Abstract
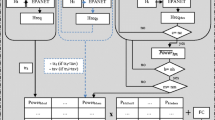
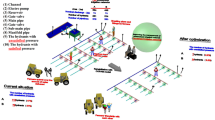
The increasing demand and price for energy are affecting all economic sectors, including irrigated agriculture. This sector has undergone substantial transformations to improve water use efficiency by adapting its open-channel distribution systems to pressurized networks, which entail greater energy consumption and hence higher energy costs. Farmers are therefore demanding measures to reduce energy costs and ensure the profitability of their farms. In this paper, previous energy optimization models focusing on network sectoring (WEBSOM) and critical points control (WECPM) are improved by incorporating an electricity tariff module that considers different energy prices according to the hour of the day and the day of the year. The model permits determining the minimum energy cost affected by different operation conditions of the network. The methodology has been analyzed in an irrigation network located in southern Spain in which different operation scenarios were evaluated: operation with and without sectors and with and without critical points control. The results show that adopting measures to improve the operation of critical points in months of peak energy demand and operation by sectors in the others leads to a 13 % cost savings compared to the baseline scenario where only pressure heads at the pumping stations are optimized. The proposed model is a decision-making support system that integrates alternative irrigation network operation scenarios with the structure of the electricity tariff.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadía R, Rocamora C, Vera J (2012) Energy efficiency in irrigation distribution networks II: applications. Biosyst Eng 111:398–411
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M (1998) Crop evapotranspiration: guidelines for computing crop water requirements. Irrigation and drainage Paper No. 56, food and agricultural organization of the United Nations (FAO), Rome
BOE (2014) Circular 3/2014, de 2 de julio, de la Comisión Nacional de los Mercados y la Competencia, por la que se establece la metodología para el cálculo de los peajes de transporte y distribución de electricidad. Boletín Oficial de Estado 175(1):57158–57184
Brazilian M, Rogner H, Howells M, Hermann S, Arent D, Gielen D, Steduto P, Mueller A, Komor P, Tol R, Yumkella K (2011) Considering the energy, water and food nexus: towards an integrated modeling approach. Energy Policy 39:7896–7906
Carrillo Cobo MT, Rodríguez Díaz JA, Montesinos P, López Luque R, Camacho Poyato E (2011) Low energy consumption seasonal calendar for sectoring operation in pressurized irrigation networks. Irrig Sci 29(2):157–169
Casado V (2012) Estrategias en el uso del agua y la energía: estudio de la Comunidad de Regantes de Fuente Palmera. Graduation thesis, University of Cordoba, Spain
Conforti P (2011) Looking ahead in world food and agriculture: perspectives to 2050. Volume of the papers for expert meeting on how to feed the world in 2050, FAO, Rome, 24–26 June 2009, Rome, FAO
Consoli S, Matarazzo B, Pappalardo N (2008) Operating rules of an irrigation purposes reservoir using multi-objective optimization. Water Resour Manag 22:551–564
Deb K, Pratap A, Agarwal S, Meyarivan T (2002) A fast elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: nSGA-II. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 6(2):182–197
Dumont A, Mayor B, López-Gunn E (2013) Is the rebound effect or Jevons paradox a useful concept for better management of water resources? Insights from the irrigation modernization process in Spain. Aquat Procedia 1:64–76
EEA (2012) Towads efficient use of water resources in Europe, EEA Report No 1/2012, European Environment Agency
Fallah-Mehdipour E, Bozorg Haddad O, Mariño MA (2012) Real-time operation of reservoir system by genetic programming. Water Resour Manag 26:4091–4103
Farmani R, Walters G, Savic D (2006) Evolutionary multi-objective optimization of the design and operation of water distribution network: total cost vs. reliability vs. water quality. J Hydroinf 8:165–179
Fernández García I, Rodríguez Díaz JA, Camacho Poyato E, Montesinos P (2013) Optimal operation of pressurized irrigation networks with several supply sources. Water Resour Manag 27:2855–2869
Fernández García I, Montesinos P, Poyato EC, Rodríguez Díaz JA (2014) Methodology for detecting critical points in pressurized irrigation networks with multiple water supply points. Water Resour Manag. doi:10.1007/s11269-014-0538-x
