Abstract
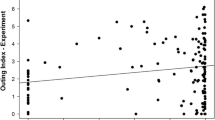
The connection between risk-taking behaviour and exploratory behaviour in young-of-the-year perch (Perca fluviatilis) was studied in aquarium experiments to see whether individual behaviour patterns could be identified in this species and also to investigate how individual behaviour is influenced by their social environment. Risk-taking was defined as the time spent foraging in an open area vs hiding in the vegetation in the presence of a piscivore. Explorative behaviour was measured as latency to enter a passage leading to an unknown area. Groups of four fish were used for the observations, and both behaviours measured were positively correlated with the mean scores of these behaviours in the other group members. Risk-taking and explorative behaviours were correlated only when data was adjusted for the behaviour of the other group members. Individuals that spent more time in the open than their companions also tended to be faster than the others to enter the passage to the unknown area and vice versa. The results indicate that there are consistent individual differences in boldness in perch, but also that behaviour could be modified according to the behaviour of group members.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armitage KB, VanVuren DH (2003) Individual differences and reproductive success in yellow-bellied marmots. Ethol Ecol Evol 15:207–233
Bell AM (2005) Behavioural differences between individuals and two populations of stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus). J Evol Biol 18:464–473
Bell AM, Stamps JA (2004) Development of behavioural differences between individuals and populations of sticklebacks, Gasterosteus aculeatus. Anim Behav 68:1339–1348
Brick O, Jakobsson S (2002) Individual variation in risk taking: the effect of a predatory threat on fighting behavior in Nannacara anomala. Behav Ecol 13:439–442
Budaev SV (1997a) Alternative styles in the European wrasse, Symphodus ocellatus: boldness-related schooling tendency. Environ Biol Fishes 49:71–78
Budaev SV (1997b) “Personality” in the guppy (Poecilia reticulata): a correlational study of exploratory behavior and social tendency. J Comp Psychol 111:399–411
Coleman K, Wilson DS (1998) Shyness and boldness in pumpkinseed sunfish: individual differences are context-specific. Anim Behav 56:927–936
Craig JF (2000) Percid fishes: systematics, ecology and exploitation. Blackwell Science, Oxford
Croft DP, James R, Ward AJW, Botham MS, Mawdsley D, Krause J (2005) Assortative interactions and social networks in fish. Oecologia 143:211–219
Croft DP, James R, Thomas POR, Hathaway C, Mawdsley D, Laland KN, Krause J (2006) Social structure and co-operative interactions in a wild population of guppies (Poecilia reticulata). Behav Ecol Sociobiol 59:644–650
Dall SRX, Houston AI, McNamara JM (2004) The behavioural ecology of personality: consistent individual differences from an adaptive perspective. Ecol Lett 7:734–739
Dingemanse NJ, de Goede P (2004) The relation between dominance and exploratory behavior is context-dependent in wild great tits. Behav Ecol 15:1023–1030
Dingemanse NJ, Reale D (2005) Natural selection and animal personality. Behaviour 142:1159–1184
Dingemanse NJ, Both C, Drent PJ, Van Oers K, Van Noordwijk AJ (2002) Repeatability and heritability of exploratory behaviour in great tits from the wild. Anim Behav 64:929–938
Dingemanse NJ, Both C, Van Noordwijk AJ, Rutten AL, Drent PJ (2003) Natal dispersal and personalities in great tits (Parus major). Proc R Soc Lond B-Biol Sci 270:741–747
Drent PJ, van Oers K, van Noordwijk AJ (2003) Realized heritability of personalities in the great tit (Parus major). Proc R Soc Lond B-Biol Sci 270:45–51
Dugatkin LA, Alfieri MS (2003) Boldness, behavioral inhibition and learning. Ethol Ecol Evol 15:43–49
Fairbanks LA, Newman TK, Bailey JN, Jorgensen MJ, Breidenthal SE, Ophoff RA, Comuzzie AG, Martin LJ, Rogers J (2004) Genetic contributions to social impulsivity and aggressiveness in vervet monkeys. Biol Psychiatry 55:642–647
Forrester GE (1991) Social rank, individual size and group composition as determinants of food consumption by humbug damselfish, Dascyllus aruanus. Anim Behav 42:701–711
Fraser DF, Gilliam JF, Daley MJ, Le AN, Skalski GT (2001) Explaining leptokurtic movement distributions: intrapopulation variation in boldness and exploration. Am Nat 158:124–135
Galef BG, Laland KN (2005) Social learning in animals: empirical studies and theoretical models. Bioscience 55:489–499
Gosling SD (2001) From mice to men: what can we learn about personality from animal research? Psychol Bull 127:45–86
