Abstract
Background
Nonunion continues to be the most frequent and challenging complication to treat following fracture fixation. Herein, we carried out a bibliometric analysis aiming to identify the key researchers, centres and research trends developed during the past 30 years in this important clinical condition.
Methods
The Science Citation Index Expanded database and the Web of Science Core Collection were interrogated for manuscripts published between 1990 and 2019 in the topic domain, utilising title, abstract, author keywords and KeyWords Plus. Overall, such citation indicators were used as TCyear, Cyear and CPPyear to help analyse the identified manuscripts.
Results
Over the prespecified period, there was a steady increase in the number of articles published in fracture nonunion. In total, 12 languages were the primary languages in the documents, with English being the most prevalent. The CPP sharply increased to reach a plateau in three full years and up to a peak in ten full years. A total of 8976 nonunion-related articles in Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED) were published in 790 journals. The 8976 articles were published by 26,079 authors among 101 different countries. There is a slightly fluctuating steady increase of articles from 116 in 1991 to 201 in 2003, and thereafter, the number of articles sharply increased to reach a plateau in 2015. Seven possible main research foci in nonunion-related research were identified including: epidemiology, classification, aetiology, diagnosis/prediction, treatment modalities, functional outcomes and health economics.
Conclusions
This bibliometric analysis revealed information on citation number, publication outputs, categories, journals, institutions, countries, research highlights and tendencies. The current research activity on fracture nonunion identified key opinion leaders and leading research institutions focusing on this important clinical condition. It is hoped that the informed included will aid to guide research work in the foreseeable future.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Failure of fracture healing with resultant nonunion remains a very challenging but potentially devastating complication following fracture surgery and has an estimated incidence of about 5–10% [1]. Despite intense research efforts, this problem continues to take a significant toll on society, including both direct and indirect costs and major disability [2]. For example, nonunion of tibial shaft fractures may have an impact to the physical health worse than other common chronic condition such as congestive heart failure, back pain, myocardial infarction, diabetes and others [2].
Bibliometric citation analysis is an established evidence-based method of mapping the literature and identifying prominent researchers and research units that have developed a particular interest in a specific topic or condition and has been commonly used in orthopaedic surgery [3]. By analysing research output per country, institutions, journals and researchers, bibliometric analysis evaluates and improves the understanding of research trends evolution over time [3]. Although the orthopaedic community has remained active in addressing this challenge, it appears that fracture nonunion research is carried out within certain specialised groups and societies. The aim of this study therefore is to carry out a quantitative description of the literature on nonunion manuscripts published until now and to gather information on institutions, journals, researchers, countries, Web of Science categories and research directions. Moreover, we wished to outline an up-to-date, clear framework of the current research and provide clues to guide the future direction of the research in this yet unsolved clinical condition.
Methods
Data were retrieved from the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED) in the Web of Science Core Collection by Clarivate Analytics and last updated on 10th February 2021. Although, by design, the Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED) is useful for literature search [4], the Web of Science database may be queried and serve as basis to establish bibliometric searches. The following keywords were used to search in SCI-EXPANDED: ‘nonunion’, ‘nonunions’, ‘non union’ and ‘non unions’. The following topic search strings were used in Web of Science Core Collection: paper title, abstract and author keywords. Search power was enhanced using KeyWords Plus which provided additional search terms extracted from the titles of papers cited in each new article listed in Current Contents [5]. As the documents that can only be found by KeyWords Plus are irrelevant to the search topic [6], those were excluded. To eliminate inherent bias of using Web of Science Core Collection for bibliometric analysis and avoid introducing unrelated publications, the ‘front-page’ filter was used to cover only the documents in which search keywords are included in the title, abstract and author keywords [6]. By using advanced search with terms of TI (title), AB (abstract) and AK (author keywords), 10,064 documents including 8976 articles having the search keywords in their ‘front page’ from 1990 to 2019 were defined as nonunion publications. Subsequently, the records were introduced into spreadsheet software (Microsoft Excel 2016, Microsoft Corporation™), and additional coding was performed for analysis [6]. The journal impact factor (IF2019) for each journal was obtained from the Journal Citation Reports (JCR) in 2019. For accuracy and simplicity, affiliations of England, Scotland, Northern Ireland and Wales were reclassified as United Kingdom (UK) [6], whereas affiliations in Hong Kong prior to 1997 were included under the heading of China [6]. Affiliations from the former USSR were checked and reclassified as being from Ukraine and Russia, respectively, whereas those from Serbia and Montenegro were grouped as Serbia [6]. In the SCI-EXPANDED database, the corresponding author is labelled as reprint author, but in this study, we used the term corresponding author [6]. In a single-institution article, the institution is classified as the first and the corresponding author’s institution [6]. In multi-corresponding-author articles, only the last corresponding author, institution and country were assigned to the article [6]. Noteworthy, it has been shown previously that the corresponding author is most likely to appear first and then last in the byline [6].
