Abstract
Purpose
Vorinostat is a histone deacetylase inhibitor that has demonstrated preclinical activity in numerous cancer models. Clinical activity has been demonstrated in patients with a variety of malignancies. Vorinostat is presently indicated for the treatment of patients with advanced cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL). Clinical investigation is ongoing for therapy of other solid tumors and hematological malignancies either as monotherapy or in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents. This review summarizes the pharmacokinetic properties of vorinostat.
Methods
Monotherapy pharmacokinetic data across a number of pharmacokinetic studies were reviewed, and data are presented. In addition, literature review was performed to obtain published Phase I and II pharmacokinetic combination therapy data to identify and characterize potential drug interactions with vorinostat. Pharmacokinetic data in special populations were also reviewed.
Results
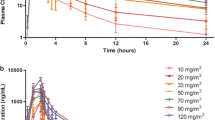
The clinical pharmacology profile of vorinostat is favorable, exhibiting dose-proportional pharmacokinetics and modest food effect. There appear to be no major differences in the pharmacokinetics of vorinostat in special populations, including varying demographics and hepatic dysfunction. Combination therapy pharmacokinetic data indicate that vorinostat has a low propensity for drug interactions.
Conclusions
Vorinostat’s favorable clinical pharmacology and drug interaction profile aid in the ease of administration of vorinostat for the treatment of advanced CTCL and will be beneficial in continued assessment for other oncologic indications. Although a number of studies have been conducted to elucidate the detailed pharmacokinetic profile of vorinostat, more rigorous assessment of vorinostat pharmacokinetics, including clinical drug interaction studies, will be informative.



Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Pharmacokinetic data units were converted from mM to µM; mM units were likely a typographical error in the Badros et al. manuscript.
References
Marks PA, Rifkind RA, Richon VM, Breslow R, Miller T, Kelly WK (2001) Histone deacetylases and cancer: causes and therapies. Nat Rev Cancer 1:194–202. doi:10.1038/35106079
Bolden JE, Peart MJ, Johnstone RW (2006) Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:769–784
Zolinza (vorinostat) [package insert] (2011) Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ
Olsen EA, Kim YH, Kuzel TM, Pacheco TR, Ross FM, Parker S, Frankel SR, Chen C, Ricker JL, Arduino JM, Duvic M (2007) Phase IIB multicenter trial of vorinostat in patients with persistent, progressive, or treatment refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 25:3109–3115. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.10.2434
Duvic M, Talpur R, Ni X, Zhang C, Hazarika P, Kelly C, Chiao JH, Reilly JF, Ricker JL, Richon VM, Frankel SR (2007) Phase 2 trial of oral vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, SAHA) for refractory cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). Blood 109:31–39. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-06-025999
Rubin EH, Agrawal NGB, Friedman EJ, Scott P, Mazina KE, Sun L, Du L, Ricker JL, Frankel SR, Gottesdiener KM, Wagner JA, Iwamoto M (2006) A study to determine the effects of food and multiple dosing on the pharmacokinetics of vorinostat given orally to patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12(23):7039–7045. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1802
Fujiwara Y, Yamamoto N, Yamada Y, Yamada K, Otsuki T, Kanazu S, Iwasa T, Hardwick JS, Tamura T (2009) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid) in Japanese patients with solid tumors. Cancer Sci 100(9):1728–1734. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01237.x
