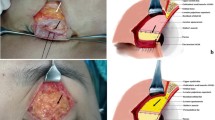
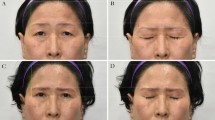
Abstract
Background
Upper eyelid aging results from comprehensive changes, and studies have failed to comprehensively address these changes.
Objectives
This study proposes a comprehensive approach to the surgical treatment of aging upper eyelids.
Methods
Data of 116 patients with aging upper eyelids were analyzed. Each eye was scored on upper eyelid laxity, degree of blepharoptosis, and upper eyelid socket depression at preoperation and 6 months after surgery. Based on average scores of both eyes, three degrees of aging were considered: mild, moderate, and severe. All patients underwent comprehensive surgical treatments. Depending on its condition, loose skin was appropriately removed, and the levator palpebrae superioris (LPS) was corrected in patients with degenerative ptosis. Meanwhile orbital septum fat was released or periumbilical fat mass was used as a filler to correct upper eyelid socket depression. All cases were summarized based on a classification and grading system. Scores were reassessed, and satisfaction survey was conducted after 6 months follow-up.
Results
The preoperative and postoperative scores of the three groups were significantly different (p < 0.05), and the difference in preoperative and postoperative scores between the three groups was also statistically significant (p < 0.05). The severe aging group had the greatest difference in score. Aside from 8 patients requiring reoperation, patients reported satisfied results after the 6 month follow-up.
Conclusions
Comprehensive surgical treatment for patients with different grades of upper eyelid aging can achieve a satisfactory effect of upper eyelid rejuvenation.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hicks K, Sclafani AP, Thomas JR (2019) Evolution of blepharoplasty. Facial Plast Surg 35:340–352
Parikh S, Most SP (2010) Rejuvenation of the upper eyelid. Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 18:427–433
Kashkouli MB, Abdolalizadeh P, Abolfathzadeh N, Sianati H, Sharepour M, Hadi Y (2017) Periorbital facial rejuvenation; applied anatomy and pre-operative assessment. J Curr Ophthalmol 29:154–168
Gulbitti HA, Bouman TK, Marten TJ, van der Lei B (2018) The orbital oval balance principle: a morphometric clinical analysis. Plast Reconstr Surg 142:451e-e461
Larsson JC, Chen TY, Lao WW (2019) Integrating fat graft with blepharoplasty to rejuvenate the Asian periorbita. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 7:e2365
Shirado M (2012) Dyslipidaemia and age-related involutional blepharoptosis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 65:e146–e150
Xiao Z, Zhang M (2010) Trapezoid excision upper blepharoplasty for Chinese women with severe laxity of pretarsal skin. Aesthetic Plast Surg 34:123–125
Lin TM, Lin TY, Chou CK, Lai CS, Lin SD (2014) Application of microautologous fat transplantation in the correction of sunken upper eyelid. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open 2:e259
Holmstrom H, Filip C (2002) Aponeurotic repair of involutional blepharoptosis. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 36:160–165
Jacobs LC, Liu F, Bleyen I, Gunn DA, Hofman A, Klaver CC, Uitterlinden AG, Neumann HA, Bataille V, Spector TD, Kayser M, Nijsten T (2014) Intrinsic and extrinsic risk factors for sagging eyelids. JAMA Dermatol 150:836–843
Branham G, Holds JB (2015) Brow/Upper lid anatomy, aging and aesthetic analysis. Facial Plast Surg Clin N Am 23:117–127
Leal Silva HG (2016) Facial laxity rating scale validation study. Dermatol Surg 42:1370–1379
Park S, Kim B, Shin Y (2011) Correction of superior sulcus deformity with orbital fat anatomic repositioning and fat graft applied to retro-orbicularis oculi fat for Asian eyelids. Aesthetic Plast Surg 35:162–170
Zuo L, Wang XX, Huang XY, Zhang JL, Du YY (2017) A modified levator resection technique involving retention of the levator palpebrae superioris muscle suspension system for treatment of congenital ptosis. Aesthetic Plast Surg 41:856–862
Pottier F, El-Shazly NZ, El-Shazly AE (2008) Aging of orbicularis oculi: anatomophysiologic consideration in upper blepharoplasty. Arch Facial Plast Surg 10:346–349
Zhang KR, Chon BH, Hwang CJ, Jellema LM, Perry JD (2019) Comparison of orbital volume in young versus senescent human skulls. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 36(2):139–143
Lai HT, Weng SF, Chang CH, Huang SH, Lee SS, Chang KP, Lai CS (2017) Analysis of levator function and ptosis severity in involutional blepharoptosis. Ann Plast Surg 78:S58–S60
Kim CY, Lee SY (2015) Distinct features in Koreans with involutional blepharoptosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 135:1693–1699
Lieberman DM, Quatela VC (2013) Upper lid blepharoplasty: a current perspective. Clin Plast Surg 40:157–165
Park J, Choi B, Baek S (2018) The effect of upper aging blepharoplasty on upper and lower eyelid position. J Craniofac Surg 29:747–750
Hsu AK, Jen A (2012) Estimation of skin removal in aging Asian blepharoplasty. Laryngoscope 122:762–766
Lin TM, Lin TY, Huang YH, Hsieh TY, Chou CK, Takahashi H, Lai CS, Lin SD (2016) Fat grafting for recontouring sunken upper eyelids with multiple folds in asians-novel mechanism for neoformation of double eyelid crease. Ann Plast Surg 76:371–375
Li XQ, Wang TL, Wang JQ (2015) Ptosis: an underestimated complication after autologous fat injection into the upper eyelid. Aesthet Surg J 35:NP147-53
Wang X, Du Y, Wu H, Zhang S, Qi X, Nie K (2019) Repair techniques for failed double-eyelids involving restoration of eyelid anatomical structure and function. Aesthetic Plast Surg 43:702–710
Chang S, Lehrman C, Itani K, Rohrich RJ (2012) A systematic review of comparison of upper eyelid involutional ptosis repair techniques: efficacy and complication rates. Plast Reconstr Surg 129:149–157
Berlin AJ, Vestal KP (1989) Levator aponeurosis surgery: a retrospective review. Ophthalmology 96:1033–1036
Kee HJ, Yang HK, Hwang JM, Park KS (2019) Evaluation and validation of sustained upgaze combined with the ice-pack test for ocular myasthenia gravis in Asians. Neuromuscul Disord 29:296–301
Funding
No funding was received for the work presented in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical Approval
This study was approved by the ethics committee of our institution and conformed to the standards outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki, as amended in 2013.
Informed Consent
All patients agreed to participate and provided written informed consent prior to study entry.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, P., Huang, H., Zhang, S. et al. A Comprehensive Approach to Upper Eyelid Rejuvenation Surgery. Aesth Plast Surg 45, 1047–1055 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-02031-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-020-02031-3