Abstract
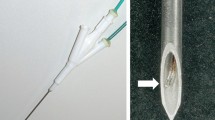
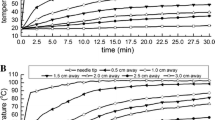
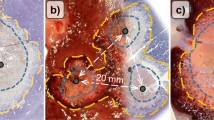
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of a newly developed perfused monopolar radiofrequency (RF) probe with an umbrella-shaped array. A perfused umbrella-shaped monopolar RF probe based on a LeVeen electrode (Boston Scientific Corp., Natick, MA, USA) with a 3-cm array diameter was developed. Five different configurations of this electrode were tested: (a) perfusion channel/endhole, (b) perfusion channel/endhole + sideholes, (c) 1 cm insulation removed at the tip, (d) 1 cm insulation removed at the tip + perfusion channel/endhole, and (e) 1 cm insulation removed at the tip + perfusion channel/endhole + sideholes. An unmodified LeVeen electrode served as a reference standard. RF ablations were performed in freshly excised bovine liver using a commercial monopolar RF system with a 200-W generator (RF 3000; Boston Scientific Corp.). Each electrode was tested 10 times applying the vendor’s recommended ablation protocol combined with the preinjection of 2 ml 0.9% saline. Volumes and shapes of the lesions were compared. Lesions generated with the original LeVeen electrode showed a mean volume of 12.74 ± 0.52 cm³. Removing parts of the insulation led to larger coagulation volumes (22.65 ± 2.12 cm³). Depending on the configuration, saline preinjection resulted in a further increase in coagulation volume (25.22 ± 3.37 to 31.28 ± 2.32 cm3). Besides lesion volume, the shape of the ablation zone was influenced by the configuration of the electrode used. We conclude that saline preinjection in combination with increasing the active tip length of the umbrella-shaped LeVeen RF probe allows the reliable ablation of larger volumes in comparison to the originally configured electrode.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ng KK, Poon RT (2005) Radiofrequency ablation for malignant liver tumor. Surg Oncol 14: 41–52
Gervais DA, Arellano RS, Mueller P (2005) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Radiol 15:960–967
Kelekis AD, Thanos L, Mylona S, et al. (2006) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors with expandable needle electrodes: current status. Eur Radiol 16:2471–2482
Pereira PL, Trübenbach J, Schmidt D (2003) Radiofrequency ablation: basic principles, techniques and challenges. Rofo 175:20–27
Goldberg SN, Dupuy DE (2001) Image-guided radiofrequency tumor ablation: challenges and opportunities—part I. J Vasc Interv Radiol 12:1021–1032
Morimoto M, Sugimori K, Shirato K, et al. (2002) Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with radiofrequency ablation: radiologic-histologic correlation during follow-up periods. Hepatology 35:1467–1475
Lee JM, Han JK, Kim SH, et al. (2005) Bipolar radiofrequency ablation using wet-cooled eletrodes: an in vitro experimental study in bovine liver. AJR 184:391–397
Tamaki K, Shimizu I, Oshio A, et al. (2004) Influence of large intrahepatic blood vessels on the gross and histological characteristics of lesions produced by radiofrequency ablation in a pig liver model. Liver Int 24:696–701
Clasen S, Schmidt D, Dietz K, et al. (2007) Bipolar radiofrequency ablation using internally cooled electrodes in ex vivo bovine liver—prediction of coagulation volume from applied energy. Invest Radiol 42:29–36
Solmi L, Nigro G, Roda E (2006) Therapeutic effectiveness of echo-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation therapy with a LeVeen needle electrode in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 12:1098–1104
Pitton MB, Herber S, Raab P, et al. (2003) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors using the LeVeen 4 cm array probe. Rofo 175:1525–1531
Goldberg SN, Ahmed M, Gazelle GS, et al. (2001) Radio-frequency thermal ablation with NaCl solution injection: effect of electrical conductivity on tissue heating and coagulationph—antom and porcine liver study. Radiology 219:157–165
Ahmed M, Lobo SM, Weinstein J, et al. (2002) Improved coagulation with saline solution pretreatment during radiofrequency tumor ablation in a canine model. J Vasc Interv Radiol 13:717–724
Giorgio A, Tarantino L, de Stefano G, et al. (2005) Complications after percutaneous saline-enhanced radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors: 3-year experience with 336 patients at a single center. AJR 184:207–211
Lubienski A, Dux M, Lubienski K, et al. (2005) Radiofrequency thermal ablation: increase in lesion diameter with continuous acetic acid infusion. CardioVasc Interv Radiol 28:789–794
Gillams AR, Lees WR. (2005) CT mapping of the distribution of saline during radiofrequency ablation with perfusion electrodes. CardioVasc Interv Radiol 28:476–480
Miao Y, Ni Y, Yu, et al. (2001) An ex vivo study on radiofrequency tumor ablation: increased lesion size by using an expandable-wet electrode. Eur Radiol 11:1841–1847
Lobo SM, Afzal KS, Kruskal JB, et al. (2004) Radiofrequency ablation: modelling the enhanced temperature response to adjuvant NaCl pre-treatment. Radiology 230:175–182
Livrhagi T, Lazzaroni S, Meloni F, et al. (2005) Risk of tumour seeding after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Surg 92:856–858
Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Dawson SL, et al. (1995) Tissue ablation with radiofrequency: effect of probe size, gauge, duration, and temperature on lesion volume. Acad Radiol 2:399–404
Goldberg SN, Hahn PF, Tanabe KK, et al. (1998) Percutaneous radiofrequency tissue ablation: Does perfusion-mediated tissue cooling limit coagulation necrosis? J Vasc Interv Radiol 9:101–111
Lee JM, Kim SH, Han JK, et al. (2005) Ex vivo experiment of saline-enhanced hepatic bipolar radiofrequency ablation with a perfused needle electrode: comparison with conventional monopolar and simultaneous monopolar modes. CardioVasc Interv Radiol 28:338–345
Clasen S, Schmidt D, Boss A, et al. (2006) Multipolar radiofrequency ablation with internally cooled electrodes: experimental study in ex vivo bovine liver with mathematic modelling. Radiology 238:881–890
Lee JM, Han JK, Kim SH, et al. (2004) Comparison of wet radiofrequency ablation with dry radiofrequency ablation and radiofrequency ablation using hypertonic saline preinjection: ex vivo bovine liver. Korean J Radiol 5:258–265
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruners, P., Pfeffer, J., Kazim, R.M. et al. A Newly Developed Perfused Umbrella Electrode for Radiofrequency Ablation: An Ex Vivo Evaluation Study in Bovine Liver. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 30, 992–998 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-007-9125-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-007-9125-3