Abstract
Purpose
Patients of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with brain metastases have limited treatment options. High-dose erlotinib (HDE) and gefitinib (HDG) have been tried in the past. This study investigates the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) disposition and safety of both, high-dose erlotinib and gefitinib regimens.
Methods
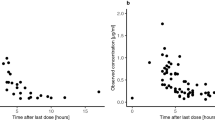
Eleven and nine patients were treated with erlotinib and gefitinib, respectively. All patients received 1 week of standard dose of erlotinib (150 mg OD) or gefitinib (250 mg OD), followed by the high dose (1500 mg weekly for erlotinib and 1250 mg OD for gefitinib) from day 8. Blood and CSF samples were collected on days 7 and 15, 4 h after the morning dose and drug levels determined using LC-MS/MS. Adverse events were documented as per CTCAE 4.03 till day 15.
Results
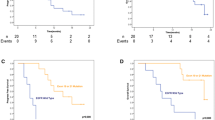
Pulsatile HDE and daily HDG resulted in 1.4- and 1.9-fold increase in CSF levels, respectively. A constant 2% CSF penetration rate was observed across both doses of erlotinib, while for gefitinib the penetration rate for high dose was half that of the standard dose suggesting a nonlinear disposition. Three patients on HDE treatment discontinued treatment after the first dose due to intolerable toxicities, whereas HDG was better tolerated with no treatment discontinuations. Since CSF disposition of gefitinib followed saturable kinetics, a lower dose of 750 mg was found to achieve CSF concentrations comparable to that of the 1250 mg dose.
Conclusions
HDG was better tolerated than HDE. CSF disposition of gefitinib was found to be saturable at a higher dose. Based on these findings, the dose of 750 mg OD should be considered for further evaluation in this setting.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Noronha V, Joshi A, Gokarn A, Sharma V, Patil V, Janu A, Purandare N, Chougule A, Jambhekar N, Prabhash K (2014) The Importance of Brain Metastasis in EGFR Mutation Positive NSCLC Patients. Chemother Res Pract 2014:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/856156
Zappa C, Mousa SA (2016) Non-small cell lung cancer: current treatment and future advances. Transl Lung Cancer Res 5:288–300
Kelly WJ, Shah NJ, Subramaniam DS (2018) Management of Brain Metastases in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Front Oncol 8:208. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2018.00208
Bartolotti M, Franceschi E, Brandes AA (2012) EGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 12:1429–1435. https://doi.org/10.1586/era.12.121
Clarke JL, Pao W, Wu N, Miller VA, Lassman AB (2010) High dose weekly erlotinib achieves therapeutic concentrations in CSF and is effective in leptomeningeal metastases from epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung cancer. J Neurooncol 99:283–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0128-6
Deng Y, Feng W, Wu J et al (2014) The concentration of erlotinib in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with brain metastasis from non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol Clin Oncol 2:116–120. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2013.190
Xie C, Fan Y, Xu X (2014) EGFR-TKI therapy for patients with brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer: a pooled analysis of published data. Onco Targets Ther 7:2075. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S67586
Karachaliou N, Rosell R (2013) Treatment of brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations: the role of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ann Palliat Med 2:114–117. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2224-5820.2013.05.02
Hochmair M (2018) Medical Treatment Options for Patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Suffering from Brain Metastases and/or Leptomeningeal Disease. Target Oncol 13:269–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11523-018-0566-1
Kimura M, Yasue F, Usami E, Kawachi S, Iwai M, Go M, Ikeda Y, Yoshimura T (2018) Cost-effectiveness and safety of the molecular targeted drugs afatinib, gefitinib and erlotinib as first-line treatments for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol Clin Oncol 9:201–206. https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2018.1640
Aguiar PNJ, Haaland B, Park W et al (2018) Cost-effectiveness of Osimertinib in the First-Line Treatment of Patients With EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol 4:1080–1084. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.1395
