Abstract
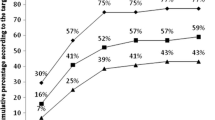
In patients with hematologic malignancies, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) following chemotherapy is widely used to mobilize peripheral blood progenitor cells (PBPCs), but there have been no trials comparing schedules of G-CSF following chemotherapy. We conducted a prospective randomized comparative observation of the mobilization with a single dose (10 μg kg once a day) or split dose (5 μg kg twice a day) of lenograstim following chemotherapy in 25 multiple myeloma (MM) and 15 non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) patients. Chemotherapy was cyclophosphamide 4 g/m2 for MM and ESHAP with or without Rituximab for NHL. The median number of harvested CD34+ cells was 19.4×106/kg and 15.8×106/kg in the single- and split-dose groups, respectively (p=0.47). Targeted collection of 5×106 CD34+ cells/kg was achieved in 18/20 patients in the single-dose group and in all 20 patients of the split-dose group (p=0.24), with the median number of sessions 1 and 2 in the single- and split-dose groups, respectively (p=0.13). We could not observe statistically significant differences between a single-dose and split-dose lenograstim following chemotherapy in enhancing the mobilization of PBPCs in MM or NHL patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perez-Simon JA, Caballero MD, Corral M, Nieto MJ, Orfao A, Vazquez L, Amigo ML, Berges C, Gonzalez M, Canizo C, Miguel JF (1998) Minimal number of circulating CD34+ cells to ensure successful leukapheresis and engraftment in autologous peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation. Transfusion 38:385–391
Feugier P, Bensoussan D, Girard F, Alla F, Schuhmacher A, Latger-Cannard V, Hulin C, Witz F, Witz B, Carret AS, Bordigoni P, Lederlin P, Janot C (2003) Hematologic recovery after autologous PBPC transplantation: importance of the number of postthaw CD34+ cells. Transfusion 43:878–884
André M, Baudoux E, Bron D, Canon JL, D’Hondt V, Fassotte MF, D’Hondt L, Fillet G, Humblet Y, Jerusalem G, Vermeulen V, Symann M, Beguin Y (2003) Phase III randomized study comparing 5 or 10 g per kg per day of filgrastim for mobilization of peripheral blood progenitor cells with chemotherapy, followed by intensification and autologous transplantation in patients with nonmyeloid malignancies. Transfusion 43:50–57
Carrion R, Serrano D, Gomez-Pineda A, Diez-Martin JL (2003) A randomised study of 10 ug/kg/day (single dose) vs 2×5 ug/kg/day (split dose) G-CSF as stem cell mobilisation regimen in high-risk breast cancer patients. Bone Marrow Transplant 32:563–567
Arbona C, Prosper F, Benet I, Mena F, Solano C, Garcia-Conde J (1998) Comparison between once a day vs twice a day G-CSF for mobilization of peripheral blood progenitor cells (PBPC) in normal donors for allogeneic PBPC transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 22:39–45
Kröger N, Renges H, Kruger W, Gutensohn K, Loliger C, Carrero I, Cortes L, Zander AR (2000) A randomized comparison of once versus twice daily recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (filgrastim) for stem cell mobilization in healthy donors for allogeneic transplantation. Br J Haematol 111:761–765
Lee V, Li CK, Shing MMK, Chik KW, Li K, Tsang KS, Zhao DC, Lai DH, Wong A, Yuen PMP (2000) Single vs twice daily G-CSF dose for peripheral blood stem cells harvest in normal donors and children with non-malignant diseases. Bone Marrow Transplant 25:931–935
Anderlini P, Donato M, Lauppe MJ, Huh YO, Martin TG, Chan KW, Champlin RE, Korbling M (2000) A comparative study of once-daily versus twice-daily filgrastim administration for the mobilization and collection of CD34+ peripheral blood progenitor cells in normal donors. Br J Haematol 109:770–772
Kröger N, Sonnenberg S, Cortes-Dericks L, Freiberger P, Mollnau H, Zander AR (2004) Kinetics of G-CSF and CD34+ cell mobilization after once or twice daily stimulation with rHu granulocyte-stimulating factor (lenograstim) in healthy volunteers: an intraindividual crossover study. Transfusion 44:104–110
Kröger N, Zeller W, Hassan HT, Krüger W, Gutensohn K, Löliger C, Zander AR (1999) Stem cell mobilization with G-CSF alone in breast cancer patients: higher progenitor cell yield by delivering divided doses (2×5 ug/kg) compared to a single dose (1×10 ug/kg). Bone Marrow Transplant 23:125–129
