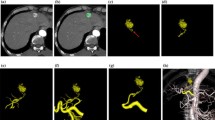
Abstract
Background
This study was designed to evaluate the utility of dual phase cone beam computed tomography (DP-CBCT) and automatic vessel detection (AVD) software to guide transarterial embolization (TAE) of angiographically challenging arterial bleedings in emergency settings.
Methods
Twenty patients with an arterial bleeding at computed tomography angiography and an inconclusive identification of the bleeding vessel at the initial 2D angiographic series were included. Accuracy of DP-CBCT and AVD software were defined as the ability to detect the bleeding site and the culprit arterial bleeder, respectively. Technical success was defined as the correct positioning of the microcatheter using AVD software. Clinical success was defined as the successful embolization. Total volume of iodinated contrast medium and overall procedure time were registered.
Results
The bleeding site was not detected by initial angiogram in 20 % of cases, while impossibility to identify the bleeding vessel was the reason for inclusion in the remaining cases. The bleeding site was detected by DP-CBCT in 19 of 20 (95 %) patients; in one case CBCT-CT fusion was required. AVD software identified the culprit arterial branch in 18 of 20 (90 %) cases. In two cases, vessel tracking required manual marking of the candidate arterial bleeder. Technical success was 95 %. Successful embolization was achieved in all patients. Mean contrast volume injected for each patient was 77.5 ml, and mean overall procedural time was 50 min.
Conclusions
C-arm CBCT and AVD software during TAE of angiographically challenging arterial bleedings is feasible and may facilitate successful embolization. Staff training in CBCT imaging and software manipulation is necessary.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keeling AN, McGrath FP, Thornton J, Brennan P, Lee MJ. Emergency percutaneous transcatheter embolisation of acute arterial hemorrhage. Ir J Med Sci. 2010;179(3):385–91.
Brooks B. The treatment of traumatic arteriovenous fistula. South Med J. 1930;23:100–6.
Angle JF, Siddiqi NH, Wallace MJ, Kundu S, Stokes L, Wojak JC, et al. Quality improvement guidelines for percutaneous transcatheter embolization: society of Interventional Radiology Standards of Practice Committee. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2010;21(10):1479–86.
Iwazawa J, Ohueo S, Hashimoto N, Mitani T. Feasibility of using vessel-detection software for the endovascular treatment of visceral arterial bleeding. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2014;20(2):160–3.
Angle JF. Cone-beam CT: vascular applications. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013;16(3):144–9.
Dijkstra ML, Eagleton MJ, Greenberg RK, Mastracci T, Hernandez A. Intraoperative C-arm cone-beam computed tomography in fenestrated/branched aortic endografting. J Vasc Surg. 2011;53(3):583–90.
van Bindsbergen L, Braak SJ, van Strijen MJ, de Vries JP. Type II endoleak embolization after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair with use of real-time three-dimensional fluoroscopic needle guidance. J Vasc Intervent Radiol. 2010;21(9):1443–7.
Lee IJ, Chung JW, Yin YH, Kim HC, Kim YI, Jae HJ, et al. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) hepatic arteriography in chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: performance depicting tumors and tumor feeders. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2015;38:1218–30.
Chiaradia M, Radaelli A, Campeggi A, Bouanane M, De La Taille A, Kobeiter H. Automatic three-dimensional detection of prostatic arteries using cone-beam CT during prostatic arterialembolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2015;26(3):413–7.
Tacher V, Radaelli A, Lin M, Geschwind JF. How I do it: cone-beam CT during transarterial chemoembolization for liver cancer. Radiology. 2015;274(2):320–34.
Patil VV, Fischman AM, Patel RS, Kim E, Lookstein RA, Tabori NE, et al. GI hemorrhage arising from splenic artery: intraprocedure cone-beam CT as problem-solving tool to aide in safe catheterization of offending vessel. Clin Imaging. 2015;39:928–30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Alessandro Radaelli declares his relationship of employee with Philips. The remaining Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study, when possible.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carrafiello, G., Ierardi, A.M., Duka, E. et al. Usefulness of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography and Automatic Vessel Detection Software in Emergency Transarterial Embolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 39, 530–537 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-015-1213-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-015-1213-1