Grommes C, Oxnard GR, Kris MG, Miller VA, Pao W, Holodny AI, Clarke JL, Lassman AB (2011) " Pulsatile" high-dose weekly erlotinib for CNS metastases from EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Neuro Oncol 13:1364–1369. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nor121
Dhruva N, Socinski MA (2009) Carcinomatous Meningitis in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Response to High-Dose Erlotinib. J Clin Oncol 27:e31–e32. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2008.21.0963
Shah NP, Kasap C, Weier C, Balbas M, Nicoll JM, Bleickardt E, Nicaise C, Sawyers CL (2008) Transient Potent BCR-ABL Inhibition Is Sufficient to Commit Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cells Irreversibly to Apoptosis. Cancer Cell 14:485–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2008.11.001
Milton DT, Azzoli CG, Heelan RT, Venkatraman E, Gomez JE, Kris MG, Krug LM, Pao W, Rizvi NA, Dunne M, Miller VA (2006) A phase I/II study of weekly high-dose erlotinib in previously treated patients with nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer 107:1034–1041. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.22088
Thappali SRS, Varanasi K, Veeraraghavan S, Arla R, Chennupati S, Rajamanickam M, Vakkalanka S, Khagga M (2012) Simultaneous Determination of Celecoxib, Erlotinib, and its Metabolite Desmethyl-Erlotinib (OSI-420) in Rat Plasma by Liquid chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry with Positive/Negative Ion-Switching Electrospray Ionisation. Sci Pharm 80:633–646. https://doi.org/10.3797/scipharm.1205-09
Porta R, Sánchez-Torres JM, Paz-Ares L et al (2011) Brain metastases from lung cancer responding to erlotinib: the importance of EGFR mutation. Eur Respir J 37:624–631. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00195609
Welsh JW, Komaki R, Amini A, Munsell MF, Unger W, Allen PK, Chang JY, Wefel JS, McGovern SL, Garland LL, Chen SS, Holt J, Liao Z, Brown P, Sulman E, Heymach JV, Kim ES, Stea B (2013) Phase II Trial of Erlotinib Plus Concurrent Whole-Brain Radiation Therapy for Patients With Brain Metastases From Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 31:895–902
Caruso A, Alvarez-Sanchez R, Hillebrecht A et al (2013) PK/PD assessment in CNS drug discovery: Prediction of CSF concentration in rodents for P-glycoprotein substrates and application to in vivo potency estimation. Biochem Pharmacol 85:1684–1699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2013.02.021
Togashi Y, Masago K, Fukudo M, Terada T, Fujita S, Irisa K, Sakamori Y, Kim YH, Mio T, Inui KI, Mishima M (2010) Cerebrospinal fluid concentration of erlotinib and its active metabolite OSI-420 in patients with central nervous system metastases of non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 5:950–955. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181e2138b
Togashi Y, Masago K, Masuda S, Mizuno T, Fukudo M, Ikemi Y, Sakamori Y, Nagai H, Kim YH, Katsura T, Mishima M (2012) Cerebrospinal fluid concentration of gefitinib and erlotinib in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 70:399–405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-012-1929-4
Masuda T, Hattori N, Hamada A, Iwamoto H, Ohshimo S, Kanehara M, Ishikawa N, Fujitaka K, Haruta Y, Murai H, Kohno N (2011) Erlotinib efficacy and cerebrospinal fluid concentration in patients with lung adenocarcinoma developing leptomeningeal metastases during gefitinib therapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 67:1465–1469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-011-1555-6
Zeng Y, Liao H, Qin T, Zhang L, Wei WD, Liang JZ, Xu F, Dinglin XX, Ma SX, Chen LK (2015) Blood-brain barrier permeability of gefitinib in patients with brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer before and during whole brain radiation therapy. Oncotarget 6:8366–8376
Fukuhara T, Saijo Y, Sakakibara T, Inoue A, Morikawa N, Kanamori M, Nakashima I, Nukiwa T (2008) Successful treatment of carcinomatous meningitis with gefitinib in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma harboring a mutated EGF receptor gene. Tohoku J Exp Med 214:359–363
Tournier N, Goutal S, Auvity S, Traxl A, Mairinger S, Wanek T, Helal OB, Buvat I, Soussan M, Caillé F, Langer O (2017) Strategies to Inhibit ABCB1- and ABCG2-Mediated Efflux Transport of Erlotinib at the Blood-Brain Barrier: A PET Study on Nonhuman Primates. J Nucl Med 58:117–122. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.116.178665
Agarwal S, Sane R, Gallardo JL, Ohlfest JR, Elmquist WF (2010) Distribution of gefitinib to the brain is limited by P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2)-mediated active efflux. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 334:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.110.167601
