Abstract
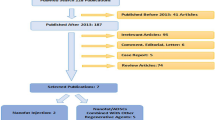
Facial skin nonsurgical resurfacing modalities, including laser, chemical peeling, and microneedling, have become common due to increasing public concern about skin aging. The potential effect of stem cell conditioned medium (CM) for antiaging has been reported in recent years, and such medium may be able to improve the efficacy of resurfacing modalities. This study investigated the efficacy of topical CM combined with resurfacing in comparison with resurfacing alone. We searched the PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases for randomized controlled trials (RCTs). We used the Cochrane risk-of-bias tool (version 2) to assess the risk of bias of the included studies and Review Manager (version 5.4) for data analysis. Means and standard deviations of outcomes, namely wrinkle, pigmentation, pore, and overall improvement, were extracted. After screening, we included five RCTs in the analysis, four of which were quantitatively analyzed. The result revealed that stem cell CM significantly reduced wrinkles (P = 0.0006), pigmentation (P = 0.004), and pores (P = 0.01) and improved overall skin condition (P < 0.0001). In summary, we suggest that stem cell CM is a safe treatment that can enhance the efficacy of facial skin nonsurgical resurfacing modalities.
Level of Evidence III This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee H, Hong Y, Kim M (2021) Structural and functional changes and possible molecular mechanisms in aged skin. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212489
Kohl E, Steinbauer J, Landthaler M, Szeimies RM (2011) Skin ageing. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 25(8):873–884. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2010.03963.x
Devgan L, Singh P, Durairaj K (2019) Minimally invasive facial cosmetic procedures. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 52(3):443–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otc.2019.02.013
Bhargava S, Goldust M, Singer H, Negbenebor N, Kroumpouzos G (2022) Evaluating resurfacing modalities in aesthetics. Clin Dermatol 40(3):274–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.01.019
Goldberg DJ (2003) Lasers for facial rejuvenation. Am J Clin Dermatol 4(4):225–234. https://doi.org/10.2165/00128071-200304040-00002
Lee JC, Daniels MA, Roth MZ (2016) Mesotherapy, microneedling, and chemical peels. Clin Plast Surg 43(3):583–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cps.2016.03.004
Lee KC, Wambier CG, Soon SL, Sterling JB, Landau M, Rullan P, Brody HJ (2019) Basic chemical peeling: superficial and medium-depth peels. J Am Acad Dermatol 81(2):313–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2018.10.079
Lo KC, Chuang WW, Lamb DJ (2003) Stem cell research: the facts, the myths and the promises. J Urol 170(6 Pt 1):2453–2458. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000087170.97532.ff
Damayanti RH, Rusdiana T, Wathoni N (2021) Mesenchymal stem cell secretome for dermatology application: a review. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 14:1401–1412. https://doi.org/10.2147/ccid.S331044
Park SR, Kim JW, Jun HS, Roh JY, Lee HY, Hong IS (2018) Stem cell secretome and its effect on cellular mechanisms relevant to wound healing. Mol Ther 26(2):606–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.09.023
Robert AW, Azevedo Gomes F, Rode MP, Marques da Silva M, Veleirinho M, Maraschin M, Stimamiglio MA (2019) The skin regeneration potential of a pro-angiogenic secretome from human skin-derived multipotent stromal cells. J Tissue Eng 10:2041731419833391. https://doi.org/10.1177/2041731419833391
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Moher D (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG, Blencowe NS, Boutron I, Higgins JPT (2019) RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 366:l4898. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l4898
Seo KY, Kim DH, Lee SE, Yoon MS, Lee HJ (2013) Skin rejuvenation by microneedle fractional radiofrequency and a human stem cell conditioned medium in Asian skin: a randomized controlled investigator blinded split-face study. J Cosmet Laser Ther 15(1):25–33. https://doi.org/10.3109/14764172.2012.748201
Zhou BR, Zhang T, Bin Jameel AA, Xu Y, Xu Y, Guo SL, Luo D (2016) The efficacy of conditioned media of adipose-derived stem cells combined with ablative carbon dioxide fractional resurfacing for atrophic acne scars and skin rejuvenation. J Cosmet Laser Ther 18(3):138–148. https://doi.org/10.3109/14764172.2015.1114638
El-Domyati M, Moftah NH, Nasif GA, Ameen SW, Ibrahim MR, Ragaie MH (2020) Facial rejuvenation using stem cell conditioned media combined with skin needling: A split-face comparative study. J Cosmet Dermatol 19(9):2404–2410. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.13594
