Abstract
Purpose
Clofarabine has proven to be effective in the treatment of adult and pediatric acute myelogenous leukemia (AML). To investigate if clofarabine could be used with success in biochemical modulation strategies, we investigated the biochemical modulation of cytarabine triphosphate (ara-CTP) by clofarabine in a myeloid leukemia cell line and the effect of this combination on cytotoxicity.
Experimental design
K562 cells were incubated with clofarabine and ara-C either sequentially or simultaneously to evaluate the combination effect on their phosphorylated metabolites. Clonogenic assays were used to determine the cytotoxicity of each agent alone and in combination. Deoxynucleotide analysis was performed to assess the effect of clofarabine on dNTPs.
Results
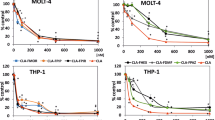
Clofarabine added either simultaneously or in sequence increased ara-CTP accumulation. The maximal modulation of ara-CTP accumulation occurred with 1 μM clofarabine. This level was achieved at the maximum tolerated dose for adult and pediatric patients with AML. With 10 μM ara-C alone, 86 μM ara-CTP had accumulated after 3 h. The optimal sequence for the drug combination, i.e., clofarabine followed 4 h later by ara-C, resulted in 248 μM ara-CTP at 3 h. Clofarabine accumulated maximally in the monophosphate form. Preincubation with ara-C did not affect the triphosphate form, but it lowered clofarabine monophosphate. Clofarabine resulted in the intracellular decrease of dATP and dGTP levels. Clonogenic assays revealed that the combination of clofarabine and ara-C produced synergistic killing of myeloid leukemia cells.
Conclusions
These findings demonstrate that combination of clofarabine followed by ara-C results in a biochemical modulation of ara-CTP and synergistic cell kill. These studies provide a compelling rationale for clinical trials using this combination regimen for adult and pediatric patients with AML.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albertioni F, Lindemalm S, Reichelova V, Pettersson B, Erikson S, Juliusson G, Liliemark JO (1998) Pharmacokinetics of cladribine in plasma and its 5′-monophosphate and 5′-triphosphate in leukemic cells of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 4:653–658
Avramis VI, Wiersma S, Krailo MD, Ramilo-Torno LV, Sharpe A, Liu-Mares W, Kowck R, Reaman GH, Sato JK, The Children’s Cancer Group (1998) Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies of fludarabine and cytosine arabinoside administered as loading boluses followed by continuous infusions after a phase I/II study in pediatric patients with relapsed leukemias. Clin Cancer Res 4:45–52
Carson DA, Wasson DB, Esparaza LM, Carrera CJ, Kipps TJ, Cottam HB (1992) Oral antilymphocyte activity and induction of apoptosis by 2-chloro-2′arabino-flouro-2′deoxyadenosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:2970–2974
Crews K, Gandhi V, Srivasta D, Razzouk B, Tong X, Behm F, Plunkett W, Raimondi S, Pui C, Rubnitz J, Stewart C, Ribeiro R (2002) Interim comparison of a continuous infusion versus a short daily infusion of cytarabine given in combination with cladribine for pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 20:4217–4223
Danhauser L, Plunkett W, Keating M, Cabanillas F (1986) 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl-2-fluoroadenine 5’-monophosphate pharmacokinetics in plasma and tumor cells of patients with relapsed leukemia and lymphoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 18:145–152
Estey EH, Keating MJ, McCredie KB, Freireich EJ, Plunkett W (1990) Cellular ara-CTP pharmacokinetics, response, and karyotype in newly diagnosed acute myelogenous leukemia. Leukemia 4:95–99
Faderl S, Gandhi V, O’Brien S, Bonate P, Cortes G, Estey E, Beran M, Wierda W, Garcia-Manero G, Ferrajoli A, Estrov Z, Giles FG, Du M, Kwari M, Keating MJ, Plunkett W, Kantarjian H (2004) Results of a phase 1–2 study of clofarabine in combination with cytarabine (ara-C) in relapsed and refractory acute leukemias. Blood (in press)
Fleischhack G, Hasan C, Graf N, Mann G, Bode U (1998) IDA-FLAG (idarubicin, fludarabine, cytarabine, G-CSF), an effective remission-induction therapy for poor-prognosis AML of childhood prior to allogeneic or autologous bone marrow transplantation: experiences of a phase II trial. Br J Haematol 102:647–655