Elmeliegy MA, Carcaboso AM, Tagen M, Bai F, Stewart CF (2011) Role of ATP-binding cassette and solute carrier transporters in erlotinib CNS penetration and intracellular accumulation. Clin Cancer Res 17:89–99. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1934
Galetti M, Petronini PG, Fumarola C, Cretella D, la Monica S, Bonelli M, Cavazzoni A, Saccani F, Caffarra C, Andreoli R, Mutti A, Tiseo M, Ardizzoni A, Alfieri RR (2015) Effect of ABCG2/BCRP Expression on Efflux and Uptake of Gefitinib in NSCLC Cell Lines. PLoS One 10:e0141795. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0141795
Weber B, Winterdahl M, Memon A, Sorensen BS, Keiding S, Sorensen L, Nexo E, Meldgaard P (2011) Erlotinib Accumulation in Brain Metastases from Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Visualization by Positron Emission Tomography in a Patient Harboring a Mutation in the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. J Thorac Oncol 6:1287–1289. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e318219ab87
Heimberger AB, Learn CA, Archer GE, McLendon R, Chewning TA, Tuck FL, Pracyk JB, Friedman AH, Friedman HS, Bigner DD, Sampson JH (2002) Brain tumors in mice are susceptible to blockade of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) with the oral, specific, EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 (iressa). Clin Cancer Res 8:3496–3502
Ceresoli GL, Cappuzzo F, Gregorc V, Bartolini S, Crinò L, Villa E (2004) Gefitinib in patients with brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer: a prospective trial. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol 15:1042–1047. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdh276
Liu W, Liu Y, Yang L et al (2016) Gefitinib for asymptomatic brain metastasis from advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Report of a favourable outcome. Thorac. Cancer 7:498–502
Namba Y, Kijima T, Yokota S, Niinaka M, Kawamura S, Iwasaki T, Takeda Y, Kimura H, Okada T, Yamaguchi T, Nakagawa M, Okumura Y, Maeda H, Ito M (2004) Gefitinib in patients with brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer: review of 15 clinical cases. Clin Lung Cancer 6:123–128. https://doi.org/10.3816/CLC.2004.n.026
Hotta K, Kiura K, Ueoka H, Tabata M, Fujiwara K, Kozuki T, Okada T, Hisamoto A, Tanimoto M (2004) Effect of gefitinib (“Iressa”, ZD1839) on brain metastases in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 46:255–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2004.04.036
Jackman DM, Cioffredi LA, Jacobs L, Sharmeen F, Morse LK, Lucca J, Plotkin SR, Marcoux PJ, Rabin MS, Lynch TJ, Johnson BE, Kesari S (2015) A Phase I trial of high dose gefitinib for patients with leptomeningeal metastases from non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 6:4527–4536
Jackman DM, Holmes AJ, Lindeman N, Wen PY, Kesari S, Borras AM, Bailey C, de Jong F, Jänne PA, Johnson BE (2006) Response and resistance in a non-small-cell lung cancer patient with an epidermal growth factor receptor mutation and leptomeningeal metastases treated with high-dose gefitinib. J Clin Oncol 24:4517–4520. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2006.06.6126
Lippitz B, Lindquist C, Paddick I, Peterson D, O’Neill K, Beaney R (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of brain metastases: the current evidence. Cancer Treat Rev 40:48–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2013.05.002
Ding PN, Lord SJ, Gebski V, Links M, Bray V, Gralla RJ, Yang JCH, Lee CK (2017) Risk of Treatment-Related Toxicities from EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: A Meta-analysis of Clinical Trials of Gefitinib, Erlotinib, and Afatinib in Advanced EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J Thorac Oncol 12:633–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2016.11.2236
Takeda M, Okamoto I, Nakagawa K (2015) Pooled safety analysis of EGFR-TKI treatment for EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 88:74–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.01.026
Burotto M, Manasanch EE, Wilkerson J, Fojo T (2015) Gefitinib and erlotinib in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis of toxicity and efficacy of randomized clinical trials. Oncologist 20:400–410. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0154
Yoshida T, Yamada K, Azuma K, Kawahara A, Abe H, Hattori S, Yamashita F, Zaizen Y, Kage M, Hoshino T (2013) Comparison of adverse events and efficacy between gefitinib and erlotinib in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: a retrospective analysis. Med Oncol 30:349. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-012-0349-y