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search, optimization and machine learning. Addison-Wesley Longman Publishing Co, Incl, Boston
Instituto Nacional de Estadística (INE) (2014). Encuesta sobre el uso del agua en el sector agrario (año 2012). Nota de prensa. Madrid. Spain. Available via http://www.ine.es/jaxi/menu.do?type=pcaxis&path=%2Ft26%2Fp067%2Fp01&file=inebase&L=0 Accessed 2015
Jiménez Bello MA, Martínez Alzamora F, Bou Soler V, Bartolí Ayala HJ (2010) Methodology for grouping intakes of pressurised irrigation networks into sectors to minimise energy consumption. Biosyst Eng 105:429–438
Lamaddalena N, Khila S (2012) Energy saving with variable speed pumps in on-demand irrigation systems. Irrig Sci 30:157–166
Lecina S, Isidoro D, Playán E, Aragües R (2010) Irrigation modernization and water conservation in Spain: the case of Riegos del Alto Aragón. Agric Water Manag 97:1663–1675
Montesinos P, García-Guzmán A, Ayuso JL (1999) Water distribution network optimization using a modified genetic algorithm. Water Resour Res 35:3467–3473
Moreno MA, Carrión PA, Planells P, Orteg JF, Tarjuelo JM (2007) Measurement and improvement of the energy efficiency at pumping stations. Biosyst Eng 98(4):479–486
Pérez Urrestarazu L, Rodríguez Díaz JA, Camacho Poyato E, López Luque R (2009) Quality of service in irrigation distribution networks: case of Palos de la Frontera irrigation district (Spain). J Irrig Drain Eng 135(6):755–762
Pratap R (2010) Getting started with Matlab. A quick introduction for Scientist and Engineers. Oxford University Press, USA
Reca J, Martínez J, Gil C, Baños R (2008) Application of several meta-heuristic techniques to the optimization of real looped water distribution networks. Water Resour Manag 22:1367–1379
Rocamora C, Vera J, Abadía R (2012) Strategy for Efficient Energy Management to solve energy problems in modernized irrigation: analysis of the Spanish case. Irrig Sci. doi:10.1007/s00271-012-0394-5
Rodríguez Díaz JA, Camacho Poyato E, Blanco Pérez M (2011) Evaluation of water and energy use in pressurized irrigation networks in Southern Spain. J Irrig Drain Eng 137(10):644–650
Rodríguez Díaz JA, Pérez Urrestarazu L, Camacho Poyato E, Montesinos P (2012a) Modernizing water distribution networks. Lessons from the Bembézar MD irrigation district, Spain. Outlook Agric 41(4):229–236
Rodríguez Díaz JA, Montesinos P, Camacho Poyato E (2012b) Detecting critical points in on-demand irrigation pressurized networks—a new methodology. Water Resour Manag 26(6):1693–1713
Rossman LA (2000) EPANET 2. Users manual. US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), USA
Savic D (2007) Single-objective vs. multio-objective optimization for integrated decision support. Proceedings of the first biennial meeting of the international environmental modeling and software society 1: 7–12 Lugano, Switzerland, 24–27 June 2007
Spanish Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Environment (MAGRAMA) (2013) Boletín Hidrológico Semanal 1. Madrid. Spain (in Spanish). Available via: http://www.magrama.gob.es/es/agua/temas/evaluacion-de-los-recursos-hidricos/boletin-hidrologico/
Spanish Ministry of Economy (2001) RD 1164/2001, de 26 de octubre, por el que se establecen tarifas de acceso a las redes de transporte y distribución de energía eléctrica
Spanish Ministry of Environment MMA (2006) Plan de Choque de Modernización de Regadíos. Spain (in Spanish), Madrid
Spanish Ministry of Food, Agriculture, and Fishery (MAPA) (2001) Plan Nacional de Regadíos. Horizonte 2008. Madrid, Spain (in Spanish)
Spanish Ministry of Industry, Energy and Tourism MINETUR (2014) Orden IET/107/2014, de 31 de enero, por la que se revisan los peajes de acceso de energía eléctrica para 2014. Spain (in Spanish), Madrid
Spanish Ministry of Industry, Tourism and Trade MINETUR (2008) Orden ITC/3860/2007, de 28 de diciembre, por la que se revisan las tarifas eléctricas a partir del 1 de enero de 2008. Spain (in Spanish), Madrid
Acknowledgments
This research is part of the TEMAER project (AGL2014-59747-C2-2-R), funded by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Garrido.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández García, I., Montesinos, P., Camacho Poyato, E. et al. Energy cost optimization in pressurized irrigation networks. Irrig Sci 34, 1–13 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-015-0475-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00271-015-0475-3