The following three citation indicators were used to investigate the citations of the publications:
-
1.
Cyear—the number of citations from the Web of Science Core Collection in a particular year. For example, C2019 refers to the number of citations in 2019 [7].
-
2.
TCyear—the total number of citations from the Web of Science Core Collection since publication year to the end of the most recent year, it is 2019 in this study [8]. This citation indicator has been commonly applied in bibliometric research in the last decade [9].
-
3.
CPPyear—citations per publication (CPP2019 = TC2019/TP); TP, total number of articles [7].
The following six publication indicators were applied to evaluate publication performance of countries and institutions [10]:
-
1.
TP—total number of articles
-
2.
IP—number of single-country or single-institution authored articles
-
3.
CP—number of internationally or inter-institutionally collaborative articles
-
4.
FP—number of first-author articles
-
5.
RP—number of corresponding-author articles
-
6.
SP—number of single-author articles
Results and discussion
Document type and language of publication
The relationship among document types and their citations per publication, CPPyear, and the APP has recently been proposed [11]. Among the 14 document types indexed by the Web of Science, a total of 10,064 nonunion-related publications were found (Table 1). The document type of ‘articles’ was by far the most prevalent, with a total of 8976 articles (89% of 10,064 documents) and an average of 4.7 APP with a maximum of 200. The document type of the ‘proceedings’ papers had the highest CPP2019 of 41, which can be attributed to the 33 highly cited proceedings papers (11% of 306 proceedings papers) with TC2019 of 100 or more [6]. Of note, in the Web of Science document classification, one document may be classified in several categories. For example, 306 documents are classified as document types for ‘proceedings papers’ and ‘articles’, so the sum of the percentages is higher than 100% [6]. Only the 8976 articles were further analysed. In total, 12 languages were the primary languages in the articles, with English, as the most prevalent (93% of the total of 8976 articles), followed by German (324 articles; 3.6% of 8976 articles) and French (178; 2.0%). Minority languages were Czech (36 articles), Turkish (25), Portuguese (6), Spanish (5), Serbian (4), Italian (3), Russian (3), Polish (2) and Hungarian (1). English language articles had higher CPP2019 of 23 than non-English with CPP2019 of 7.5.
Historical publication and citation trends
To understand publications in a specific research topic and their citation trends, a relationship between citations per publication (CPPyear) and article life was proposed [12]. The article life with CPP for all the 8976 nonunion articles is displayed in Fig. 1. It takes CPPs about three full years to reach a plateau and up to a peak in ten full years. A comparison of the medical-related topics was also shown in Fig. 1. Articles related to nonunion had longer citation life than some medical topics; a peak appeared in four and five full year for breast reconstruction [6] and child sexual abuse [13] research, respectively.
