Abstract
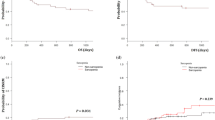
Sarcopenia reportedly predicts poor outcomes in elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). However, because previous studies only involved elderly patients, it is difficult to generalize these results to all patients with DLBCL. We retrospectively analyzed 207 patients with DLBCL who received the R-CHOP or R-THP-COP regimen between June 2004 and May 2014. Sarcopenia was measured by the analysis of CT images at the L3 level before treatment. The surface of muscular tissues was selected according to the CT Hounsfield unit. This value was normalized for stature in order to calculate the L3 skeletal muscle index (L3 SMI, cm2/m2). Median age at diagnosis in the 121 males and 86 females was 67 years (range, 19–86 years). The sex-specific cutoffs for the L3 SMI were determined by receiver operator curve (ROC) analysis. Sarcopenic patients were older than non-sarcopenic patients, with a median age of 70 and 65 years, respectively (p < 0.001). Other International Prognostic Index factors were not significantly different when comparing sarcopenic and non-sarcopenic patients. With a median follow-up of 50.4 months, the 3-year overall survival (OS) was 70 % in the sarcopenic group and 85 % in the non-sarcopenic group (p = 0.0260). In a subgroup analysis by gender, there was a significant difference in the OS when comparing sarcopenic and non-sarcopenic patients in males but not in females (p = 0.0003, p = 0.4440, respectively). Sarcopenia is an independent prognostic factor in male patients with DLBCL.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, Thiele J, Vardiman JW (2008) WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues, 4th edn. IARC, Lyon
Coiffier B, Lepage E, Briere J, Herbrecht R, Tilly H, Bouabdallah R, Morel P, Van Den Neste E, Salles G, Gaulard P, Reyes F, Lederlin P, Gisselbrecht C (2002) CHOP chemotherapy plus rituximab compared with CHOP alone in elderly patients with diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med 346(4):235–242. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa011795
Sehn LH, Donaldson J, Chhanabhai M, Fitzgerald C, Gill K, Klasa R, MacPherson N, O’Reilly S, Spinelli JJ, Sutherland J, Wilson KS, Gascoyne RD, Connors JM (2005) Introduction of combined CHOP plus rituximab therapy dramatically improved outcome of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in British Columbia. J Clin Oncol 23(22):5027–5033. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.09.137
Pfreundschuh M, Trumper L, Osterborg A, Pettengell R, Trneny M, Imrie K, Ma D, Gill D, Walewski J, Zinzani PL, Stahel R, Kvaloy S, Shpilberg O, Jaeger U, Hansen M, Lehtinen T, Lopez-Guillermo A, Corrado C, Scheliga A, Milpied N, Mendila M, Rashford M, Kuhnt E, Loeffler M, MabThera International Trial G (2006) CHOP-like chemotherapy plus rituximab versus CHOP-like chemotherapy alone in young patients with good-prognosis diffuse large-B-cell lymphoma: a randomised controlled trial by the MabThera International Trial (MInT) Group. Lancet Oncol 7(5):379–391. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70664-7
The International Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project (1993) A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med 329(14):987–994. doi:10.1056/NEJM199309303291402
Hara T, Tsurumi H, Takemura M, Goto H, Yamada T, Sawada M, Takahashi T, Moriwaki H (2000) Serum-soluble fas level determines clinical symptoms and outcome of patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Am J Hematol 64(4):257–261
Goto N, Tsurumi H, Takemura M, Hara T, Sawada M, Kasahara S, Kanemura N, Yamada T, Shimizu M, Takahashi T, Tomita E, Seishima M, Takami T, Moriwaki H (2006) Serum-soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 (sTNF-R2) level determines clinical outcome in patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Eur J Haematol 77(3):217–225. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0609.2006.00702.x
Goto H, Tsurumi H, Takemura M, Ino-Shimomura Y, Kasahara S, Sawada M, Yamada T, Hara T, Fukuno K, Goto N, Okuno M, Takami T, Seishima M, Moriwaki H (2005) Serum-soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) level determines clinical outcome in patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: in combination with the International Prognostic Index. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 131(2):73–79. doi:10.1007/s00432-004-0600-9