Gandhi V, Plunkett W (1998) Modulation of arabinosylnucleoside metabolism by arabinosylnucleotides in human leukemia cells. Cancer Res 48:329–334
Gandhi V, Nowak B, Keating MJ, Plunkett W (1989) Modulation of arabinosylcytosine metabolism by arabinosyl-2-fluoroadenine in lymphocytes from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: implications for combination therapy. Blood 74:2070–2075
Gandhi V, Kemena A, Keating MJ, Plunkett W (1992) Fludarabine infusion potentiates arabinosylcytosine metabolism in lymphocytes of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Res 52:897–903
Gandhi V, Estey E, Keating MJ, Plunkett W (1993) Fludarabine potentiates metabolism of arabinosylcytosine in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia during therapy. J Clin Oncol 11:116–124
Gandhi V, Kemena A, Keating MJ, Plunkett W (1993) Cellular pharmacology of fludarabine triphosphate in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells during fludarabine therapy. Leuk Lymphoma 10:49–56
Gandhi V, Robertson LE, Keating MJ, Plunkett W (1994) Combination of fludarabine and arabinosylcytosine for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: clinical efficacy and modulation of arabinosylcytosine pharmacology. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 34:30–36
Gandhi V, Kantarjian H, Faderl S, Bonate P, Du M, Ayres M, Rios MB, Keating MJ, Plunkett W (2003) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of plasma clofarabine and cellular clofarabine triphosphate in patients with acute leukemias. Clin Cancer Res 9:6335–6342
Ghaddar HM, Plunkett W, Kantarjian HM, Pierce S, Freireich EJ, Keating MJ, Estey EH (1994) Long-term results following treatment of newly diagnosed acute myelogenous leukemia with continuous-infusion high-dose cytosine arabinoside. Leukemia 8:1269–1274
Hwang TL, Yung WK, Estey EH, Fields WS (1985) Central nervous system toxicity with high-dose ara-C. Neurology 35:1475–1479
Jeha S, Gandhi V, Chan KW, McDonald L, Ramirez I, Madden R, Rytting M, Keating M, Plunkett W, Kantarjian H (2004) Clofarabine, a novel nucleoside analog, is active in pediatric patients with advanced leukemia. Blood 103:784–789
Kantarjian H, Estey EH, Plunkett W, Keating MJ, Walters RS, Iacoboni S, McCredie KB, Freireich EJ (1986) Phase I–II and pharmacologic studies of high-dose cytosine arabinoside in refractory leukemia. Am J Med 81:387–394
Kantarjian HM, Gandhi V, Cortes J, Verstovsek S, Du M, Garcia-Manero G, Giles F, Faderl S, O’Brien S, Jeha S, Davis J, Shaked Z, Craig A, Keating M, Plunkett W, Freireich EJ (2003) Phase II clinical and pharmacology study of clofarabine in patients with refractory or relapsed acute leukemia. Blood 102:2379–2386
Kantarjian HM, Gandhi V, Kozuch P, Faderl S, Giles F, Cortes J, O’Brien S, Ibrahim N, Khuri F, Du M, Rios MB, Jeha S, McLaughlin P, Plunkett W, Keating M (2003) Phase I clinical and pharmacology study of clofarabine in patients with solid and hematologic cancers. J Clin Oncol 21:1167–1173
Keating MJ, O’Brien S, Lerner S, Koller C, Beran M, Robertson LE, Freirech EJ, Estey E, Kantarjian H (1998) Long-term follow-up of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) receiving fludarabine regimens as initial therapy. Blood 92:1165–1171
Kemena A, Gandhi V, Shewach DS, Keating MJ, Plunkett W (1992) Inhibition of fludarabine metabolism by arabinosylcytosine during therapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 31:193–199
Krance RA, Hurwitz CA, Head DR, Raimondi SC, Behm FG, Crews KR, Srivastava DK, Mahmoud H, Roberts WM, Tong X, Blakley RL, Ribeiro RC (2001) Experience with 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine in previously untreated children with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic diseases. J Clin Oncol 19:2804–2811
Kufe D, Spriggs D, Egan EM, Munroe D (1984) Relationships among ara-CTP pools, formation of (ara-C) DNA, and cytotoxicity of human leukemic cells. Blood 64:54–58
Marcucci G, Byrd JC, Dai G, Klisovic MI, Kourlas PJ, Young DC, Cataland SR, Fisher DB, Lucas D, Chan KK (2003) Phase 1 and pharmacodynamic studies of G3139, a Bcl-2 antisense oligonucleotide, in combination with chemotherapy in refractory or relapsed acute leukemia. Blood 101:425–432
