Abstract
Purpose
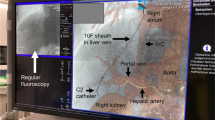
This study was designed to evaluate the feasibility of endovascular guidance by means of live fluoroscopy fusion with magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and computed tomography angiography (CTA).
Methods
Fusion guidance was evaluated in 20 endovascular peripheral artery interventions in 17 patients. Fifteen patients had received preinterventional diagnostic MRA and two patients had undergone CTA. Time for fluoroscopy with MRA/CTA coregistration was recorded. Feasibility of fusion guidance was evaluated according to the following criteria: for every procedure the executing interventional radiologists recorded whether 3D road-mapping provided added value (yes vs. no) and whether PTA and/or stenting could be performed relying on the fusion road-map without need for diagnostic contrast-enhanced angiogram series (CEAS) (yes vs. no). Precision of the fusion road-map was evaluated by recording maximum differences between the position of the vasculature on the virtual CTA/MRA images and conventional angiography.
Results
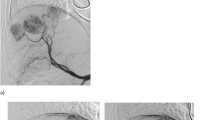
Average time needed for image coregistration was 5 ± 2 min. Three-dimensional road-map added value was experienced in 15 procedures in 12 patients. In half of the patients (8/17), intervention was performed relying on the fusion road-map only, without diagnostic CEAS. In two patients, MRA roadmap showed a false-positive lesion. Excluding three patients with inordinate movements, mean difference in position of vasculature on angiography and MRA/CTA road-map was 1.86 ± 0.95 mm, implying that approximately 95 % of differences were between 0 and 3.72 mm (2 ± 1.96 standard deviation).
Conclusions
Fluoroscopy with MRA/CTA fusion guidance for peripheral artery interventions is feasible. By reducing the number of CEAS, this technology may contribute to enhance procedural safety.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Selvin E, Erlinger TP (2004) Prevalence of and risk factors for peripheral arterial disease in the United States: results from the national health and nutrition examination survey, 1999–2000. Circulation 110(6):738–743
Harris K (2008) The worldwide burden of peripheral artery disease. Inter-society consensus for the management of peripheral artery disease (TASC II). Available at: http://www.radiolodzy-interwencyjni.pl/forms/961.pdf. Accessed 24 Nov 2013
Raval AN, Karmarkar PV, Guttman MA, Ozturk C, Sampath S, DeSilva R, Aviles RJ, Xu M, Wright VJ, Schenke WH, Kocaturk O, Dick AJ, Raman VK, Atalar E, McVeigh ER, Lederman RJ (2006) Real-time magnetic resonance imaging-guided endovascular recanalization of chronic total arterial occlusion in a swine model. Circulation 113(8):1101–1107
Buecker A, Adam GB, Neuerburg JM, Kinzel S, Glowinski A, Schaeffter T, Rasche V, van Vaals JJ, Guenther RW (2002) Simultaneous real-time visualization of the catheter tip and vascular anatomy for MR-guided PTA of iliac arteries in an animal model. J Magn Reson Imaging 16(2):201–208
Fink C, Bock M, Umathum R, Volz S, Zuehlsdorff S, Grobholz R, Kauczor HU, Hallscheidt P (2004) Renal embolization: feasibility of magnetic resonance-guidance using active catheter tracking and intraarterial magnetic resonance angiography. Invest Radiol 39(2):111–119
Klein AJ, Tomkowiak MT, Vigen KK, Hacker TA, Speidel MA, Vanlysel MS, Shah N, Raval AN (2012) Multimodality image fusion to guide peripheral artery chronic total arterial occlusion recanalization in a swine carotid artery occlusion model: unblinding the interventionalist. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 80(7):1090–1098
van der Hoeven BL, Schalij MJ, Delgado V (2012) Multimodality imaging in interventional cardiology. Nat Rev Cardiol 9(6):333–346
Kobeiter H, Nahum J, Becquemin JP (2011) Zero-contrast thoracic endovascular aortic repair using image fusion. Circulation 124(11):e280–e282