Prado CM, Baracos VE, McCargar LJ, Mourtzakis M, Mulder KE, Reiman T, Butts CA, Scarfe AG, Sawyer MB (2007) Body composition as an independent determinant of 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy toxicity. Clin Cancer Res 13(11):3264–3268. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-3067
Prado CM, Lieffers JR, McCargar LJ, Reiman T, Sawyer MB, Martin L, Baracos VE (2008) Prevalence and clinical implications of sarcopenic obesity in patients with solid tumours of the respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts: a population-based study. Lancet Oncol 9(7):629–635. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70153-0
Prado CM, Baracos VE, McCargar LJ, Reiman T, Mourtzakis M, Tonkin K, Mackey JR, Koski S, Pituskin E, Sawyer MB (2009) Sarcopenia as a determinant of chemotherapy toxicity and time to tumor progression in metastatic breast cancer patients receiving capecitabine treatment. Clin Cancer Res 15(8):2920–2926. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2242
Tan BH, Birdsell LA, Martin L, Baracos VE, Fearon KC (2009) Sarcopenia in an overweight or obese patient is an adverse prognostic factor in pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15(22):6973–6979. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1525
Antoun S, Baracos VE, Birdsell L, Escudier B, Sawyer MB (2010) Low body mass index and sarcopenia associated with dose-limiting toxicity of sorafenib in patients with renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol 21(8):1594–1598. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdp605
Lanic H, Kraut-Tauzia J, Modzelewski R, Clatot F, Mareschal S, Picquenot JM, Stamatoullas A, Lepretre S, Tilly H, Jardin F (2014) Sarcopenia is an independent prognostic factor in elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with immunochemotherapy. Leuk Lymphoma 55(4):817–823. doi:10.3109/10428194.2013.816421
Tsurumi H, Yamada T, Sawada M, Kasahara S, Kanemura N, Kojima Y, Fukuno K, Hara T, Saio M, Takahashi T, Oyama M, Ozawa K, Takami T, Moriwaki H (2004) Biweekly CHOP or THP-COP regimens in the treatment of newly diagnosed aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. A comparison of doxorubicin and pirarubicin: a randomized phase II study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 130(2):107–113. doi:10.1007/s00432-003-0508-9
Hara T, Tsurumi H, Goto N, Kitagawa J, Kanemura N, Yoshikawa T, Kasahara S, Goto H, Fukuno K, Yamada T, Sawada M, Yasuda I, Katsumura N, Takahashi T, Takami T, Moriwaki H (2010) Phase II study of rituximab combined with THP-COP as first-line therapy for patients younger than 70 years with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 136(1):65–70. doi:10.1007/s00432-009-0637-x
Kasahara S, Hara T, Tsurumi H, Goto N, Kitagawa J, Kanemura N, Yoshikawa T, Goto H, Fukuno K, Yamada T, Sawada M, Takahashi T, Takami T, Moriwaki H (2011) Phase II study of the tetrahydropyranyl adriamycin-cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisolone regimen combined with rituximab as first-line treatment for elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 52(4):629–634. doi:10.3109/10428194.2011.555024
Carbone PP, Kaplan HS, Musshoff K, Smithers DW, Tubiana M (1971) Report of the committee on Hodgkin’s disease staging classification. Cancer Res 31(11):1860–1861
Sehn LH, Berry B, Chhanabhai M, Fitzgerald C, Gill K, Hoskins P, Klasa R, Savage KJ, Shenkier T, Sutherland J, Gascoyne RD, Connors JM (2007) The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. Blood 109(5):1857–1861. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-08-038257
Miller AA, Salewski E (1994) Prospects for pirarubicin. Med Pediatr Oncol 22(4):261–268
Takagi T, Oguro M (1987) (2″-R)-4′-o-Tetrahydropyranyladriamycin, a new anthracycline derivative: its effectiveness in lymphoid malignancies. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 20(2):151–154
Tsurumi H, Hara T, Goto N, Kanemura N, Kasahara S, Sawada M, Yasuda I, Yamada T, Shimizu M, Takami T, Moriwaki H (2007) A phase II study of a THP-COP regimen for the treatment of elderly patients aged 70 years or older with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Hematol Oncol 25(3):107–114. doi:10.1002/hon.815
Sawada M, Tsurumi H, Yamada T, Hara T, Fukuno K, Goto H, Shimizu M, Kasahara S, Yoshikawa T, Kanemura N, Oyama M, Takami T, Moriwaki H (2002) A prospective study of P-IMVP-16/CBDCA: a novel salvage chemotherapy for patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma who had previously received CHOP therapy as first-line chemotherapy. Eur J Haematol 68(6):354–361
