Abstract
Background
The etiology and clinical treatment of capsular contracture remain unresolved as the causes may be multifactorial. Triamcinolone acetonide applied in the pocket during surgery was reported to be ineffective in prevention of capsular contracture. However, if injected 4–6 weeks after surgery or as a treatment for capsular contracture, decreased applanation tonometry measurements and pain were observed. It was assumed that intraoperative application of triamcinolone was not effective because its effect does not last long enough. However, betadine, antibiotics, and fibrin were found to be effective in preventing capsular contracture with intraoperative applications and are more effective in the early phases of wound healing than in later stages. The role of triamcinolone acetonide in capsule formation is unknown. The purpose of this study was to determine if triamcinolone acetonide modulates breast capsule formation or capsular contracture in the early phases of wound healing in a rabbit model.
Methods
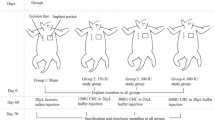
Rabbits (n = 19) were implanted with one tissue expander and two breast implants and were killed at 4 weeks. Implant pocket groups were (1) Control (n = 10) and (2) Triamcinolone (n = 9). Pressure/volume curves and histological, immunological, and microbiological evaluations were performed. Operating room air samples and contact skin samples were collected for microbiological evaluation.
Results
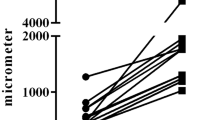
In the triamcinolone group, a decreased capsular thickness, mild and mononuclear inflammation, and negative or mild angiogenesis were observed. There were no significant differences in intracapsular pressure, fusiform cell density, connective tissue, organization of collagen fibers, and microbiological results between the groups. There was no significant difference in the dialysate levels of IL-8 and TNF-α, but correlation between IL-8 and TNF-α was observed.
Conclusion
Triamcinolone acetonide during breast implantation influences early capsule formation and may reduce capsular contracture.
Level of Evidence III
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors at www.springer.com/00266.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham DJ, Shiwen X, Black CM, Sa S, Xu Y, Leask A (2000) Tumor necrosis factor alpha suppresses the induction of connective tissue growth factor by transforming growth factor beta in normal and scleroderma fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 275:15220–15225
Adams WP Jr, Conner WC, Barton FE Jr, Rohrich RJ (2000) Optimizing breast pocket irrigation: an in vitro study and clinical implications. Plast Reconstr Surg 105:334–338; discussion 339–343
Adams WP Jr, Conner WC, Barton FE Jr, Rohrich RJ (2001) Optimizing breast-pocket irrigation: the post-betadine era. Plast Reconstr Surg 107:1596–1601
Adams WP Jr, Haydon MS, Raniere J Jr, Trott S, Marques M, Feliciano M, Robinson JB Jr, Tang L, Brown SA (2006) A rabbit model for capsular contracture: development and clinical implications. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:1214–1219; discussion 1220–1221
Adams WP Jr, Rios JL, Smith SJ (2006) Enhancing patient outcomes in aesthetic and reconstructive breast surgery using triple antibiotic breast irrigation: six-year prospective clinical study. Plast Reconstr Surg 118:46S–52S
Ajmal N, Riordan CL, Cardwell N, Nanney LB, Shack RB (2003) The effectiveness of sodium 2-mercaptoethane sulfonate (mesna) in reducing capsular formation around implants in a rabbit model. Plast Reconstr Surg 112:1455–1461; discussion 1462–1463
Baker BL, Whitaker WL (1950) Interference with wound healing by the local action of adrenocortical steroids. Endocrinology 46:544–551
Barnsley GP, Sigurdson LJ, Barnsley SE (2006) Textured surface breast implants in the prevention of capsular contracture among breast augmentation patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:2182–2190