Momparler RL, Fischer GA (1968) Mammalian deoxynucleoside kinase. I. Deoxycytidine kinase: purification, properties, and kinetic studies with cytosine arabinoside. J Biol Chem 243:4298–4304
Montgomery JA, Shortnacy-Fowler AT, Clayton SD, Riordan JM, Secrist JA (1983) Synthesis and biologic activity of 2′ fluoro-2-halo derivatives of 9-β-d-arabinofuranosyladenine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 113:35–43
Parker WB, Shaddix SC, Chang CH, White EL, Rose LM, Brockman RW, Shortnacy AT, Montgomery JA, Secrist JA III, Bennett LL Jr (1991) Effects of 2-chloro-9-(2-deoxy-2-flouro-b-d-arabinofuranosyl) adenine on K562 cellular metabolism and the inhibition of human ribonucleotide reductase and DNA polymerases by its 5′-triphosphate. Cancer Res 51:2386–2394
Parker WB, Bapat AR, Shen JX, Townsend AJ, Cheng YC (1998) Interaction of 2-halogenated dATP analogs (F, Cl, and Br) with human DNA polymerases, DNA primase, and ribonucleotide reductase. Mol Pharmacol 34:485–491
Parker WB, Shaddix SC, Rose LM, Waud WR, Shewach DS, Tiwari KN, Secrist JA III (1999) Comparison of the mechanism of cytotoxicity of 2-chloro-9-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-d-arabinofuranosyl), 2-chloro-9-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-d-ribofuranosyl) adenine, 2-chloro-9-(2-deoxy-2, 2-difluoro-β-ribofuranosyl) adenine in CEM cells. Mol Pharmacol 55:515–520
Piro LD, Carrera CJ, Carson DA, Beutler E (1990) Lasting remissions in hairy-cell leukemia induced by a single infusion of 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine. N Engl J Med 322:1117–1121
Rodriguez CO Jr, Plunkett W, Paff MT, Du M, Nowak B, Ramakrishna P, Keating MJ, Gandhi V (2000) A high-pressure liquid chromatography method for the determination and quantitation of arabinosylguanine triphosphate and fludarabine triphosphate in human cells. J Chromatogr B 745:421–430
Santana VM, Hurwitz CA, Blakley RL, Crom WR, Luo X, Roberts WM, Ribeiro R, Mahmoud H, Krance RA (1994) Complete hematologic remissions induced by 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine in children with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 84:1237–1242
Schiffer CA (2001) Acute myeloid leukemia in adults: where do we go from here? Cancer Chemother Pharmacol [Suppl] 48:S45–S52
Seymour JF, Huang P, Plunkett W, Gandhi V (1996) Influence of fludarabine on pharmacokinetics of cytarabine: implications for a continuous infusion schedule. Clin Cancer Res 2:653–658
Sherman PA, Fyfe FA (1989) Enzymatic assay for deoxynucleotide triphosphates using synthetic oligonucleotides as template primer. Anal Biochem 180:222–229
Spasokoukotskaja T, Sasvari-Szekely M, Keszler G, Albertioni F, Eriksson S, Staub M (1999) Treatment of normal and malignant cells with nucleoside analogues and etoposide enhances deoxycytidine kinase activity. Eur J Cancer 35:1862–1867
Virchis A, Koh M, Rankin P, Mehta A, Potter M, Hoffbrand AV, Prentice HG (2004) Fludarabine, cytosine arabinoside, granulocyte-colony stimulating factor with or without idarubicin in the treatment of high risk acute leukaemia or myelodysplastic syndromes. Br J Haematol 124:26–32
Xie KC, Plunkett W (1995) Metabolism and actions of 2-chloro-9-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-d-arabinofuranosyl) adenine in human lymphoblastoid cells. Cancer Res 55:2847–2852
Xie KC, Plunkett W (1996) Deoxynucleotide pool deletion and sustained inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase and DNA synthesis after treatment of human lymphoblastoid cells with 2-chloro-9-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-d-arabinofuranosyl) adenine. Cancer Res 56:3030–3037
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants CA55164 and CA57629 from the National Cancer Institute, Department of Health and Human Services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cooper, T., Ayres, M., Nowak, B. et al. Biochemical modulation of cytarabine triphosphate by clofarabine. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 55, 361–368 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-004-0906-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-004-0906-y