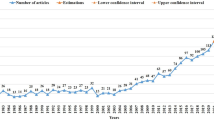
Both publications and citation trends in a research topic were proposed [6]. A relationship between the annual number of articles (TP) and their citations per publication (CPP2019 = TC2019/TP) throughout the years is shown in Fig. 2. The ‘jump’ between 1990 and 1991 is an artefact that arises from a policy change by the Web of Science with respect to abstract information [14]. The majority of articles have no abstract information in SCI-EXPANDED before 1991. There is a slightly fluctuating steady increase of articles from 116 in 1991 to 201 in 2003 and thereafter, the number of articles sharply increased to reach a plateau in 2015, fluctuating in the mid-550s. Based on Fig. 2, it takes CPPs about 14 years to reach a plateau. Articles related to nonunion had longer life than some medical-related topics, for example, breast reconstruction with 10 years[6] and child sexual abuse with 8 years [13]. Articles published in nonunion could be cited longer with average year of 14 than that of breast reconstruction and child sexual abuse with ten and eight years, respectively.
Web of Science categories and journals
Journal Citation Reports (JCR) indexed 9381 journals across 178 Web of Science categories in SCI-EXPANDED in 2019. A total of 8976 nonunion-related articles in SCI-EXPANDED were published in 790 journals which are classified among the 115 Web of Science categories in SCI-EXPANDED. Table 2 shows the top ten productive Web of Science categories with number of articles (TP), APP, CPP2019 and number of journals in a category. A total of 7407 articles (83% of 8975 articles with category information in SCI-EXPANDED) were published in the top two categories: orthopaedics (6223 articles; 69% of 8975 articles) and surgery (4334 articles; 48%). Comparing the top ten productive categories in healthcare sciences, articles published in category of clinical neurology had the highest CPP2019 of 34, while articles in general and internal medicine had lower CPP2019 of 6.1. Articles published in category of biomedical engineering had the highest APP of 6.5, while articles in paediatrics had lower APP of 4.2. The evolution of nonunion article trends in the top five productive Web of Science categories is shown in Fig. 3. Articles in categories of orthopaedics and surgery had similar trends from 1990 to 2008; however, orthopaedics shows a sharper increasing trend since 2009. The number of articles published, as well as trends in the remaining three categories, is similar.
The top ten most productive journals are listed in Table 3, including IF2019, APP, CPP2019 and Web of Science category. All the top ten journals were classified in the category of orthopaedics and six in surgery. The Injury-International Journal of the Care of the Injured published the most articles (657 articles; 7.3% of 8976 articles). Comparison of the articles published in the top ten journals showed that articles published in the Spine had the highest APP of 5.2, while the Journal of Hand Surgery-American Volume and the Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research had an APP of 3.8, respectively. Articles published in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume had the highest CPP2019 of 71, while articles published in International Orthopaedics had a CPP2019 of 14. According to IF2019, the top three articles have an IF2019 of more than 30 (Lancet, Nature Biotechnology, and BMJ-British Medical Journal).
Publication performance of countries, institutions and authors
The 8976 articles were published by 26,079 authors among 101 different countries. Altogether, 7976 (89% of 8976 articles) were authored from a single country, with the articles being from 79 different countries. Internationally, authored collaborative articles were less common (993 articles, 11%) with authors from 85 different countries. The six publication indicators [10] were applied to compare the top ten productive countries (Table 4). Five European countries, three Asia countries and two American countries were ranked in the top ten of publications. The USA dominated the top in the six publication indicators with a TP of 3262 articles (36% of 8969 articles), an IP of 2726 articles (34% of 7976 single-country authored articles), a CP of 536 articles (54% of 993 internationally collaborative articles), an FP of 2996 articles (33% of 8969 first-author articles), an RP of 2939 articles (33% of 8832 corresponding-author articles) and an SP of 148 articles (39% of 378 single-author articles).
