Abstract
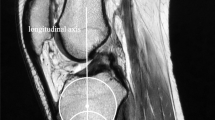
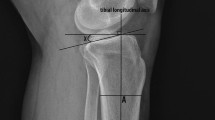
Posterior tibial slope (PTS) is an important parameter of sagittal alignment associated with postoperative stability and kinematics after total knee arthroplasty (TKA). However, data are limited regarding the innate gender differences in PTS in Koreans. The current study separately measured the PTS of the medial and lateral tibial plateau on magnetic resonance images of 511 patients with knee joint osteoarthritis who had Kellgren and Lawrence grade 3 and 4 (430 women, 81 men) and compared the measurements between and within the genders. The tibia was then rotated to the tibial plateau with the tibial centroid axis and the PTS was evaluated from best-fit planes on the surface of the proximal tibia and individually for the medial, lateral, and overall plateaus. The average overall PTS was 10.0° ± 3.5°. The average overall PTS of the female and male patients was 10.2° ± 3.4° and 8.8° ± 4.0°, respectively. The average medial PTS was 10.4° ± 4.0°, significantly greater than the mean lateral PTS of 8.7° ± 3.9° (P < 0.05). The average medial and lateral tibial slopes for female patients were 10.7° ± 3.8° and 8.8° ± 3.8°, respectively, while the average medial and lateral tibial slopes for male patients were 8.9° ± 4.8° and 7.9° ± 4.7°, respectively. The medial and overall PTS were significantly greater in female patients than in male patients (P < 0.05). The results showed a gender difference in PTS and that medial PTS was greater than lateral PTS. These findings have clinical relevance in knee reconstructive surgery for determining ideal placement of the posterior slope tibial component. Surgeons should be aware of variability and gender differences in the tibial slope of patients undergoing TKA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai B, Kummer FJ, Sala DA, Koval KJ, Wolinsky PR (2001) Effect of articular step-off and meniscectomy on joint alignment and contact pressures for fractures of the lateral tibial plateau. J Orthop Trauma 15(2):101–106
Bonin N, Ait Si Selmi T, Donell ST, Dejour H, Neyret P (2004) Anterior cruciate reconstruction combined with valgus upper tibial osteotomy: 12 years follow-up. Knee 11(6):431–437
Brandon ML, Haynes PT, Bonamo JR, Flynn MI, Barrett GR, Sherman MF (2006) The association between posterior-inferior tibial slope and anterior cruciate ligament insufficiency. Arthroscopy 22(8):894–899
Brooks P (2009) Seven cuts to the perfect total knee. Orthopedics 32(9):1
Chiu K, Zhang S, Zhang G (2000) Posterior slope of tibial plateau in Chinese. J Arthroplasty 15(2):224–227
Dejour H, Bonnin M (1994) Tibial translation after anterior cruciate ligament rupture: two radiological tests compared. J Bone Joint Surg Br 76(5):745–749
Faschingbauer M, Sgroi M, Juchems M, Reichel H, Kappe T (2014) Can the tibial slope be measured on lateral knee radiographs? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22(12):3163–3167
Gromov K, Korchi M, Thomsen MG, Husted H, Troelsen A (2014) What is the optimal alignment of the tibial and femoral components in knee arthroplasty? Acta Orthop 85(5):480–487
Haddad B, Konan S, Mannan K, Scott G (2012) Evaluation of the posterior tibial slope on MR images in different population groups using the tibial proximal anatomical axis. Acta Orthop Belg 78(6):757–763
Hashemi J, Chandrashekar N, Gill B, Beynnon BD, Slauterbeck JR, Schutt RC Jr, Mansouri H, Dabezies E (2008) The geometry of the tibial plateau and its influence on the biomechanics of the tibiofemoral joint. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90(12):2724–2734
Ho JPY, Merican AM, Hashim MS, Abbas AA, Chan CK, Mohamad JA (2017) Three-Dimensional Computed Tomography Analysis of the Posterior Tibial Slope in 100 Knees. J Arthroplasty 32(10):3176–3183
Hofmann AA, Bachus KN, Wyatt RW (1991) Effect of the tibial cut on subsidence following total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 269:63–69
Igbigbi PS, Msamati BC, Matanje B (2003) Normal axial angles of the knee joint in adult indigenous Malawians. East Afr Med J 80(8):415–418
Insall JN, Windsor RE, Scott WN (1993) Surgery of the knee, 2nd edn. Churchill Livingstone, New York
Jenny JY, Boeri C, Ballonzoli L, Meyer N (2005) Difficulties and reproducibility of radiological measurement of the proximal tibial axis according to Levigne. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 91(7):658–663