Bastos EM, Neto MS, Alves MT, Garcia EB, Santos RA, Heink T, Pereira JB, Ferreira LM (2007) Histologic analysis of zafirlukast’s effect on capsule formation around silicone implants. Aesthetic Plast Surg 31:559–565
Batra M, Bernard S, Picha G (1995) Histologic comparison of breast implant shells with smooth, foam, and pillar microstructuring in a rat model from 1 day to 6 months. Plast Reconstr Surg 95:354–363
Bibby S, Healy B, Steele R, Kumareswaran K, Nelson H, Beasley R (2010) Association between leukotriene receptor antagonist therapy and Churg-Strauss syndrome: an analysis of the FDA AERS database. Thorax 65:132–138
Brohim RM, Foresman PA, Hildebrandt PK, Rodeheaver GT (1992) Early tissue reaction to textured breast implant surfaces. Ann Plast Surg 28:354–362
Broughton G 2nd, Janis JE, Attinger CE (2006) The basic science of wound healing. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:12S–34S
Burkhardt BR, Dempsey PD, Schnur PL, Tofield JJ (1986) Capsular contracture: a prospective study of the effect of local antibacterial agents. Plast Reconstr Surg 77:919–932
Caffee HH (2002) Capsule injection for the prevention of contracture. Plast Reconstr Surg 110:1325–1328
Caffee HH, Rotatori DS (1993) Intracapsular injection of triamcinolone for prevention of contracture. Plast Reconstr Surg 92:1073–1077
Camirand A, Doucet J, Harris J (1999) Breast augmentation: compression–a very important factor in preventing capsular contracture. Plast Reconstr Surg 104:529–538; discussion 539–541
Del Pozo JL, Tran NV, Petty PM, Johnson CH, Walsh MF, Bite U, Clay RP, Mandrekar JN, Piper KE, Steckelberg JM, Patel R (2009) Pilot study of association of bacteria on breast implants with capsular contracture. J Clin Microbiol 47:1333–1337
Devi SL, Viswanathan P, Anuradha CV (2010) Regression of liver fibrosis by taurine in rats fed alcohol: effects on collagen accumulation, selected cytokines and stellate cell activation. Eur J Pharmacol 647:161–170
Ehrlich HP, Hunt TK (1968) Effects of cortisone and vitamin A on wound healing. Ann Surg 167:324–328
Embrey M, Adams EE, Cunningham B, Peters W, Young VL, Carlo GL (1999) A review of the literature on the etiology of capsular contracture and a pilot study to determine the outcome of capsular contracture interventions. Aesthetic Plast Surg 23:197–206
Ersek RA (1991) Firestorm fibrosis: the fast fibrotic phenomenon. Ann Plast Surg 26:494–498
Ersek RA, Salisbury AV (1997) Textured surface, nonsilicone gel breast implants: four years’ clinical outcome. Plast Reconstr Surg 100:1729–1739
Frangou J, Kanellaki M (2001) The effect of local application of mitomycin-C on the development of capsule around silicone implants in the breast: an experimental study in mice. Aesthetic Plast Surg 25:118–128
Gancedo M, Ruiz-Corro L, Salazar-Montes A, Rincon AR, Armendariz-Borunda J (2008) Pirfenidone prevents capsular contracture after mammary implantation. Aesthetic Plast Surg 32:32–40
Goldman R (2004) Growth factors and chronic wound healing: past, present, and future. Adv Skin Wound Care 17:24–35
Grotendorst GR, Soma Y, Takehara K, Charette M (1989) EGF and TGF-alpha are potent chemoattractants for endothelial cells and EGF-like peptides are present at sites of tissue regeneration. J Cell Physiol 139:617–623
Gryskiewicz JM (2003) Investigation of accolate and singulair for treatment of capsular contracture yields safety concerns. Aesthetic Surg J 23:98–101
Handel N, Jensen JA, Black Q, Waisman JR, Silverstein MJ (1995) The fate of breast implants: a critical analysis of complications and outcomes. Plast Reconstr Surg 96:1521–1533
Henry G, Garner WL (2003) Inflammatory mediators in wound healing. Surg Clin North Am 83:483–507
Ksander GA (1979) Effects of diffused soluble steroid on capsules around experimental breast prostheses in rats. Plast Reconstr Surg 63:708–716
Lawrence WT, Diegelmann RF (1994) Growth factors in wound healing. Clin Dermatol 12:157–169
Marques M, Brown SA, Oliveira I, Cordeiro MN, Morales-Helguera A, Rodrigues A, Amarante J (2010) Long-term follow-up of breast capsule contracture rates in cosmetic and reconstructive cases. Plast Reconstr Surg 126:769–778
