Abstract
Purpose
Scapulothoracic bursitis is a painful condition of the scapulothoracic articulation, which may be caused by various pathological anatomical associations. We have arthroscopically observed a constant bare area of bone on the costal scapula surface in patients with scapulothoracic bursitis, contradictory to traditional anatomical reports of scapular muscle relations. We undertook a cadaveric study to further define this anatomical feature.
Methods
Twelve cadaveric shoulders were dissected. The costal surface of the scapula was systematically examined for the presence of a superomedial bare area in each shoulder by three independent clinicians, with dimensions measured using digital calipers.
Results
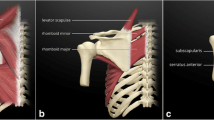
In all shoulders, there was a clearly defined bare area of bone on the superomedial aspect of the costal surface of the scapula between the serratus anterior insertion and subscapularis origin. The bare area was typically crescenteric in shape, with variable length (mean 22.3 ± 6.0 mm) and width (10.8 ± 2.8 mm). The bare area length (p = 0.043) and width (p = 0.033) were significantly greater in female shoulders compared to male shoulders.
Conclusions
We have established the presence of the superomedial bare area of the costal scapula surface. With an absence of overlying subscapularis muscle, this bare area carries the potential for scapulothoracic impingement, and should be considered as a possible aetiological factor in all patients presenting with scapulothoracic bursitis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal A, Wahee P, Aggarwal AK, Kaur H, Sahni D (2012) Anatomical considerations for safe scapular resection in snapping scapula syndrome. Surg Radiol Anat 34:43–47
Aggarwal A, Wahee P, Kaur H, Aggarwal AK, Sahni D (2011) Variable osseous anatomy of costal surface of scapula and its implications in relation to snapping. Surg Radiol Anat 33:135–140
Boinet W (1867) Fait clinique. Bull Mem Sec Chir Paris 8:458
Carlson HL, Haig AJ, Stewart DC (1997) Snapping scapula syndrome: three case reports and an analysis of the literature. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 78:506–511
Edelson JG (1996) Variations in the anatomy of the scapula with reference to the snapping scapula. Clin Orthop Relat Res 322:111–115
Fukunaga S, Futani H, Yoshiya S (2007) Endoscopically assisted resection of a scapula osteochondroma causing snapping scapula syndrome. World J Surg Oncol 5:37
Harrison AK, Flatow EL (2011) Subacromial impingement syndrome. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 19:701–708
Kuhn JE, Plancher KD, Hawkins RJ (1998) Symptomatic scapulothoracic crepitus and bursitis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 6:267–273
Kuhne M, Boniquit N, Ghodadra N, Romeo AA, Provencher MT (2009) The snapping scapula: diagnosis and treatment. Arthroscopy 25:1298–1311
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Lazar MA, Kwon YW, Rokito AS (2009) Snapping scapula syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91:2251–2262
Lehtinen JT, Macy JC, Cassinelli E, Warner JJ (2004) The painful scapulothoracic articulation: surgical management. Clin Orthop Relat Res 423:99–105
Milch H, Burman MS (1933) Snapping scapula and humerus varus. Report of six cases. Arch Surg 26:570–588
Mozes G, Bickels J, Ovadia D, Dekel S (1999) The use of three-dimensional computed tomography in evaluating snapping scapula syndrome. Orthopedics 22:1029–1033
Parsons TA (1973) The snapping scapula and subscapular exostoses. J Bone Joint Surg Br 55:345–349
Percy EC, Birbrager D, Pitt MJ (1988) Snapping scapula: review of the literature and representation of 14 cases. Can J Surg 31:248–250
Sinnatamby CS, Last RJ (2011) Last’s anatomy: regional and applied. Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier, Edinburgh
Standring S, Gray H (2008) Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Wood VE, Verska JM (1989) The snapping scapula in association with the thoracic outlet syndrome. Arch Surg 124:1335–1337
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to sincerely thank Mr. Sheldon Bont for the production of Fig. 2. The authors declare that the experiments involved in this study comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boyle, M.J., Misur, P., Youn, SM. et al. The superomedial bare area of the costal scapula surface: a possible cause of snapping scapula syndrome. Surg Radiol Anat 35, 95–98 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-012-1007-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-012-1007-y