Ramalingam SS, Parise RA, Ramananthan RK, Lagattuta TF, Musguire LA, Stoller RG, Potter DM, Argiris AE, Zweibel JA, Egorin MJ, Belani CP (2007) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of vorinostat, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel for advanced solid malignancies. Clin Cancer Res 13(12):3605–3610. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0162
Kelly WK, O’Connor OA, Krug LM, Chiao JH, Heaney M, Curley T, MacGregore-Cortelli B, Tong W, Secrist JP, Schwartz L, Richardson S, Chu E, Olgac S, Marks PA, Scher H, Richon VM (2005) Phase I study of an oral histone deacetylase inhibitor, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:3923–3931. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.14.167
Munster PN, Rubin EH, Van Belle S, Friedman E, Patterson JK, Van Dyck K, Li X, Comisar W, Chodakewitz JA, Wagner JA, Iwamoto M (2009) A single supratherapeutic dose of vorinostat does not prolong the QTc interval in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15(22):7077–7084. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1214
Galanis E, Jaeckle KA, Maurer MJ, Reid JM, Ames MM, Hardwick JS, Reilly JF, Loboda A, Nebozhyn M, Fantin VR, Richon VM, Scheithauer B, Giannini C, Flynn PJ, Moore DF, Zwiebel J, Buckner JC (2009) Phase II trial of vorinostat in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: a north central cancer treatment group study. J Clin Oncol 27(12):2052–2058. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.19.0694
Fouladi M, Park JR, Stewart CF, Gilbertson RJ, Schaiquevich P, Sun J, Reid MJ, Ames MM, Speights R, Ingle AM, Zweibel J, Blaney SM, Adamson PC (2010) Pediatric phase I trial and pharmacokinetic study of vorinostat: a Children’s Oncology Group phase I consortium report. J Clin Oncol 28:3623–3629. doi:12.1200/JCO.2009.25.9119
Zolinza (vorinostat) [Japan package insert] (2011) Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan
Balliet RM, Chen G, Gallagher CJ, Dellinger RW, Sun D, Lazarus P (2009) Characterization of UGTs active against SAHA and association between SAHA glucuronidation activity phenotype with UGT genotype. Cancer Res 69:2981–2989. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4143
Pajkovic N, Koeplinger KA, Baker MP, Soli ED, Fauty SE, Sandhu P (2006) In vitro metabolism of vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid), a novel anticancer agent [abstract]. In: Proceedings of the 54th ASMS Meeting, Seattle, Washington
Sandhu P, Andrews P, Baker MP, Koeplinger KA, Soli ED, Miller T, Baillie TA (2007) Disposition of vorinostat, a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor and anticancer agent, in preclinical species. Drug Metab Lett 1:153–161
Watanabe T, Kato H, Kobayashi Y, Yamasaki S, Morita-Hoshi Y, Yokoyama H, Morishima Y, Ricker JL, Otsuki T, Miyagi-Maesima A, Matsuno Y, Tobinai K (2010) Potential efficacy of the oral histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat in a phase I trial in follicular and mantle cell lymphoma. Cancer Sci 101:196–200. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01360.x
Wong NS, Seah EZH, Wang LZ, Yeo WL, Yap HL, Chuah B, Lim YW, Ang PCS, Tai BC, Lim R, Goh BC, Lee SC (2011) Impact of UDP-gluconoryltransferase 2B17 genotype on vorinostat metabolism and clinical outcomes in Asian women with breast cancer. Pharmacogenet Genomics 21:760–768. doi:10.1097/FPC.0b013e32834a8639
Kelly WK, Richon VM, O’Connor OA, Curley T, MacGregor-Curtelli B, Tong W, Klang M, Schwartz L, Richardson S, Rosa E, Drobnjak M, Cordon-Cordo C, Chiao JH, Rifkind R, Marks PA, Scher H (2003) Phase I clinical trial of histone deacetylase inhibitor: suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid administered intravenously. Clin Cancer Res 9:3578–3588
Ramalingam SS, Kummar S, Sarantopoulos J, Shibata S, LoRusso P, Yerk M, Holleran J, Lin Y, Beumer JH, Harvey RD, Ivy SP, Belani CP, Egorin MJ (2010) Phase I study of vorinostat in patients with advanced solid tumors and hepatic dysfunction: a National Cancer Institute Organ Dysfunction working group study. J Clin Oncol 28:4507–4512. doi:10.1200/JCO.2010.30.2307
