Abstract
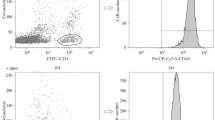
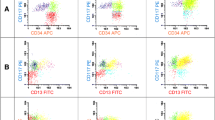
Flow-cytometric analysis of peripheral blood lymphocytes was performed in 96 patients with chronic idiopathic neutropenia of adults (CINA) and in 36 age- and sex-matched healthy volunteers (controls) using a panel of monoclonal antibodies. Patients were classified arbitrarily into group A (68 patients with 2500–1500 neutrophils/μl) and group B (28 patients with neutrophil counts below 1500/μl). We found that CINA patients displayed low numbers of peripheral blood lymphocytes compared with the controls, which correlated with the numbers of circulating neutrophils. This decrease was due mainly to the reduction of T lymphocytes and, to lesser degree, to the decline of NK cells. Both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells decreased, so that the CD4+/CD8+ cell ratio remained within normal range. Moreover, decrease of T lymphocytes was due essentially to the diminution of CD45RO+ T-cell subsets (CD4+/CD45RO+ and CD8+/CD45RO+), while CD45RA+ T cells did not change. A highly significant positive correlation was found between the numbers of CD45RO+ T cells and the numbers of circulating neutrophils. All these alterations were more pronounced in the patients of group B than in those of group A. NK cells were found to be significantly reduced in the patients of group B, but not in those of group A. The numbers of both CD16+ and CD56+ cells correlated with the numbers of circulating neutrophils. Patients of group B had also low numbers of CD57+ cells, probably due to the reduction of T cells and NK cells. B cells did not change significantly. No significant changes were found also in the numbers of lymphocytes carrying activation-related cell surface markers. We concluded that lymphocyte reduction in CINA patients is due mainly to the diminution of CD45RO+ cells, and we postulated that the most probable explanation for this abnormality is an increased extravasation of these cells, which pass into the tissues following an accelerated adhesion to endothelial cells. This hypothesis and its relationship with the underlying neutropenia in CINA patients remain to be clarified.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 30 October 1996 / Accepted: 4 June 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kyriakou, D., Papadaki, H., Sakellariou, D. et al. Flow-cytometric analysis of peripheral blood lymphocytes in patients with chronic idiopathic neutropenia of adults. Ann Hematol 75, 103–110 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002770050322
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002770050322