Hoss E, Kollipara R, Alhaddad M, Boen M, Goldman MP (2020) Red deer umbilical cord-derived stem cell conditioned media combined with ablative resurfacing of the face. J Drugs Dermatol 19(11):1044–1048. https://doi.org/10.36849/jdd.2020.5246
Lee HJ, Lee EG, Kang S, Sung JH, Chung HM, Kim DH (2014) Efficacy of microneedling plus human stem cell conditioned medium for skin rejuvenation: a randomized, controlled, blinded split-face study. Ann Dermatol 26(5):584–591. https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2014.26.5.584
Prakoeswa CRS, Pratiwi FD, Herwanto N, Citrashanty I, Indramaya DM, Murtiastutik D, Rantam FA (2019) The effects of amniotic membrane stem cell-conditioned medium on photoaging. J Dermatolog Treat 30(5):478–482. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2018.1530438
Wang X, Shu X, Huo W, Zou L, Li L (2018) Efficacy of protein extracts from medium of Adipose-derived stem cells via microneedles on Asian skin. J Cosmet Laser Ther 20(4):237–244. https://doi.org/10.1080/14764172.2017.1400171
Badran KW, Nabili V (2018) Lasers, microneedling, and platelet-rich plasma for skin rejuvenation and repair. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am 26(4):455–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsc.2018.06.007
Kim WS, Park BS, Park SH, Kim HK, Sung JH (2009) Antiwrinkle effect of adipose-derived stem cell: activation of dermal fibroblast by secretory factors. J Dermatol Sci 53(2):96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2008.08.007
Kim WS, Park BS, Kim HK, Park JS, Kim KJ, Choi JS, Sung JH (2008) Evidence supporting antioxidant action of adipose-derived stem cells: protection of human dermal fibroblasts from oxidative stress. J Dermatol Sci 49(2):133–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdermsci.2007.08.004
Liu Q, Luo Z, He S, Peng X, Xiong S, Wang Y, Gao BZ (2013) Conditioned serum-free medium from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells has anti-photoaging properties. Biotechnol Lett 35(10):1707–1714. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1242-2
Abdel-Maguid EM, Awad SM, Hassan YS, El-Mokhtar MA, El-Deek HE, Mekkawy MM (2021) Efficacy of stem cell-conditioned medium vs. platelet-rich plasma as an adjuvant to ablative fractional CO(2) laser resurfacing for atrophic post-acne scars: a split-face clinical trial. J Dermatolog Treat 32(2):242–249. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2019.1630701
El-Domyati M, Moftah NH, Nasif GA, Ragaie MH, Ibrahim MR, Ameen SW (2019) Amniotic fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cell products combined with microneedling for acne scars: a split-face clinical, histological, and histometric study. J Cosmet Dermatol. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.13039
Putri WE, Endaryanto A, Rantam FA, Prakoeswa CRS (2021) Mesenchymal stem cells-conditioned medium (Secretome) in skin aging: a systematic review. Int J Pharm Res 13(2):613–635. https://doi.org/10.31838/ijpr/2021.13.02.020
Montero-Vilchez T, Sierra-Sánchez Á, Sanchez-Diaz M, Quiñones-Vico MI, Sanabria-de-la-Torre R, Martinez-Lopez A, Arias-Santiago S (2021) Mesenchymal stromal cell-conditioned medium for skin diseases: a systematic review. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:654210. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.654210
Sohn SJ, Yu JM, Lee EY, Nam YJ, Kim J, Kang S, Kang S (2018) Anti-aging properties of conditioned media of epidermal progenitor cells derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 8(2):229–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13555-018-0229-2
Kim YJ, Seo DH, Lee SH, Lee SH, An GH, Ahn HJ, Kang KS (2018) Conditioned media from human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells stimulate rejuvenation function in human skin. Biochem Biophys Rep 16:96–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrep.2018.10.007
Vashi NA, Wirya SA, Inyang M, Kundu RV (2017) Facial hyperpigmentation in skin of color: special considerations and treatment. Am J Clin Dermatol 18(2):215–230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-016-0239-8
Solano F (2020) Photoprotection and skin pigmentation: melanin-related molecules and some other new agents obtained from natural sources. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071537
Kim WS, Park SH, Ahn SJ, Kim HK, Park JS, Lee GY, Sung JH (2008) Whitening effect of adipose-derived stem cells: a critical role of TGF-beta 1. Biol Pharm Bull 31(4):606–610. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.31.606