Piekarz RL, Frye AR, Wright JJ, Steinberg SM, Liewehr DJ, Rosing DR, Sachdev V, Fojo T, Bates SE (2006) Cardiac studies in patients treated with depsipeptide, FK228, in a phase II trial for T-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res 12:3762–3773
Bates SE, Rosing DR, Fojo T, Piekarz RL (2006) Challenges of evaluating the cardiac effects of anticancer agents. Clin Cancer Res 12:3871–3874
Badros A, Burger AM, Phillip S, Niesvizky R, Kolla SS, Goloubeva O, Harris C, Zwiebel J, Wright JJ, Espinoza-Delgado I, Baer MR, Holleran JL, Egorin MJ, Grant S (2009) Phase I study of vorinostat in combination with bortezomib for relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 15(16):5250–5257. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2850
Velcade (bortezomib) [package insert] (2010) Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Cambridge, MA
Carboplatin [package insert] (2005) Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Irvine, CA
Taxol (paclitaxel) [package insert] (2011) Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Princeton, NJ
Beijnen JH, Schellens JHM (2004) Drug interactions in oncology. Lancet Oncol 5:489–496
Zhu WG, Lakshmanan RR, Beal MD, Otterson GA (2001) DNA methyltransferase inhibition enhances apoptosis induced by histone deacetylase inhibitors. Cancer Res 61:1327–1333
Stathis A, Hotte SJ, Chen EX, Hirte HW, Oza AM, Moretto P, Webster S, Laughlin A, Stayner LA, McGill S, Wang L, Zhang WJ, Espinoza-Delgado I, Holleran JL, Egorin MJ, Siu LL (2011) Phase I study of decitabine in combination with vorinostat in patients with advanced solid tumors and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Clin Cancer Res 17:1582–1590. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1893
Dacogen (decitabine) [package insert] (2010) Eisai Inc., Woodcliff Lake, NJ
Fakih MG, Pendyala L, Fetterly G, Toth K, Zwiebel JA, Espinoza-Delgado I, Litwin A, Rustum YM, Ross ME, Holleran JL, Egorin MJ (2009) A phase I, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study on vorinostat in combination with 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin in patient with refractory colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15(9):3189–3195. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2999
Schneider BJ, Kalemkerian GP, Bradley D, Smith DC, Egorin MJ, Daignault S, Dunn R, Hussain M (2012) Phase I study of vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, NSC 701852) in combination with docetaxel in patients with advanced and relapsed solid malignancies. Invest New Drugs 30:249–257. doi:10.1007/s10637-101-9503-6
Hubbert C, Guardiola A, Shao R, Kawaguchi Y, Ito A, Nixon A, Yoshida M, Wang XF, Yao TP (2002) HDAC6 is a microtubule-associated deacetylase. Nature 417:455–458
Taxotere (docetaxel) [package insert] (2010) sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC, Bridgewater, NJ
Munster P, Marchion D, Bicaku E, Schmitt M, Lee JH, DeConti R, Simon G, Fishman M, Minton S, Garrett C, Chiappori A, Lush R, Sullivan D, Daud A (2007) Phase I trial of histone deacetylase inhibition by valproic acid followed by the topoisomerase II inhibitor epirubicin in advanced solid tumors: a clinical and translation study. J Clin Oncol 25:1979–1985. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.08.6165
Munster PN, Marchion D, Thomas S, Egorin M, Minton S, Springett G, Lee JH, Simon G, Chiappori A, Sullivan D, Daud A (2009) Phase I trial of vorinostat and doxorubicin in solid tumours: histone deacetylase 2 expression as a predictive marker. Br J Cancer 101:1044–1050. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605293
Rubex (doxorubicin) [package insert] (2001) Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Princeton, NJ
Dickson MA, Rathkopf DE, Carvajal RD, Grant S, Roberts JD, Reid JM, Ames MM, McGovern RM, Lefkowitz RA, Gonen M, Cane LM, Dials JF, Schwartz GK (2011) A phase I pharmacokinetic study of pulse-dose vorinostat with flavopiridol in solid tumors. Invest New Drugs 29:1004–1012. doi:10.1007/s10637-010-9447-x