Lee JL, Kim S, Kim SW, Kim EK, Kim SB, Kang YK, Lee J, Kim MW, Park CJ, Chi HS, Huh J, Kim SH, Suh C (2005) ESHAP plus G-CSF as an effective peripheral blood progenitor cell mobilization regimen in pretreated non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: comparison with high-dose cyclophosphamide plus G-CSF. Bone Marrow Transplant 35:449–454
Suh C, Kim S, Kim SH, Kim EK, Lee JL, Park KU, Park JS, Lee JS, Kim WK, Chi HS, Park CJ, Kim SW (2004) Initiation of peripheral blood progenitor cell harvest based on peripheral blood hematopoietic progenitor cell counts enumerated by the Sysmex SE9000. Transfusion 44:1762–1768
Park KU, Kim SH, Suh C, Kim S, Lee SJ, Park JS, Cho HJ, Kim KW, Lee K, Kim HJ, Park J, Min YJ, Kim JG, Kim T, Lee JH, Kim SB, Kim SW, Lee KH, Lee JS, Kim WK, Park CJ, Chi HS (2001) Correlation of hematopoietic progenitor cell count determined by the SE-automated hematology analyzer with CD34+ cell count by flow cytometry in leukapheresis products. Am J Hematol 67:42–47
Lee JL, Kim S, Lee GW, Ryu MH, Kim EK, Kim S, Kim WK, Lee JS, Park KU, Suh C (2003) Clinical usefulness of hematopoietic progenitor cell counts in predicting optimal timing of peripheral blood stem cell harvest. J Korean Med Sci 18:27–35
Lee JL, Kim S, Lee GW, Ryu MH, Kim E, Kim S, Kim WK, Lee JS, Kim SH, Suh C (2003) The efficacy of high-dose melphalan with autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma. Yonsei Med J 44:800–810
Caballero MD, Rubio V, Rifon J, Heras I, García-Sanz R, Vázquez L, Vidriales B, del Cañizo MC, Corral M, Gonzalez M, León A, Jean-Paul E, Rocha E, Moraleda JM, San Miguel JF (1997) BEAM chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell support in lymphoma patients: analysis of efficacy, toxicity and prognostic factors. Bone Marrow Transplant 20:451–458
Socinski MA, Elias A, Schnipper L, Cannistra SA, Antman KH, Griffin JD (1988) Granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor expands the circulating haemopoietic progenitor cell compartment in man. Lancet 331:1194–1198
Duhrsen U, Villeval JL, Boyd J, Kannourakis G, Morstyn G, Metcalf D (1988) Effects of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor on hematopoietic progenitor cells in cancer patients. Blood 72:2074–2081
Russell NH, McQuaker G, Stainer C, Byrne JL, Haynes AP (1998) Stem cell mobilisation in lymphoproliferative diseases. Bone Marrow Transplant 22:935–940
Kessinger A, Sharp JG (2003) The whys and hows of hematopoietic progenitor and stem cell mobilization. Bone Marrow Transplant 31:319–329
Lee JL, Kim S, Lee GW, Ryu MH, Kim EK, Kim S, Kim WK, Lee JS, Suh C (2003) Collection of peripheral blood progenitor cells: analysis of factors predicting the yields. Transfus Apher Sci 29:29–37
Koenigsmann M, Jentsch-Ullrich K, Mohren M, Becker E, Heim M, Franke A (2004) The role of diagnosis in patients failing peripheral blood progenitor cell mobilization. Transfusion 44:777–784
Fruehauf S, Seggewiss R (2003) It’s moving day: factors affecting peripheral blood stem mobilization and strategies for improvement. Br J Haematol 122:360–375
Martin-Murea S, Voso MT, Hohaus S, Pforsich M, Fruehauf S, Goldschmidt H, Hegenbart U, Haas R (1998) The dose of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor administered following cytotoxic chemotherapy is not related to the rebound level of circulating CD34+ haematopoietic progenitor cells during marrow recovery. Br J Haematol 101:582–585
Acknowledgements
We thank the nursing staff of ward 84 for their skillful care of patients receiving autologous stem cell transplantation. We are obliged to the technical staff at the Department of Diagnostic Laboratory Medicine for their excellent cooperation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S., Kim, HJ., Park, J.S. et al. Prospective randomized comparative observation of single- vs split-dose lenograstim to mobilize peripheral blood progenitor cells following chemotherapy in patients with multiple myeloma or non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Ann Hematol 84, 742–747 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-005-1103-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-005-1103-8