Hirakawa T, Yamaguchi H, Yokose N, Gomi S, Inokuchi K, Dan K (2010) Importance of maintaining the relative dose intensity of CHOP-like regimens combined with rituximab in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol 89(9):897–904. doi:10.1007/s00277-010-0956-7
Morley JE, Baumgartner RN, Roubenoff R, Mayer J, Nair KS (2001) Sarcopenia. J Lab Clin Med 137(4):231–243. doi:10.1067/mlc.2001.113504
Prado CM, Birdsell LA, Baracos VE (2009) The emerging role of computerized tomography in assessing cancer cachexia. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care 3(4):269–275. doi:10.1097/SPC.0b013e328331124a
Shen W, Punyanitya M, Wang Z, Gallagher D, St-Onge MP, Albu J, Heymsfield SB, Heshka S (2004) Total body skeletal muscle and adipose tissue volumes: estimation from a single abdominal cross-sectional image. J Appl Physiol 97(6):2333–2338. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00744.2004
Mitsiopoulos N, Baumgartner RN, Heymsfield SB, Lyons W, Gallagher D, Ross R (1998) Cadaver validation of skeletal muscle measurement by magnetic resonance imaging and computerized tomography. J Appl Physiol 85(1):115–122
Mourtzakis M, Prado CM, Lieffers JR, Reiman T, McCargar LJ, Baracos VE (2008) A practical and precise approach to quantification of body composition in cancer patients using computed tomography images acquired during routine care. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 33(5):997–1006. doi:10.1139/H08-075
Zweig MH, Campbell G (1993) Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) plots: a fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clin Chem 39(4):561–577
Kanda Y (2013) Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant 48(3):452–458. doi:10.1038/bmt.2012.244
Fearon K, Strasser F, Anker SD, Bosaeus I, Bruera E, Fainsinger RL, Jatoi A, Loprinzi C, MacDonald N, Mantovani G, Davis M, Muscaritoli M, Ottery F, Radbruch L, Ravasco P, Walsh D, Wilcock A, Kaasa S, Baracos VE (2011) Definition and classification of cancer cachexia: an international consensus. Lancet Oncol 12(5):489–495. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70218-7
Fearon KC, Glass DJ, Guttridge DC (2012) Cancer cachexia: mediators, signaling, and metabolic pathways. Cell Metab 16(2):153–166. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2012.06.011
Richards CH, Roxburgh CS, MacMillan MT, Isswiasi S, Robertson EG, Guthrie GK, Horgan PG, McMillan DC (2012) The relationships between body composition and the systemic inflammatory response in patients with primary operable colorectal cancer. PLoS One 7(8):e41883. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0041883
Argiles JM, Busquets S, Lopez-Soriano FJ (2005) The pivotal role of cytokines in muscle wasting during cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37(10):2036–2046. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2005.03.014
Gabay C, Kushner I (1999) Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med 340(6):448–454. doi:10.1056/NEJM199902113400607
Richards CH, Leitch EF, Horgan PG, Anderson JH, McKee RF, McMillan DC (2010) The relationship between patient physiology, the systemic inflammatory response and survival in patients undergoing curative resection of colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 103(9):1356–1361. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605919
Roxburgh CS, Platt JJ, Leitch EF, Kinsella J, Horgan PG, McMillan DC (2011) Relationship between preoperative comorbidity, systemic inflammatory response, and survival in patients undergoing curative resection for colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 18(4):997–1005. doi:10.1245/s10434-010-1410-8
McMillan DC, Canna K, McArdle CS (2003) Systemic inflammatory response predicts survival following curative resection of colorectal cancer. Br J Surg 90(2):215–219. doi:10.1002/bjs.4038
Aleman MR, Santolaria F, Batista N, de La Vega M, Gonzalez-Reimers E, Milena A, Llanos M, Gomez-Sirvent JL (2002) Leptin role in advanced lung cancer. A mediator of the acute phase response or a marker of the status of nutrition? Cytokine 19(1):21–26
Hanahan D, Coussens LM (2012) Accessories to the crime: functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 21(3):309–322. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2012.02.022
