Abstract
Purpose
To determine, by means of an ex vivo study, the effect of different NaCl concentrations on the extent of coagulation obtained during radiofrequency (RF) ablation performed using a digitally controlled perfusion device.
Method
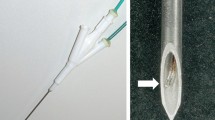
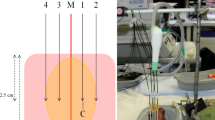
Twenty-eight RF ablations were performed with 40 W for 10 min using continuous NaCl infusion in fresh excised bovine liver. For perfusion, NaCl concentrations ranging from 0 (demineralized water) to 25% were used. Temperature, the amount of energy, and the dimensions of thermal-induced white coagulation were assessed for each ablation. These parameters were compared using the nonparametric Mann-Whitney test. Correlations were calculated according to the Spearman test.
Results
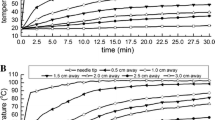
RF ablation performed with 0.9% to 25% concentrations of NaCl produced a mean volume of coagulation of 30.7 ± 3.8 cm3, with a mean short-axis diameter of 3.6 ± 0.2 cm. The mean amount of energy was 21,895 ± 1,674 W and the mean temperature was 85.4 ± 12.8°C. Volume of coagulation, short-axis diameter, and amount of energy did not differ significantly among NaCl concentrations (p > 0.5). A correlation was found between the NaCl concentration and the short-axis diameter of coagulation (r = 0.64) and between the NaCl concentration and the mean temperature (r = 0.67), but not between the NaCl concentration and volume of coagulation.
Conclusion
In an ex vivo model, continuous perfusion with high NaCl concentrations does not significantly improve the volume of thermal-induced coagulation. This may be because the use of a low-power generator cannot sufficiently exploit the potential advantage of better tissue conductivity provided by NaCl perfusion.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rhim H, Goldberg N, Dodd III GD, Solbiati L, Lim HK, Tonolini M et al. (2001) Essential techniques for successful radio-frequency thermal ablation of malignant hepatic tumors. Radiographics 21:17–39
Solbiati L, Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Ierace T, Meloni F, Dellanoce M, Cova L, Halpern EF, Gazelle GS (2001) Percutaneous radio-frequency ablation of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer: Long term results in 117 patients. Radiology 221:159–166
Curley SA, Izzo F, Elis LM, Nicolas Vauthey J, Vallone P (2000) Radio-frequency ablation of hepatocellular cancer in 110 patients with cirrhosis. Ann Surg 232:381–391
Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S, Meloni F, Solbiati L, Gazelle GS (1999) Small hepatocellular carcinoma: Treatment with radio-frequency ablation versus ethanol injection. Radiology 210:655–661
Shibata T, Iimuro Y, Yamamoto Y, Maetani Y, Ametani F, Itoh K, Konishi J (2002) Small hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison of radio-frequency ablation and percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy. Radiology 223:331–337
Lencioni RA, Allgaier HP, Cioni D, Olschewski M, Deibert P, Crocetti L, Frings H, Laubenberger J, Zuber I, Blum HE, Bartolozzi C (2003) Small hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: Randomized comparison of radio-frequency thermal ablation versus percutaneous ethanol injection. Radiology 228:235–240
Atwell TD, Charboneau JW, Que FG, Rubin J, Lewis BD, Nagorney DM, Callstrom MR, Farrell MA, Pitot HC, Hobday TJ (2005) Treatment of neuroendocrine cancer metastatic to the liver: The role of ablative techniques. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 28:409–421
Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Lazzaroni S, Meloni F, Ierace T, Solbiati L, Gazelle GS (2000)Hepatocellular carcinoma: Radiofrequency ablation of medium and large lesions. Radiology 214:761–768
de Baere T, Elias D, Dromain C, Din MG, Kuoch V, Ducreux M, Boige V, Lassau N, Marteau V, Lasser P, Roche A (2000) Radiofrequency ablation of 100 hepatic metastases with a mean follow-up of more than one year. AJR Am J Roentgenol 175:1619–1625
Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Solbiati L, Rittman WJ, Mueller PR (1996) Radiofrequency tissue ablation: Increased lesion diameter with a perfusion electrode. Acad Radiol 3:636–644
Miao Y, Ni Y, Mulier S, Wang K, Hoey MF, Mulier P, Penninckx F, Yu J, De Scheerder I, Baert AL, Marchal G (1997) Ex vivo experiment on radiofrequency liver ablation with saline infusion through a screw-tip canulated electrode. J Surg Res 71:19–24
Goldberg SN, Ahmed M, Gazelle GS, Kruskal JB, Huertas JC, Halpern EF, Oliver BS, Lenkinski RE (2001) Radio-frequency thermal ablation with NaCl solution injection: Effect of electrical conductivity on the tissue heating and coagulation-phantom and porcine liver study. Radiology 219:157–165
Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Monti F, Bizzini A, Lazzaroni S, Meloni F, Pellicano S, Solbiati L, Gazelle GS (1997) Saline-enhanced radio-frequency tissue ablation in the treatment of liver metastases. Radiology 202:205–210
Ahmed M, Lobo SM, Weinstein J, Kruskal JB, Gazelle GS, Halpern EF, Afzal SK, Lenkinski RE, Goldberg SN (2002) Improved coagulation with saline solution pretreatment during radiofrequency tumor ablation in a canine model. J Vasc Interv Radiol 13:717–724