Grand TC, Dill LM (1999) Predation risk, unequal competitors and the ideal free distribution. Evol Ecol Res 1:389–409
Huntingford FA (1976) The relation between anti-predator behaviour and aggression among conspecifics in the three-spined stickleback, Gasterosteus aculeatus. Anim Behav 24:245–260
Hurlbert SH (1984) Pseudoreplication and the design of ecological field experiments. Ecol Monogr 54:187–211
Johnsson JI (1993) Big and brave—size selection affects foraging under risk of predation in juvenile rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Anim Behav 45:1219–1225
Kelley JL, Magurran AE (2003) Learned predator recognition and antipredator responses in fishes. Fish Fish 4:216–226
Koolhaas JM, Korte SM, De Boer SF, Van Der Vegt BJ, Van Reenen CG, Hopster H, De Jong IC, Ruis MAW, Blokhuis HJ (1999) Coping styles in animals: current status in behavior and stress-physiology. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:925–935
Krause J, Ruxton GD (2002) Living in groups. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Laland KN (2004) Social learning strategies. Learn Behav 32:4–14
Magnhagen C (2006) Risk-taking behaviour in foraging young-of-the-year perch varies with population size structure. Oecologia 147:734–743
Magnhagen C, Staffan F (2003) Social learning in young-of-the-year perch encountering a novel food type. J Fish Biol 63:824–829
Magnhagen C, Staffan F (2005) Is boldness affected by group composition in young-of-the-year perch (Perca fluviatilis)? Behav Ecol Sociobiol 57:295–303
Metcalfe NB (1986) Intraspecific variation in competitive ability and food intake in salmonids: consequences for energy budgets and growth rates. J Fish Biol 28:525–531
Neff BD, Sherman PW (2004) Behavioral syndromes versus Darwinian algorithms. Trends Ecol Evol 19:621–622
Øverli Ø, Pottinger TG, Carrick TR, Øverli E, Winberg S (2002) Differences in behaviour between rainbow trout selected for high- and low-stress responsiveness. J Exp Biol 205:391–395
Reale D, Gallant BY, Leblanc M, Festa-Bianchet M (2000) Consistency of temperament in bighorn ewes and correlates with behaviour and life history. Anim Behav 60:589–597
Riechert SE, Hedrick AV (1993) A test for correlations among fitness-linked behavioral traits in the spider Agelenopsis aperta (Araneae, Agelenidae). Anim Behav 46:669–675
Sih A, Watters JV (2005) The mix matters: behavioural types and group dynamics in water striders. Behaviour 142:1417–1431
Sih A, Bell A, Johnson JC (2004) Behavioral syndromes: an ecological and evolutionary overview. Trends Ecol Evol 19:372–378
Sneddon LU (2003) The bold and the shy: individual differences in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). J Fish Biol 62:971–975
Svartberg K, Forkman B (2002) Personality traits in the domestic dog (Canis familiaris). Appl Anim Behav Sci 79:133–155
Utne ACW, Brännäs E, Magnhagen C (1997) Individual responses to predation risk and food density in perch (Perca fluviatilis L.). Can J Zool 75:2027–2035
van Oers K, Drent PJ, de Goede P, van Noordwijk AJ (2004) Realized heritability and repeatability of risk-taking behaviour in relation to avian personalities. Proc R Soc Lond B-Biol Sci 271:65–73
Ward AJW, Thomas P, Hart PJB, Krause J (2004) Correlates of boldness in three-spined sticklebacks (Gasterosteus aculeatus). Behav Ecol Sociobiol 55:561–568
Westerberg M, Staffan F, Magnhagen C (2004) Influence of predation risk on individual competitive ability and growth in Eurasian perch, Perca fluviatilis. Anim Behav 67:273–279
Wilson DS, Coleman K, Clark AB, Biederman L (1993) Shy-bold continuum in pumpkinseed sunfish (Lepomis gibbosus): an ecological study of a psychological trait. J Comp Psychol 107:250–260
Wilson DS, Clark AB, Coleman K, Dearstyne T (1994) Shyness and boldness in humans and other animals. Trends Ecol Evol 9:442–446
Acknowledgements
The experiments in this study comply with the current laws of Sweden and were approved by the local ethics committee of the Swedish National Board for Laboratory Animals (CFN). The study was financially supported by C.F. Lundströms Foundation. Hans Rönnholm was a resourceful help during fish collection and experiment set-up. Two anonymous referees provided useful comments for the improvement of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Krause
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magnhagen, C. Social influence on the correlation between behaviours in young-of-the-year perch. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 61, 525–531 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-006-0280-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-006-0280-3