Morris ME, Rodriguez-Cruz V, Felmlee MA (2017) SLC and ABC Transporters: Expression, Localization, and Species Differences at the Blood-Brain and the Blood-Cerebrospinal Fluid Barriers. AAPS J 19:1317–1331. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-017-0110-8
Baselga J, Rischin D, Ranson M, Calvert H, Raymond E, Kieback DG, Kaye SB, Gianni L, Harris A, Bjork T, Averbuch SD, Feyereislova A, Swaisland H, Rojo F, Albanell J (2002) Phase I safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic trial of ZD1839, a selective oral epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with five selected solid tumor types. J Clin Oncol 20:4292–4302. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2002.03.100
van Zandwijk N (2003) Tolerability of gefitinib in patients receiving treatment in everyday clinical practice. Br J Cancer 89(Suppl 2):S9–S14. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6601477
Armour AA, Watkins CL (2010) The challenge of targeting EGFR: experience with gefitinib in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Eur Respir Rev 19:186–196. https://doi.org/10.1183/09059180.00005110
Wolf M, Swaisland H, Averbuch S (2004) Development of the novel biologically targeted anticancer agent gefitinib: determining the optimum dose for clinical efficacy. Clin Cancer Res 10:4607–4613. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0058
Herbst RS, Maddox A-M, Rothenberg ML, Small EJ, Rubin EH, Baselga J, Rojo F, Hong WK, Swaisland H, Averbuch SD, Ochs J, LoRusso PM (2002) Selective oral epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 is generally well-tolerated and has activity in non-small-cell lung cancer and other solid tumors: results of a phase I trial. J Clin Oncol 20:3815–3825. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2002.03.038
Xue C, Hong S, Li N, Feng W, Jia J, Peng J, Lin D, Cao X, Wang S, Zhang W, Zhang H, Dong W, Zhang L (2015) Randomized, Multicenter Study of Gefitinib Dose-escalation in Advanced Non-small-cell Lung Cancer Patients Achieved Stable Disease after One-month Gefitinib Treatment. Sci Rep 5:10648. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep10648
Costa DB, Nguyen K-SH, Cho BC, Sequist LV, Jackman DM, Riely GJ, Yeap BY, Halmos B, Kim JH, Janne PA, Huberman MS, Pao W, Tenen DG, Kobayashi S (2008) Effects of erlotinib in EGFR mutated non-small cell lung cancers with resistance to gefitinib. Clin Cancer Res 14:7060–7067. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1455
Peters S, Bexelius C, Munk V, Leighl N (2016) The impact of brain metastasis on quality of life, resource utilization and survival in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Treat Rev 45:139–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctrv.2016.03.009
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to Tata Memorial Centre for funding this study.
We thank the patients and their families for participating in this trial.
Funding
This work was supported by the Tata Memorial Centre intramural grant, Mumbai, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. Vikram Gota and Dr. Kumar Prabhash were involved in conceiving and designing the study. Drs. Kumar Prabhash, Vijay Patil, Vanita Noronha and Amit Joshi provided medical care to the trial participants. Ms. Deepali Patil was involved in collecting the patient data. Mr. Murari Gurjar was responsible for analysing patient samples. Ms. Sadhana Kannan was involved in statistical analysis. Ms. Bharati Shriyan was involved in analysing the data, drafting the manuscript and preparing for the publication. Dr. Manjunath Nookala and Mr. Anand Patil were involved in fine tuning the manuscript. Dr. Vikram Gota was also involved in interpreting the data and reviewing the manuscript critically.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee (TMC-ACTREC IEC-III, Registration number: ECR/149/Inst/MH/2013) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent for publication
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 13.8 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shriyan, B., Patil, D., Gurjar, M. et al. Safety and CSF distribution of high-dose erlotinib and gefitinib in patients of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with brain metastases. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 76, 1427–1436 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-020-02926-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-020-02926-9