Abstract
Background
The use of neuromuscular blocking agents may affect intraoperative neuromonitoring during thyroid surgery. A selective neuromuscular recovery protocol was evaluated in a retrospective cohort study during human thyroid neural monitoring surgery.
Methods
One hundred and twenty-five consecutive patients undergoing thyroidectomy with intraoperative neuromonitoring followed a selective neuromuscular block recovery protocol—single intubating dose of rocuronium followed by sugammadex if needed at the first vagal stimulation (V1).
Results
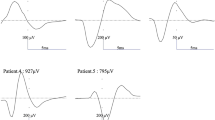
Data from 120 of 125 patients could be analysed. Fifteen (12.5%) patients needed sugammadex reversal to obtain an EMG response at the first vagal stimulation (V1). In the remaining 105 patients, spontaneous recovery of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular block was sufficient for a successful first vagal stimulation (V1).
Conclusions
In patients undergoing thyroid surgery, routine reversal of rocuronium block with sugammadex is not mandatory for reliable intraoperative neuromonitoring. A selective neuromuscular block recovery approach may be a valuable and more cost-efficient alternative to routine reversal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Combes X, Andriamifidy L, Dufresne E et al (2007) Comparison of two induction regimens using or not using muscle relaxant: impact on postoperative upper airway discomfort. Br J Anaesth 99:276–281. doi:10.1093/bja/aem147
Marusch F, Hussock J, Haring G et al (2005) Influence of muscle relaxation on neuromonitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve during thyroid surgery. Br J Anaesth 94:596–600. doi:10.1093/bja/aei110
Dralle H, Sekulla C, Lorenz K et al (2008) Intraoperative monitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve in thyroid surgery. World J Surg 32:1358–1366. doi:10.1007/s00268-008-9483-2
Wu C-W, Wang M-H, Chen C-C et al (2015) Loss of signal in recurrent nerve neuromonitoring: causes and management. Gland Surg 4:19–26. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2227-684X.2014.12.03
Lu I-C, Wu C-W, Chang P-Y et al (2016) Reversal of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade by sugammadex allows for optimization of neural monitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Laryngoscope 126:1014–1019. doi:10.1002/lary.25577
Brunaud L, Fuchs-Buder T (2016) In response to Reversal of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade by sugammadex allows for optimization of neural monitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Laryngoscope. doi:10.1002/lary.25990
Fuchs-Buder T, Claudius C, Skovgaard LT et al (2007) Good clinical research practice in pharmacodynamic studies of neuromuscular blocking agents II: the Stockholm revision. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 51:789–808. doi:10.1111/j.1399-6576.2007.01352.x
Blobner M, Eriksson LI, Scholz J et al (2010) Reversal of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade with sugammadex compared with neostigmine during sevoflurane anaesthesia: results of a randomised, controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol 27(10):874–881
Meyhoff CS, Lund J, Jenstrup MT et al (2009) Should dosing of rocuronium in obese patients be based on ideal or corrected body weight? Anesth Analg 109:787–792. doi:10.1213/ane.0b013e3181b0826a
Fontenot TE, Randolph GW, Setton TE et al (2015) Does intraoperative nerve monitoring reliably aid in staging of total thyroidectomies? Laryngoscope 125:2232–2235. doi:10.1002/lary.25133
Lu I-C, Chu K-S, Tsai C-J et al (2008) Optimal depth of NIM EMG endotracheal tube for intraoperative neuromonitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve during thyroidectomy. World J Surg 32:1935–1939. doi:10.1007/s00268-008-9549-1
Lu I-C, Tsai C-J, Wu C-W et al (2011) A comparative study between 1 and 2 effective doses of rocuronium for intraoperative neuromonitoring during thyroid surgery. Surgery 149:543–548. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2010.11.006
Lundstrøm LH, Møller AM, Rosenstock C et al (2009) Avoidance of neuromuscular blocking agents may increase the risk of difficult tracheal intubation: a cohort study of 103,812 consecutive adult patients recorded in the Danish Anaesthesia Database. Br J Anaesth 103:283–290. doi:10.1093/bja/aep124
Mencke T, Echternach M, Kleinschmidt S et al (2003) Laryngeal morbidity and quality of tracheal intubation: a randomized controlled trial. Anesthesiology 98:1049–1056
Dell-Kuster S, Levano S, Burkhart CS et al (2015) Predictors of the variability in neuromuscular block duration following succinylcholine: a prospective, observational study. Eur J Anaesthesiol 32:687–696. doi:10.1097/EJA.0000000000000308
Schreiber J-U, Lysakowski C, Fuchs-Buder T, Tramèr MR (2005) Prevention of succinylcholine-induced fasciculation and myalgia: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Anesthesiology 103:877–884
Fuchs-Buder T, Schmartz D (2016) The never ending story or the search for a nondepolarising alternative to succinylcholine. Eur J Anaesthesiol 30:583–584. doi:10.1097/EJA.0b013e32836315c3
Fuchs-Buder T, Meistelman C, Raft J (2013) Sugammadex: clinical development and practical use. Korean J Anesthesiol 65:495–500. doi:10.4097/kjae.2013.65.6.495
Esteves S (2015) Can residual paralysis be avoided?: A critical appraisal of the use of sugammadex. Eur J Anaesthesiol 32:663–665. doi:10.1097/EJA.0000000000000294
Fuchs-Buder T, Schreiber J-U, Meistelman C (2009) Monitoring neuromuscular block: an update. Anaesthesia 64(Suppl 1):82–89. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2044.2008.05874.x
Meistelman C, Plaud B, Donati F (1992) Rocuronium (ORG 9426) neuromuscular blockade at the adductor muscles of the larynx and adductor pollicis in humans. Can J Anaesth (J Can d’anesthésie) 39:665–669. doi:10.1007/BF03008227
Schlaich N, Mertzlufft F, Soltész S, Fuchs-Buder T (2000) Remifentanil and propofol without muscle relaxants or with different doses of rocuronium for tracheal intubation in outpatient anaesthesia. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 44:720–726
Funding
This work was funded only by departmental resources.
Authors’ contributions
Denis Schmartz, Laurent Brunaud and Thomas Fuchs-Buder conceived and designed the study; Ombeline Empis de Vendin and Laurent Brunaud acquired the data; Ombeline Empis de Vendin, Denis Schmartz, Laurent Brunaud and Thomas Fuchs-Buder analysed and interpreted the data; Ombeline Empis de Vendin, Denis Schmartz, Laurent Brunaud and Thomas Fuchs-Buder drafted the manuscript; Ombeline Empis de Vendin, Denis Schmartz, Laurent Brunaud and Thomas Fuchs-Buder critically revised the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Ombeline Empis de Vendin, Denis Schmartz and Laurent Brunaud declare no conflict of interest. Thomas Fuchs-Buder received lecture honoraria from MSD, France.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Empis de Vendin, O., Schmartz, D., Brunaud, L. et al. Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Monitoring and Rocuronium: A Selective Sugammadex Reversal Protocol. World J Surg 41, 2298–2303 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-017-4004-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-017-4004-9