Heading
Abstract
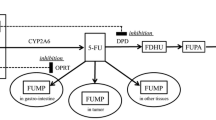
Purpose. S-1 is a novel oral fluorouracil antitumor drug that combines tegafur (FT), 5-chloro-2,4-dihydroxypyridine (CDHP), which inhibits dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD), and potassium oxonate (Oxo). As 50% of CDHP is excreted in the urine, renal dysfunction may directly affect the DPD inhibitory effect and lead to increased 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) concentrations. We sought to determine the influence of impaired renal function on the pharmacokinetics of S-1 in an animal model and in patients with gastric cancer.
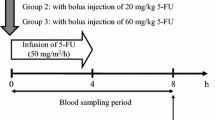
Methods. An experimental renal failure model induced by cisplatin was developed in rabbits, and plasma concentrations of FT, 5-FU, CDHP and Oxo were determined after S-1 injection. Four patients with various degrees of renal impairment with unresectable gastric cancer were recruited to the study, and the pharmacokinetics in these four patients were analyzed following single and consecutive S-1 administrations.
Results. In experimental renal failure, plasma clearance of CDHP and 5-FU was retarded corresponding to the degree of renal impairment and there was a close correlation between creatinine clearance (CLcr) and plasma CDHP and 5-FU clearance. In the single administration study, half standard dose was used in three patients (CLcr ≥50 ml/min) and one-third in the other (CLcr <50 ml/min). In patients with CLcr more than 75 ml/min, Cmax, Tmax, AUC(0–∞), and T1/2 of 5-FU and CDHP were not different between single and consecutive administrations. In contrast, in patients with mild and moderate renal dysfunction (CLcr 55 and 36 ml/min, respectively), the T1/2 values of CDHP with consecutive administrations (7.6 and 15.3 h, respectively) were longer than the values with single administration (4.6 and 8.2 h, respectively). The T1/2 of 5-FU was 5.7 h with single administration and 8.5 h with consecutive administration in patients with moderate renal impairment. The AUC(0–∞) of 5-FU with consecutive administrations (3089.7 ng·h/ml) was far greater than with single administration (430.4 ng·h/ml). There was also a strong correlation between CLcr and plasma CDHP clearance. Based on the pharmacokinetics following multiple consecutive administrations, S-1 administration resulted in no severe adverse reactions in any of the four patients.
Conclusions. CDHP clearance was prolonged in the presence of renal impairment, leading to a delayed T1/2, and high AUC of 5-FU. These findings demonstrate that administration of S-1 to patients with impaired renal function may need individualized dosing and pharmacokinetic monitoring.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikeda, M., Furukawa, H., Imamura, H. et al. Pharmacokinetic study of S-1, a novel oral fluorouracil antitumor agent in animal model and in patients with impaired renal function. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 50, 25–32 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-002-0457-z
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-002-0457-z