Abstract
Purpose
Our experience with endovascular embolization (EVE) of the bronchial artery (BA) originating from the upper portion of the aortic arch (AA) in six patients is described.
Methods
Altogether, 818 patients with hemoptysis underwent multidetector row computed tomography angiography (MDCTA) before EVE or AA angiography during EVE. Aberrant BAs originating from the upper portion of the AA were the source of massive hemoptysis in six patients (0.73 %). MDCT angiograms and/or Digital subtraction angiograms were retrospectively reviewed. Selective catheterization and embolization were performed.
Results
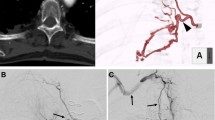
The ostia of the BAs were located on the superior surface of the AA between the brachiocephalic trunk and left common carotid artery in three patients, the junction of the aorta and medial surface of the left subclavian artery in two, and the posterior wall of the upper portion of the AA in one. The six BAs comprised two common trunks, three single right sides, and one single left side. The targeted vessels were successfully catheterized and embolized by a coaxial microcatheter system using polyvinyl alcohol particles. Other pathologic BAs and nonbronchial systemic arteries also were embolized. Bleeding was immediately controlled in all patients with no recurrence of hemoptysis. No procedure-related complications occurred.
Conclusions
Application of EVE of anomalous origin of BAs in patients with hemoptysis is important, as demonstrated in the six reported patients. MDCTA before EVE or AA angiography during EVE is critical to avoid missing a rare aberrant BA originating from the upper portion of the AA.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
Bronchial artery
- EVE:
-
Endovascular embolization
- AA:
-
Aortic arch
- MDCTA:
-
Multidetector row computed tomography angiography
References
Remy J, Arnaud A, Fardou H, Giraud R, Voisin C (1977) Treatment of hemoptysis by embolization of bronchial arteries. Radiology 122:33–37
Sancho C, Escalante E, Dominguez J, Vidal J, Lopez E, Valldeperas J, Montañá XJ (1998) Embolization of bronchial arteries of anomalous origin. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 21:300–304
Yoon W, Kim JK, Kim YH, Chung TW, Kang HK (2002) Bronchial and nonbronchial systemic artery embolization for life-threatening hemoptysis: a comprehensive review. Radiographics 22:1395–1409
Hartmann IJ, Remy-Jardin M, Menchini L, Teisseire A, Khalil C, Remy J (2007) Ectopic origin of bronchial arteries: assessment with multidetector helical CT angiography. Eur Radiol 17:1943–1953
Yu-Tang Goh P, Lin M, Teo N, En Shen Wong D (2002) Embolization for hemoptysis: a six -year review. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 25:17–25
McPherson S, Routh WD, Nath H, Keller FS (1990) Anomalous origin of bronchial arteries: potential pitfall of embolotherapy for hemoptysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol 1:86–88
Uflacker R, Kaemmerer A, Picon PD et al (1985) Bronchial artery embolization in the management of hemoptysis: technical aspects and long-term results. Radiology 157:637–644
Remy-Jardin M, Bouaziz N, Dumont P, Brillet PY, Bruzzi J, Remy J (2004) Bronchial and nonbronchial systemic arteries at multi-detector row CT angiography: comparison with conventional angiography. Radiology 233:741–749
Chun HJ, Byun JY, Yoo SS, Choi BG (2003) Added benefit of thoracic aortography after transarterial embolization in patients with hemoptysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:1577–1581
Phillips S, Ruttley MS (2000) Bronchial artery embolization: the importance of preliminary thoracic aortography. Clin Radiol 55:317–319
Khalil A, Parrot A, Nedelcu C, Fartoukh M, Marsault C, Carette MF (2008) Severe hemoptysis of pulmonary arterial origin: signs and role of multidetector row CT angiography. Chest 133:212–219
Cauldwell EM, Siekert RG, Lininger RE (1948) The bronchial arteries: an anatomic study of 150 human cadavers. Surg Gynecol Obstet 86:395–412
O’Rahilly R, Debson H, Summerfield TK (1950) Subclavian origin of bronchial arteries. Anat Rec 108:227–239
Gailloud P, Albayram S, Heck DV et al (2002) Superior bronchial artery arising from the left common carotid artery: embryology and clinical considerations. J Vasc Interv Radiol 13:851–853
Boyden EA (1970) The developing bronchial arteries in a fetus of the twelfth week. Am J Anat 129:357–368
Amrhein TJ, Kim C, Smith TP et al (2011) Bronchial artery arising from the left vertebral artery: case report and review of the literature. J Clin Imaging Sci 1:62
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, S., Sun, XW., Yu, D. et al. Endovascular Embolization of Bronchial Artery Originating from the Upper Portion of Aortic Arch in Patients with Massive Hemoptysis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 37, 94–100 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-013-0638-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-013-0638-7