Kim DW, Jeon BJ, Hwang NH, Kim MS, Park SH, Dhong ES, Lee BI (2014) Adipose-derived stem cells inhibit epidermal melanocytes through an interleukin-6-mediated mechanism. Plast Reconstr Surg 134(3):470–480. https://doi.org/10.1097/prs.0000000000000431
Xu Y, Guo S, Wei C, Li H, Chen L, Yin C, Zhang C (2016) The Comparison of adipose stem cell and placental stem cell in secretion characteristics and in facial antiaging. Stem Cells Int 2016:7315830. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7315830
Kim BY, Choi JW, Park KC, Youn SW (2013) Sebum, acne, skin elasticity, and gender difference — which is the major influencing factor for facial pores? Skin Res Technol 19(1):e45-53. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0846.2011.00605.x
Lee SJ, Seok J, Jeong SY, Park KY, Li K, Seo SJ (2016) Facial pores: definition, causes, and treatment options. Dermatol Surg 42(3):277–285. https://doi.org/10.1097/dss.0000000000000657
Park CS, Park JH, Kim CR, Lee JH (2021) Objective analysis of volume restoration in atrophic acne scars and skin pores: a split study using human stem cell-conditioned media. J Dermatolog Treat 32(1):73–77. https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2019.1628915
Lee SH (2020) Effects of human endothelial progenitor cell and its conditioned medium on oocyte development and subsequent embryo development. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21217983
Kim CH, Kim DH, Oh SH, Song SY (2015) Human embryonic stem cell-derived endothelial precursor cell conditioned medium reduces the thickness of the capsule around silicone implants in rats. Ann Plast Surg 75(3):348–352. https://doi.org/10.1097/sap.0000000000000123
Joseph A, Baiju I, Bhat IA, Pandey S, Bharti M, Verma M, Taru Sharma G (2020) Mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned media: a novel alternative of stem cell therapy for quality wound healing. J Cell Physiol 235(7–8):5555–5569. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29486
Bhardwaj R, Ansari MM, Parmar MS, Chandra V, Sharma GT (2016) Stem cell conditioned media contains important growth factors and improves in vitro buffalo embryo production. Anim Biotechnol 27(2):118–125. https://doi.org/10.1080/10495398.2015.1118383
Vizoso FJ, Eiro N, Cid S, Schneider J, Perez-Fernandez R (2017) Mesenchymal stem cell secretome: toward cell-free therapeutic strategies in regenerative medicine. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091852
Takeuchi R, Katagiri W, Endo S, Kobayashi T (2019) Exosomes from conditioned media of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote bone regeneration by enhancing angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 14(11):e0225472. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0225472
He C, Zheng S, Luo Y, Wang B (2018) Exosome theranostics: biology and translational medicine. Theranostics 8(1):237–255. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.21945
Xunian Z, Kalluri R (2020) Biology and therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Cancer Sci 111(9):3100–3110. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14563
Zhang J, Li S, Li L, Li M, Guo C, Yao J, Mi S (2015) Exosome and exosomal microRNA: trafficking, sorting, and function. Genomics Proteomics Bioinform 13(1):17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2015.02.001
Hu S, Li Z, Cores J, Huang K, Su T, Dinh PU, Cheng K (2019) Needle-free injection of exosomes derived from human dermal fibroblast spheroids ameliorates skin photoaging. ACS Nano 13(10):11273–11282. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b04384
Ha DH, Kim SD, Lee J, Kwon HH, Park GH, Yang SH, Yi YW (2020) Toxicological evaluation of exosomes derived from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 115:104686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2020.104686
Xiong M, Zhang Q, Hu W, Zhao C, Lv W, Yi Y, Wu M (2020) Exosomes from adipose-derived stem cells: the emerging roles and applications in tissue regeneration of plastic and cosmetic surgery. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:574223. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.574223
Acknowledgments
This manuscript was edited by Wallace Academic Editing. This study was partially supported by Taipei Municipal Wanfang Hospital (managed by Taipei Medical University) (grant number: 111TMU-WFH-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Statement of Human and Animal Rights, or Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, TJ., Huang, YL., Kang, YN. et al. Effectiveness of Topical Conditioned Medium of Stem Cells in Facial Skin Nonsurgical Resurfacing Modalities for Antiaging: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Aesth Plast Surg 47, 799–807 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-03168-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-022-03168-z