Dijkstra ML, Eagleton MJ, Greenberg RK, Mastracci T, Hernandez A (2011) Intraoperative C-arm cone-beam computed tomography in fenestrated/branched aortic endografting. J Vasc Surg 53(3):583–590
Sailer AM, de Haan MW, Peppelenbosch AG, Jacobs MJ, Wildberger JE, Schurink GW (2014) CTA with fluoroscopy image fusion guidance in endovascular complex aortic aneurysm repair. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 47(4):349–356
Sadek M, Berland TL, Maldonado TS, Rockman CB, Mussa FF, Adelman MA, Veith FJ, Cayne NS (2014) Use of preoperative magnetic resonance angiography and the Artis zeego fusion program to minimize contrast during endovascular repair of an iliac artery aneurysm. Ann Vasc Surg 28(1):261.e1–5
Bargellini I, Turini F, Bozzi E, Lauretti D, Cicorelli A, Lunardi A, Cioni R, Bartolozzi C (2013) Image fusion of preprocedural CTA with real-time fluoroscopy to guide proper hepatic artery catheterization during transarterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma: a feasibility study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 36(2):526–530
Versluis B, Backes WH, van Eupen MG, Jaspers K, Nelemans PJ, Rouwet EV, Teijink JA, Mali WP, Schurink GW, Wildberger JE, Leiner T (2011) Magnetic resonance imaging in peripheral arterial disease: reproducibility of the assessment of morphological and functional vascular status. Invest Radiol 46(1):11–24
Romero JM, Bover J, Fite J, Bellmunt S, Dilmé JF, Camacho M, Vila L, Escudero JR (2012) The modification of diet in renal disease 4-calculated glomerular filtration rate is a better prognostic factor of cardiovascular events than classical cardiovascular risk factors in patients with peripheral arterial disease. J Vasc Surg 56(5):1324–1330
Hölscher B, Heitmeyer C, Fobker M, Breithardt G, Schaefer RM, Reinecke H (2008) Predictors for contrast media-induced nephropathy and long-term survival: prospectively assessed data from the randomized controlled Dialysis-Versus-Diuresis (DVD) trial. Can J Cardiol 24(11):845–850
Laskey WK, Jenkins C, Selzer F, Marroquin OC, Wilensky RL, Glaser R, Cohen HA, Holmes DR Jr (2007) NHLBI Dynamic Registry Investigators. Volume-to-creatinine clearance ratio: a pharmacokinetically based risk factor for prediction of early creatinine increase after percutaneous coronary intervention. J Am Coll Cardiol 50(7):584–590
Manke C, Nitz WR, Djavidani B, Strotzer M, Lenhart M, Völk M, Feuerbach S, Link J (2001) MR imaging-guided stent placement in iliac arterial stenoses: a feasibility study. Radiology 219(2):527–534
Sailer AM, Schurink GWH, Wildberger JE, de Graaf R, van Zwam WH, de Haan MW, Kemerink GJ, Jeukens CRLPN (2014) Radiation exposure of abdominal cone beam computed tomography. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00270-014-0900-7
Jens S, Koelemay MJ, Reekers JA, Bipat S (2013) Diagnostic performance of computed tomography angiography and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography in patients with critical limb ischaemia and intermittent claudication: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Radiol 23(11):3104–3114
Conflict of interest
Anna M. Sailer, Rick de Graaf, Willem H. Van Zwam, Geert Willem H. Schurink, Patricia J. Nelemans have no conflicts of interest. Michiel W. de Haan reports an institutional Grant from Philips Medical Systems. Joachim E. Wildberger reports institutional grants from Siemens Healthcare, Bayer Healthcare, GE Healthcare, Philips Medical Systems, Agfa Healthcare; personal fees from Bayer, Siemens, from null, outside the submitted work. Marco Das reports institutional Grants from Philips Medical Systems, Siemens Healthcare, Bayer Healthcare and GE Healthcare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sailer, A.M., de Haan, M.W., de Graaf, R. et al. Fusion Guidance in Endovascular Peripheral Artery Interventions: A Feasibility Study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 38, 314–321 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-014-0951-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-014-0951-9