Hagenauer B, Salamon A, Thalhammer T, Kunert O, Haslinger E, Klinger P, Senderowicz AM, Sausville EA, Jager W (2001) In vitro glucuronidation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor flavopiridol by rat and human liver microsomes: involvement of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases 1A1 and 1A9. Drug Metab Dispos 29:407–414
Grem JL (2006) 5-Fluoropyrimidines. In: Chabner BA, Longo DL (eds) Cancer chemotherapy and biotherapy, 4th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Leucovorin calcium [package insert] (2003) Mayne Pharma (USA) Inc., Paramus, NJ
Yamasaki D, Tsujimoto M, Ohdo S, Ohtani H, Sawada Y (2007) Possible mechanisms for the pharmacokinetic interaction between phenytoin and folinate in rats. Ther Drug Monit 29:404–411
Eloxatin (oxaliplatin) [package insert] (2009) sanofi-aventis U.S. LLC, Bridgewater, NJ
Fakih MG, Fetterly G, Egorin MJ, Muindi JR, Espinoza-Delgado I, Zwiebel JA, Litwin A, Holleran JL, Wang K, Diasio RB (2010) A phase I, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic study of two schedules of vorinostat in combination with 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin in patients with refractory solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 16:3786–3794. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0547
Garcia-Manero G, Yang H, Bueso-Ramos C, Ferrajoli A, Cortes J, Wierda WG, Faderl S, Koller C, Morris G, Rosmer G, Loboda A, Fantin VR, Randolph SS, Hardwick JS, Reilly JF, Chen C, Ricker JL, Secrist JP, Richon VM, Frankel SR, Kantarjian HM (2008) Phase 1 study of the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid [SAHA]) in patients with advanced leukemias and myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood 111:1060–1066. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-06-098061
Sanchez-Gonzalez B, Yang H, Bueso-Ramos C, Hoshino K, Quintas-Cardama A, Richon VM, Garcia-Manero G (2006) Antileukemia activity of the combination of an anthracycline with a histone deacetylase inhibitor. Blood 108(4):1174–1182. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-09-008086
Kadia TM, Yang H, Ferrajoli A, Maddipotti S, Schroeder C, Madden TL, Holleran JL, Egorin MJ, Ravandi F, Thomas DA, Newsome W, Sanchez-Gonzalez B, Zweibel JA, Espinoza-Delgado I, Kantarjian HM, Garcia-Manero G (2010) A phase I study of vorinostat in combination with idarubicin in relapsed or refractory leukaemia. Br J Hematol 150:72–82. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08211.x
Idamycin (idarubicin) [package insert] (2006) Pfizer Inc., New York, NY
Doroshow JH (2006) Anthracyclines and Anthracenediones. In: Chabner BA, Longo DL (eds) Cancer chemotherapy and biotherapy, 4th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Nadin L, Murray M (1999) Participation of CYP2C8 in retinoic acid 4-hydroxylation in human hepatic microsomes. Biochem Pharmacol 58:1201–1208
Allen JG, Bloxham DP (1989) The pharmacology and pharmacokinetics of the retinoids. Pharmacol Ther 40:1–27
Perucca E (2005) Clinically relevant drug interactions with antiepileptic drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol 61:246–255. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02529.x
Acknowledgments
Deepest appreciation and thanks go to all of the patients who participated in the clinical studies referenced above.
Conflict of interest
M. Iwamoto, E. Friedman, N. Agrawal, P. Sandhu, E. Rubin, and J. Wagner are all current employees of Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Whitehouse Station, NJ, and may own stock or hold stock options in the company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwamoto, M., Friedman, E.J., Sandhu, P. et al. Clinical pharmacology profile of vorinostat, a histone deacetylase inhibitor. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 72, 493–508 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2220-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2220-z