Abstract
Background
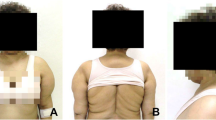
Benign symmetric lipomatosis, also known as Madelung disease, is a rare disorder characterized by fat distribution around the shoulders, arms, and neck in the context of chronic alcoholism. Complete excision of nonencapsulated lipomas is difficult. However, reports describing conservative therapeutic measures for lipomatosis are rare.
Methods
The authors present the case of a 42-year-old man with a diagnosis of benign symmetric lipomatosis who had multiple, large, symmetrical masses in his neck. Multiple phosphatidylcholine injections in the neck were administered 4 weeks apart, a total of seven times to achieve lipolysis.
Results
The patient’s lipomatosis improved in response to the injections, and he achieved good cosmetic results.
Conclusions
Intralesional injection, termed mesotherapy, using phosphatidylcholine is a potentially effective therapy for benign symmetric lipomatosis that should be reconsidered as a therapeutic option for this disease.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
References
Ruzicka T, Vieluf D, Landthaler M et al (1987) Benign symmetrical lypomatosis. J Am Acad Dermatol 17:663–674
Smith PD, Stadelmann WK, Wassermann RJ et al (1998) Benign symmetric lipomatosis (Madelung’s disease). Ann Plast Surg 41:671
Becker-Wegerich P, Steuber M, Olbrisch R, Ruzicka T, Auburger G, Hofhaus G (1998) Defects of mitochondrial respiratory chain in multiple symmetric lipomatosis. Arch Dermatol Res 290:652–655
Berkovic SF, Andermann F, Shoubridge EA, Carpenter S, Robitaille Y, Andermann E et al (1991) Mitochondrial dysfunction in multiple symmetrical lipomatosis. Ann Neurol 29:566–569
Klopstock T, Naumann M, Seibel P, Shalke B, Reiners K, Reichmann H (1997) Mitochomdrial DNA mutations in multiple symmetric lipomatosis. Mol Cell Biochem 174:271–275
Leung NW, Gaer J, Beggs D et al (1987) Multiple symmetrical lipomatosis: effect of oral salbutanol. Clin Endocrinol 27:601
Adamo C, Vescio G, Battaglia M, Gallelli G, Musella S (2001) Madelung’s disease: case report and discussion of treatment options. Ann Plast Surg 46:43–45
Martinez-Escribano JA, Gonzalez R, Quecedo E, Febrer I (1999) Efficacy of lipotectomy and liposuction in the treatment of multiple symmetric lipomatosis. Int J Dermatol 38:551–554
Faga A, Valdatta LA, Thione A, Buoro M (2001) Ultrasound assisted liposuction for the palliative treatment of Madelung’s disease: a case report. Aesth Plast Surg 25:181
Pistor M (1979) Un Defi Therapeutiche: la Mesotherapie, 3rd edn. Maloine, Paris, pp 1–50
Matarasso A, Pfeifer TM (2005) Mesotherapy for body contouring. Plast Reconstr Surg 115:1420–1424
Rittes PG (2003) The use of phosphatidylcholine for collection of localized fat deposits. Aesth Plast Surg 27:315–318
Rohrich R (2005) Mesotherapy: what is it? Does it work? Plast Reconstr Surg 115:1425
Rotunda A, Kolodney M (2006) Mesotherapy and phosphatidylcholine injections: historical clarification and review. Dermatol Surg 32:465–480
Rose PT, Morgan M (2005) Histological changes associated with mesotherapy for fat dissolution. J Cosmet Laser Ther 7:17–19
Rotunda A, Suzuki H, Moy R, Kolodney M (2004) Detergent effects of sodium deoxycholate are a major feature of an injectable phosphatidylcholine formulation used for localized fat dissolution. Dermatol Surg 30:1001–1008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hasegawa, T., Matsukura, T. & Ikeda, S. Mesotherapy for Benign Symmetric Lipomatosis. Aesth Plast Surg 34, 153–156 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-009-9374-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-009-9374-4