25–31
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by: Associazione Italiana per la Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC), Milan Grant IG 8856.
Conflict of interest
No authors have conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tiseo, M., Ippolito, M., Scarlattei, M. et al. Predictive and prognostic value of early response assessment using 18FDG-PET in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with erlotinib. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 73, 299–307 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2356-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2356-x