Marques M, Brown SA, Rodrigues-Pereira P, Natalia M, Cordeiro DS, Morales-Helguera A, Cobrado L, Queiros L, Freitas R, Fernandes J, Correia-Sa I, Rodrigues AG, Amarante J (2011) Animal model of implant capsular contracture: effects of chitosan. Aesthetic Surg J 31:540–550
Marques M, Brown SA, Cordeiro ND, Rodrigues-Pereira P, Cobrado ML, Morales-Helguera A, Lima N, Luis A, Mendanha M, Goncalves-Rodrigues A, Amarante J (2011) Effects of fibrin, thrombin, and blood on breast capsule formation in a preclinical model. Aesthetic Surg J 31:302–309
Marques M, Brown SA, Cordeiro ND, Rodrigues-Pereira P, Cobrado ML, Morales-Helguera A, Queiros L, Luis A, Freitas R, Goncalves-Rodrigues A, Amarante J (2011) Effects of coagulase-negative staphylococci and fibrin on breast capsule formation in a rabbit model. Aesthetic Surg J 31:420–428
Morimoto Y, Gai Z, Tanishima H, Kawakatsu M, Itoh S, Hatamura I, Muragaki Y (2008) TNF-alpha deficiency accelerates renal tubular interstitial fibrosis in the late stage of ureteral obstruction. Exp Mol Pathol 85:207–213
Perrin ER (1976) The use of soluble steroids within inflatable breast prostheses. Plast Reconstr Surg 57:163–166
Pohlman TH, Stanness KA, Beatty PG, Ochs HD, Harlan JM (1986) An endothelial cell surface factor(s) induced in vitro by lipopolysaccharide, interleukin 1, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases neutrophil adherence by a CDw18-dependent mechanism. J Immunol 136:4548–4553
Rohatagi S, Hochhaus G, Mollmann H, Barth J, Galia E, Erdmann M, Sourgens H, Derendorf H (1995) Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation of triamcinolone acetonide after intravenous, oral, and inhaled administration. J Clin Pharmacol 35:1187–1193
Rohrich RJ, Kenkel JM, Adams WP (1999) Preventing capsular contracture in breast augmentation: in search of the Holy Grail. Plast Reconstr Surg 103:1759–1760
Schilling JA (1976) Wound healing. Surg Clin North Am 56:859–874
Sconfienza LM, Murolo C, Callegari S, Calabrese M, Savarino E, Santi P, Sardanelli F (2011) Ultrasound-guided percutaneous injection of triamcinolone acetonide for treating capsular contracture in patients with augmented and reconstructed breast. Eur Radiol 21:575–581
Siggelkow W, Faridi A, Spiritus K, Klinge U, Rath W, Klosterhalfen B (2003) Histological analysis of silicone breast implant capsules and correlation with capsular contracture. Biomaterials 24:1101–1109
Smahel J, Hurwitz PJ, Hurwitz N (1993) Soft tissue response to textured silicone implants in an animal experiment. Plast Reconstr Surg 92:474–479
Spano A, Palmieri B, Taidelli TP, Nava MB (2008) Reduction of capsular thickness around silicone breast implants by zafirlukast in rats. Eur Surg Res 41:8–14
Tamboto H, Vickery K, Deva AK (2010) Subclinical (biofilm) infection causes capsular contracture in a porcine model following augmentation mammaplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 126:835–842
Tilg H, Ceska M, Vogel W, Herold M, Margreiter R, Huber C (1992) Interleukin-8 serum concentrations after liver transplantation. Transplantation 53:800–803
Wolfram D, Rainer C, Niederegger H, Piza H, Wick G (2004) Cellular and molecular composition of fibrous capsules formed around silicone breast implants with special focus on local immune reactions. J Autoimmun 23:81–91
Yilmaz T, Cordero-Coma M, Federici TJ (2011) Pharmacokinetics of triamcinolone acetonide for the treatment of macular edema. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 7(10):1327–1335
Zeplin PH, Larena-Avellaneda A, Schmidt K (2010) Surface modification of silicone breast implants by binding the antifibrotic drug halofuginone reduces capsular fibrosis. Plast Reconstr Surg 126:266–274
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marques, M., Brown, S., Correia-Sá, I. et al. The Impact of Triamcinolone Acetonide in Early Breast Capsule Formation in a Rabbit Model. Aesth Plast Surg 36, 986–994 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-9888-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-9888-z