Jiang C-C, Yip K, Liu T (1994) Posterior slope angle of the medial tibial plateau. J Formos Med Assoc 93(6):509–512
Kang KT, Kim SH, Son J, Lee YH, Kim S, Chun HJ (2017) Probabilistic evaluation of the material properties of the in vivo subject-specific articular surface using a computational model. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 105(6):1390–1400
Kang KT, Son J, Kwon OR, Baek C, Heo DB, Park KM, Kim HJ, Koh YG (2016) Morphometry of femoral rotation for total knee prosthesis according to gender in a Korean population using three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. Knee 23(6):975–980
Kang KT, Son J, Kwon OR, Baek C, Heo DB, Park KM, Kim HJ, Koh YG (2017) Effects of measurement methods for tibial rotation axis on the morphometry in Korean populations by gender. Knee 24(1):23–30
Kapandji IA (1987) The physiology of the joints: annotated diagrams of the mechanics of the human joints, vol 2. Churchill Livingstone, Lower Limb
Khattak MJ, Umer M, Davis ET, Habib M, Ahmed M (2010) Lower-limb alignment and posterior tibial slope in Pakistanis: a radiographic study. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 18(1):22–25
Kim KH, Bin SI, Kim JM (2012) The correlation between posterior tibial slope and maximal angle of flexion after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res 24(3):158–163
Kwak DS, Surendran S, Pengatteeri YH, Park SE, Choi KN, Gopinathan P, Han SH, Han CW (2007) Morphometry of the proximal tibia to design the tibial component of total knee arthroplasty for the Korean population. Knee 14(4):295–300
Lonner JH, Laird MT, Stuchin SA (1996) Effect of rotation and knee flexion on radiographic alignment in total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res 331:102–106
Lotke P (2003) Primary total knees: standard principles and techniques. J Knee Arthroplasty 49:1
Lustig S, Scholes CJ, Stegeman TJ, Oussedik S, Coolican MR, Parker DA (2012) Sagittal placement of the femoral component in total knee arthroplasty predicts knee flexion contracture at one-year follow-up. Int Orthop 36(9):1835–1839
Nunley RM, Ellison BS, Zhu J, Ruh EL, Howell SM, Barrack RL (2012) Do patient-specific guides improve coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res 470(3):895–902
Ostermeier S, Hurschler C, Windhagen H, Stukenborg-Colsman C (2006) In vitro investigation of the influence of tibial slope on quadriceps extension force after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 14(10):934–939
Singh G, Tan JH, Sng BY, Awiszus F, Lohmann CH, Nathan SS (2013) Restoring the anatomical tibial slope and limb axis may maximise post-operative flexion in posterior-stabilised total knee replacements. Bone Joint J 95(10):1354–1358
Sorin G, Pasquier G, Drumez E, Arnould A, Migaud H, Putman S (2016) Reproducibility of digital measurements of lower-limb deformity on plain radiographs and agreement with CT measurements. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 102(4):423–428
Weinberg DS, Williamson DF, Gebhart JJ, Knapik DM, Voos JE (2017) Differences in medial and lateral posterior tibial slope: an osteological review of 1090 tibiae comparing age, sex, and race. Am J Sports Med 45(1):106–113
Yang B, Song CH, Yu JK, Yang YQ, Gong X, Chen LX, Wang YJ, Wang J (2014) Intraoperative anthropometric measurements of tibial morphology: comparisons with the dimensions of current tibial implants. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22(12):2924–2930
Yue B, Varadarajan KM, Ai S, Tang T, Rubash HE, Li G (2011) Differences of knee anthropometry between Chinese and white men and women. J Arthroplasty 26(1):124–130
Zhang Y, Wang J, Xiao J, Zhao L, Li ZH, Yan G, Shi ZJ (2014) Measurement and comparison of tibial posterior slope angle in different methods based on three-dimensional reconstruction. Knee 21(3):694–698
Funding
There was no funding for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koh, YG., Nam, JH., Chung, HS. et al. Morphometric study of gender difference in osteoarthritis posterior tibial slope using three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging. Surg Radiol Anat 42, 667–672 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-020-02429-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-020-02429-3