Abstract
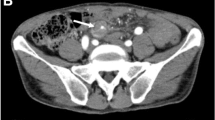
Segmental arterial mediolysis (SAM) is an uncommon self-limited disorder that can cause abdominal catastrophes through massive bleeding or bowel infarction. The former arise from arterial aneurysms, and the latter from arterial stenosis or occlusions. Although this is an acute self-limiting disease, the catastrophic consequence, originating from intra-abdominal hemorrhage (arterial dilatation, aneurysms, dissecting hematomas) or bowel infarction (arterial stenosis, arterial occlusions), is not rare. The identification of these lesions is very important in the differential diagnosis of suspected patients with complaints of abdominal pain with hemorrhage. We report computerized tomography angiography and digital subtraction angiography findings of three cases with abdominal SAM, who were treated with endovascular management due to abdominal bleeding. Angiography showed arterial dilatations, aneurysms, and occlusions of visceral arteries in all three cases, The string-of-beads appearance was present in only one case. Bleeding stopped immediately after embolization of three cases and follow-up revealed no evidence of recurrences at 23, 18, and 15 months, respectively, Arterial coil embolization is an effective treatment modality for bleeding complications of SAM. Close follow-up is recommended, primarily to ascertain the fate of the nontreated arterial lesions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Slavin RE, Gonzalez-Vitale JC (1996) Segmental mediolytic arteritis: a clinical pathologic study. Lab Invest 35:23–29
Slavin RE, Cafferty L, Cartwright J (1989) Segmental mediolytic arteritis: a clinicopathologic and ultrastructural study of two cases. Am J Surg Pathol 13:558–568
Sakano T, Morita K, Imaki M et al (1997) Segmental arterial mediolysis studied by repeated angiography. Br J Radiol 70:656–658
Michael M, Widmer U, Wildermuth S et al (2006) Segmental arterial mediolysis: cTA findings at presentation and follow-up. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187:1463–1469
Inada K, Maeda M, Ikeda T (2007) Segmental arterial mediolysis: unrecognized cases culled from cases of ruptured aneurysm of abdominal visceral arteries reported in the Japanese literature. Pathol Res Pract 203:771–778
Lie JT (1996) Systemic, cerebral, and pulmonary segmental mediolytic arteriopathy: villainous masqueraders of vasculitis. Cardiovasc Pathol 5:305–314
Slavin RE, Saeki K, Bhagavan B et al (1995) Segmental arterial mediolysis: a precursor to fibromuscular dysplasia? Mod Pathol 8:287–294
Lie JT (1992) Segmental mediolytic arteritis, not an arteritis but a variant of arterial fibromuscular dysplasia. Arch Pathol Lab Med 116:238–241
Slavin RE (in press) Segmental arterial mediolysis: course, sequelae, prognosis, and pathologic-radiologic correlation. Cardiovasc Pathol. doi:10.1016/j.carpath.2008.09.001)
Rengstorff DS, Baker EL, Wack J et al (2004) Intra-abdominal hemorrhage caused by segmental arterial mediolysis of the inferior mesenteric artery: report of a case. Dis Colon Rectum 47:769–772
Ryan JM, Suhocki PV, Smith TP (2000) Coil embolization of segmental arterial mediolysis of the hepatic artery. J Vasc Interv Radiol 11:865–868
Serter S, Oran I, Parildar M et al (2007) Fibromuscular dysplasia-related renal artery stenosis associated with aneurysm: successive endovascular therapy. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 30:297–299
Parildar M, Oran I, Memis A (2003) Embolization of visceral pseudoaneurysms with platinum coils and N-butyl cyanoacrylate. Abdom Imaging 28:36–40
Eifinger F, Fries J, Bald R et al (2004) Segmental arterial mediolysis in a preterm. J Perinatol 24:461–464
Slavin RE, Inada K (2007) Segmental arterial mediolysis with accompanying venous angiopathy: a clinical pathologic review, report of 3 new cases, and comments on the role of endothelin-1 in its pathogenesis. Int J Surg Pathol 15:121–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davran, R., Cinar, C., Parildar, M. et al. Radiological Findings and Endovascular Management of Three Cases with Segmental Arterial Mediolysis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 33, 601–606 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-009-9651-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-009-9651-2