Abstract
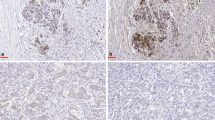
Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) is a non-receptor, cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase that is involved in the regulation of cellular signaling, migration, apoptosis, and cell cycle progression. Previous reports have shown that FAK is expressed in various kinds of cancer tissues and cancer cell lines; however, no information is available about human pancreatic carcinoma specimens. Tissue such specimens were obtained from 50 patients who underwent pancreatic resection for pancreatic invasive ductal carcinoma at our institute from 1996 to 2002. Immunohistochemical analysis of FAK was performed in the resected specimens. Focal adhesion kinase expression in seven human pancreatic cancer cell lines was analyzed by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis and Western blot analysis. Focal adhesion kinase expression was detected in 24 of 50 cases (48%). There was a statistically significant correlation between FAK expression and tumor size (P = 0.004), although FAK expression did not significantly correlate with other factors such as tumor histological grade, lymph node metastasis, distant metastasis, histological stage, and overall survival. Reverse transcription PCR analysis and Western blot analysis showed that FAK was expressed in all seven pancreatic cancer cell lines. Focal adhesion kinase expression was not directly related to clinicopathological factors except tumor size in pancreatic carcinoma. Focal adhesion kinase expression may not be a prognostic marker for pancreatic cancer patients.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schaller MD, Borgman CA, Cobb BS, et al. pp125FAK a structurally distinctive protein-tyrosine kinase associated with focal adhesions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992;89:5192–5196
Kornberg L, Earp HS, Parsons JT, et al. Cell adhesion or integrin clustering increases phosphorylation of a focal adhesion-associated tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem 1992;267:23439–23442
Gabarra-Niecko V, Schaller MD, Dunty JM. FAK regulates biological processes important for the pathogenesis of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003;22:359–374
Sieg DJ, Hauck CR, Ilic D, et al. FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration. Nat Cell Biol 2000;2:249–256
Cance WG, Harris JE, Iacocca MV, et al. Immunohistochemical analyses of focal adhesion kinase expression in benign and malignant human breast and colon tissues: correlation with preinvasive and invasive phenotypes. Clin Cancer Res 2000;6:2417–2423
Owens LV, Xu L, Dent GA, et al. Focal adhesion kinase as a marker of invasive potential in differentiated human thyroid cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 1996;3:100–105
Agochiya M, Brunton VG, Owens DW, et al. Increased dosage and amplification of the focal adhesion kinase gene in human cancer cells. Oncogene 1999;18:5646–5653
Judson PL, He X, Cance WG, et al. Overexpression of focal adhesion kinase, a protein tyrosine kinase, in ovarian carcinoma. Cancer 1999;86:1551–1556
Miyazaki T, Kato H, Nakajima M, et al. FAK overexpression is correlated with tumour invasiveness and lymph node metastasis in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 2003;89:140–145
Mori T, Doi R, Koizumi M, et al. CXCR4 antagonist inhibits stromal cell-derived factor 1-induced migration and invasion of human pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 2004;3:29–37
Schaller MD, Hildebrand JD, Shannon JD, et al. Autophosphorylation of the focal adhesion kinase, pp125FAK, directs SH2-dependent binding of pp60src. Mol Cell Biol 1994;14:1680–1688
Chen HC, Guan JL. Association of focal adhesion kinase with its potential substrate phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994;91:10148–10152
Zhang X, Chattopadhyay A, Ji QS, et al. Focal adhesion kinase promotes phospholipase C-gamma1 activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999;96:9021–9026
Han DC, Guan JL. Association of focal adhesion kinase with Grb7 and its role in cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:24425–24430
Itoh S, Maeda T, Shimada M, et al. Role of expression of focal adhesion kinase in progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:2812–2817
Su JM, Gui L, Zhou YP, et al. Expression of focal adhesion kinase and alpha5 and beta1 integrins in carcinomas and its clinical significance. World J Gastroenterol 2002;8:613–618
Kornberg LJ. Focal adhesion kinase expression in oral cancers. Head Neck 1998;20:634–639
Wang D, Grammer JR, Cobbs CS, et al. p125 Focal adhesion kinase promotes malignant astrocytoma cell proliferation in vivo. J Cell Sci 2000;113(Pt 23):4221–4230
Gabarra-Niecko V, Keely PJ, Schaller MD. Characterization of an activated mutant of focal adhesion kinase: ‘SuperFAK’. Biochem J 2002;365(Pt 3):591–603
Aguirre Ghiso JA. Inhibition of FAK signaling activated by urokinase receptor induces dormancy in human carcinoma cells in vivo. Oncogene 2002;21:2513–2524
Trede M, Schwall G, Saeger HD. Survival after pancreatoduodenectomy. 118 consecutive resections without an operative mortality. Ann Surg 1990;211:447–458
Bakkevold KE, Arnesjo B, Dahl O, et al. Adjuvant combination chemotherapy (AMF) following radical resection of carcinoma of the pancreas and papilla of Vater—results of a controlled, prospective, randomised multicentre study. Eur J Cancer 1993;29A:698–703
Sohn TA, Campbell KA, Pitt HA, et al. Quality of life and long-term survival after surgery for chronic pancreatitis. J Gastrointest Surg 2000;4:355–364; discussion 364–355
Millikan KW, Deziel DJ, Silverstein JC, et al. Prognostic factors associated with resectable adenocarcinoma of the head of the pancreas. Am Surg 1999;65:618–623; discussion 623–614
Meyer W, Jurowich C, Reichel M, et al. Pathomorphological and histological prognostic factors in curatively resected ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Surg Today 2000;30:582–587
Duxbury MS, Ito H, Benoit E, et al. RNA interference targeting focal adhesion kinase enhances pancreatic adenocarcinoma gemcitabine chemosensitivity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2003;311:786–792
Duxbury MS, Ito H, Zinner MJ, et al. Focal adhesion kinase gene silencing promotes anoikis and suppresses metastasis of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Surgery 2004;135:555–562
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants-in-aid 17390364 and 17659409 from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Furuyama, K., Doi, R., Mori, T. et al. Clinical Significance of Focal Adhesion Kinase in Resectable Pancreatic Cancer. World J. Surg. 30, 219–226 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-0165-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-005-0165-z