Mamlouk S, Wielockx B (2013) Hypoxia-inducible factors as key regulators of tumor inflammation. Int J Cancer 132(12):2721–2729. doi:10.1002/ijc.27901
Dodson S, Baracos VE, Jatoi A, Evans WJ, Cella D, Dalton JT, Steiner MS (2011) Muscle wasting in cancer cachexia: clinical implications, diagnosis, and emerging treatment strategies. Annu Rev Med 62:265–279. doi:10.1146/annurev-med-061509-131248
Riihijarvi S, Taskinen M, Jerkeman M, Leppa S (2011) Male gender is an adverse prognostic factor in B-cell lymphoma patients treated with immunochemotherapy. Eur J Haematol 86(2):124–128. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0609.2010.01541.x
Carella AM, de Souza CA, Luminari S, Marcheselli L, Chiappella A, di Rocco A, Cesaretti M, Rossi A, Rigacci L, Gaidano G, Merli F, Spina M, Stelitano C, Hohaus S, Barbui A, Puccini B, Miranda EC, Guida A, Federico M (2013) Prognostic role of gender in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with rituximab containing regimens: a Fondazione Italiana Linfomi/Grupo de Estudos em Molestias Onco-Hematologicas retrospective study. Leuk Lymphoma 54(1):53–57. doi:10.3109/10428194.2012.691482
Micheli A, Ciampichini R, Oberaigner W, Ciccolallo L, de Vries E, Izarzugaza I, Zambon P, Gatta G, De Angelis R, Group EW (2009) The advantage of women in cancer survival: an analysis of EUROCARE-4 data. Eur J Cancer 45(6):1017–1027. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2008.11.008
Muller C, Murawski N, Wiesen MH, Held G, Poeschel V, Zeynalova S, Wenger M, Nickenig C, Peter N, Lengfelder E, Metzner B, Rixecker T, Zwick C, Pfreundschuh M, Reiser M (2012) The role of sex and weight on rituximab clearance and serum elimination half-life in elderly patients with DLBCL. Blood 119(14):3276–3284. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-09-380949
Riggio O, Angeloni S, Ciuffa L, Nicolini G, Attili AF, Albanese C, Merli M (2003) Malnutrition is not related to alterations in energy balance in patients with stable liver cirrhosis. Clin Nutr 22(6):553–559
Peng S, Plank LD, McCall JL, Gillanders LK, McIlroy K, Gane EJ (2007) Body composition, muscle function, and energy expenditure in patients with liver cirrhosis: a comprehensive study. Am J Clin Nutr 85(5):1257–1266
Alberino F, Gatta A, Amodio P, Merkel C, Di Pascoli L, Boffo G, Caregaro L (2001) Nutrition and survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 17(6):445–450
Gusella M, Toso S, Ferrazzi E, Ferrari M, Padrini R (2002) Relationships between body composition parameters and fluorouracil pharmacokinetics. Br J Clin Pharmacol 54(2):131–139
Cosqueric G, Sebag A, Ducolombier C, Thomas C, Piette F, Weill-Engerer S (2006) Sarcopenia is predictive of nosocomial infection in care of the elderly. Br J Nutr 96(5):895–901
Spina M, Balzarotti M, Uziel L, Ferreri AJ, Fratino L, Magagnoli M, Talamini R, Giacalone A, Ravaioli E, Chimienti E, Berretta M, Lleshi A, Santoro A, Tirelli U (2012) Modulated chemotherapy according to modified comprehensive geriatric assessment in 100 consecutive elderly patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncologist 17(6):838–846. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2011-0417
Marchesi F, Cenfra N, Altomare L, Dessanti ML, Mecarocci S, Cerchiara E, Rago A, D’Andrea M, Tomarchio V, Olimpieri OM, Tirindelli MC, Mengarelli A, Petti MC, Avvisati G, Cimino G (2013) A retrospective study on 73 elderly patients (>/=75years) with aggressive B-cell non Hodgkin lymphoma: clinical significance of treatment intensity and comprehensive geriatric assessment. J Geriatr Oncol 4(3):242–248. doi:10.1016/j.jgo.2013.04.003
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM, Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F, Martin FC, Michel JP, Rolland Y, Schneider SM, Topinkova E, Vandewoude M, Zamboni M, European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older P (2010) Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing 39(4):412–423. doi:10.1093/ageing/afq034
Acknowledgments
We thank Mss. Chiyoko Sano, Hitomi Fujisawa, Shoko Sumi, Eriko Kunishima, and Miho Yagi for their secretarial assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakamura, N., Hara, T., Shibata, Y. et al. Sarcopenia is an independent prognostic factor in male patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann Hematol 94, 2043–2053 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-015-2499-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-015-2499-4