Abstract.
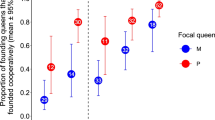
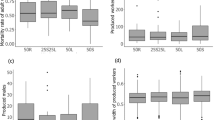
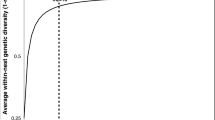
Previous studies have shown that colony social organization in Solenopsis invicta is under strong genetic control. Colonies containing some proportion of workers with the Bb or bb genotypes at the gene Gp-9 display polygyne social organization (multiple reproductive queens per colony), whereas colonies with only BB workers express monogyne organization (single reproductive queen per colony). The hypothesis that the presence of workers bearing the b allele confers the polygyne social phenotype on a colony leads to the prediction that social organization can be manipulated by experimentally altering frequencies of adult workers bearing this allele. We did this by replacing queens in colonies of each social form with single queens of the alternate form, which differ in Gp-9 genotype. As worker Gp-9 genotype compositions changed, experimental colonies switched to the alternate social organization. These switches occurred when frequencies of workers with the b allele passed an identifiable threshold, such that colonies with fewer than 5% such workers behaved like monogyne colonies and those with more than 10% behaved like polygyne colonies. Our data thus confirm the prediction that colony social organization in this ant can be altered by manipulating adult worker genotype compositions, and thereby support the hypothesis that the expression of polygyny requires the presence of adult workers bearing the b allele at Gp-9.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ross, .K., Keller, .L. Experimental conversion of colony social organization by manipulation of worker genotype composition in fire ants (Solenopsis invicta). Behav Ecol Sociobiol 51, 287–295 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-001-0431-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-001-0431-5