Miao Y, Ni Y, Yu J, Zhang H, Baert A, Marchal G (2001) An ex vivo study on radiofrequency tissue ablation: Increased lesion size by using an “expandable-wet” electrode. Eur Radiol 11:1841–1847
Kettenbach J, Kostler W, Rucklinger E, Gustorff B, Hupfl M, Wolf F, Peer K, Weigner M, Lammer J, Muller W, Goldberg SN (2003) Percutaneous saline-enhanced radiofrequency ablation of unresectable hepatic tumors: guidelines Initial experience in 26 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:1537–1545
Solazzo SA, Liu Z, Lobo SM, Ahmed M, Hines-Peralta AU, Lenkinski RE, Goldberg SN (2005) Radiofrequency ablation: Importance of background tissue electrical conductivity. An agar phantom and computer modeling study. Radiology 236:495–502
Burdio F, Burdio JM, Navarro A, Ros P, Guemes A, Sousa R, Tejero E, Lozano R (2004) Electric influence of NaCl concentration into the tissue in radiofrequency ablation. Radiology 232:932
Burdio F, Guemes A, Burdio JM, Navarro A, Sousa R, Castiella T, Cruz I, Burzaco O, Lozano R (2003) Bipolar saline-enhanced electrode for radiofrequency ablation: Results of experimental study of in vivo porcine liver. Radiology 229:447–456
Lee JM, Kim SH, Han JK, Sohn KL, Choi BI (2005) Ex vivo experiment of saline-enhanced hepatic bipolar radiofrequency ablation with a perfused needle electrode: Comparison with conventional monopolar and simultaneous monopolar modes. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 28:338–345
Schmidt D, Trübenbach J, Brieger J, Koenig C, Putzhammer H, Duda SH, Claussen CD, Pereira PL (2003) Automated saline-enhanced radiofrequency thermal ablation: Initial results in ex vivo bovine livers. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180:163–165
Gazelle GS, Goldberg SN, Solbiati L, Livraghi T (2000) Tumor ablation with radio-frequency energy. Radiology 217:633–646
Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Mueller PR (2000) Thermal ablation therapy for focal malignancy: A unified approach to understand principles, techniques, and diagnosis imaging guidance. AJR Am J Roentgenol 174:323–331
Mulier S, Miao Y, Mulier P, Dupas B, Pereira P, de Baere T, Lencioni R, Leveillee R, Marchal G, Michel L, Ni Y (2005) Electrodes and multiple electrode systems for radiofrequency ablation: A proposal for updated terminology. Eur Radiol 15:798–808
Curley SA, Izzo F, Delrio P, Ellis LM, Granchi J, Vallone P, Fiore F, Pignata S, Daniele B, Cremona F (1999) Radiofrequency ablation of unresectable primary and metastatic hepatic malignancies: Guidelines. Results in 123 patients. Ann Surg 230:1–8
Solbiati L, Goldberg SN, Ierace T, Livraghi T, Sironi S, Gazelle GS (1997) Hepatic metastases: Percutaneous radio-frequency ablation with cooled-tip electrodes. Radiology 205:367–374
Miao Y, Ni Y, Yu J, Marchal G (2000) A comparative study on validation of a novel cooled-wet electrode for radiofrequency liver ablation. Invest Radiol 35:438–444
Honda N, Guo Q, Ushida H, Ohishi H, Hiasa Y (1994) Percutaneous hot saline injection therapy for hepatic tumors: An alternative to percutaneous ethanol injection therapy. Radiology 190:53–57
Liu Z, Lobo SM, Humphries S, Horkan C, Solazzo SA, Hines-Peralta AU, Lenkinski RE, Goldberg SN (2005) Radiofrequency tumor ablation: Insight into improved efficacy using computer modeling. AJR Am J Roentgenol 184:1347–1352
Lobo SM, Afzal KS, Ahmed M, Kruskal JB, Lenkinski RE, Goldberg SN (2004) Radiofrequency ablation: Modeling the enhanced temperature response to adjuvant NaCl pretreatment. Radiology 230:175–182
Pereira PL, Trubenbach J, Schenk M, Subke J, Kroeber S, Schaefer I, Remy CT, Schmidt D, Brieger J, Claussen CD (2004) Radiofrequency ablation: In vivo comparison of four commercially available devices in pig livers. Radiology 232:482–489
Gillams AR, Lees WR (2005) CT mapping of the distribution of saline during radiofrequency ablation with perfusion electrodes. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 28:476–480
Boehm T, Malich A, Goldberg SN, Reichenbach JR, Hilger I, Hauff P, Reinhardt M, Fleck M, Kaiser WA (2002) Radio-frequency tumor ablation: Guidelines. Internally cooled electrode versus saline enhanced technique in an aggressive rabbit tumor model. Radiology 222:805–813
Pereira PL, Schenk M, Truebenbach J, Brieger J, Kroeber S, Schmidt D (2002) Liver injury after radiofrequency ablation under physiological perfusion in a porcine model. Radiology 225(P):638–639
Stephen H, Stephen T (1963) Solubilities of inorganic and organic compounds, vol 1, part 1. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 108–109
Disclosure
P.L.P. was supported in part through research collaboration with Berchtold and funds from MITT/BMBF project 16SV 1352.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aubé, C., Schmidt, D., Brieger, J. et al. Influence of NaCl Concentrations on Coagulation, Temperature, and Electrical Conductivity Using a Perfusion Radiofrequency Ablation System: An Ex Vivo Experimental Study. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 30, 92–97 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-006-0091-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-006-0091-y