In total, 4192 articles (47% of 8969 articles) were articles authored within single institution and 4777 (53%) were inter-institutionally collaborative articles. The six publication indicators [10] were applied to compare the top 11 productive institutions with TP of 70 or more (Table 5). Nine of the top 11 most productive institutions are in the USA and one in Canada and China, respectively. The Mayo Clinic in the USA took the leading position for the four publication indicators with a TP of 134 articles (1.5% of 8969 articles), an IP of 67 articles (1.6% of 4192 single institute articles), an FP of 92 articles (1.0% of 8969 first-author articles) and a RP of 93 articles (1.1% of 8,831 corresponding-author articles), while the University of Toronto in Canada ranked top with a CP of 82 articles (1.7% of 4777 inter-institutionally collaborative articles). The Chang Gung Memorial Hospital in Taiwan published the most single-author article with an SP of nine articles (2.4% of 378 single-author articles). The Hospital for Special Surgery in the USA, the New York University (NYU) in the USA, the Washington University in the USA and the Shanghai Jiao Tong University in China had no single-author articles.
In experimental science, the accepted convention is that the most important positions are first and last authors and one of these usually includes the corresponding author [6]. The first author generally is the person who contributed most to the work, including conducting research and writing of the manuscript [6]. The corresponding author is perceived as the author contributing significantly to the article independently of the author position [15]. The corresponding author supervised the planning and execution of the study and the writing of the paper [16]. Table 6 listed the top ten most productive authors. P.V. Giannoudis at the University of Leeds in the UK published the most nonunion articles followed by J.B. Jupiter at the Massachusetts General Hospital in the USA and C.C. Wu at the Chang Gung University in Taiwan. Publication performance of authors was further analysed with the Y-index which is related to the number of first-author publications (FP) and corresponding-author publications (RP). The Y-index combines two parameters (j, h), to evaluate the publication potential and contribution characteristics as a single index. This indicator has been used to compare authors in medical topics, such as occupational therapy [17], child sexual abuse [13] and breast reconstruction [6]. The Y-index is defined as [7]:
where j is the publication potential, a constant related to publication quantity, and h is publication characteristics which can describe the proportion of RP to FP. The greater the value of j, the greater the number of first- and corresponding-author articles by the author. Different values of h represent different proportions of corresponding-author articles from first-author articles.
-
h = π/2, j is the number of corresponding-author articles.
-
π/2 > h > 0.7854 indicates more corresponding-author articles.
-
h = 0.7854 indicates the same number of first- and corresponding-author articles.
-
0.7854 > h > 0 indicates more first-author articles.
-
h = 0, j is the number of first-author articles.
Y-index was applied to evaluate the authors in 8551 (95%) of the 8976 nonunion articles with both of first-author and corresponding-author information in SCI-EXPANDED.
A total of 8551 articles were published by 25,219 authors in which 16,991 authors (67% of 25,219 authors) had no first- or corresponding-author articles with Y-index = (0, 0); 1596 (6.3%) authors published only corresponding-author articles with h = π/2; 446 (1.8%) authors published more corresponding-author articles with π/2 > h > 0.7854; 3613 (14%) authors published the same number of first- and corresponding-author articles with h = 0.7854; 242 (1.0%) authors published more first-author articles with 0.7854 > h > 0; and 2331 (9.2%) authors published only first-author articles with h = 0. Figure 4 shows distribution of the Y-index (j, h) of the top 15 authors with j ≥ 19. Each dot represents one value of the Y-index that could be one author or many authors, for example, P. Hernigou and S.D. Boden who share the same Y-index = (21, 0.9273). C.C. Wu from the Chang Gung University in Taiwan had the highest publication potential with a j of 70 and Y-index = (70, 0.7854). Wu published 42 nonunion articles including 36 first-author articles and 35 corresponding-author articles (Table 6). Wu published not only the most first-author articles and the corresponding-author articles but also the most single-single articles. However, Wu’s nonunion articles had lower CPP2019, followed by D. Ring from the Massachusetts General Hospital of Harvard University in the USA as the corresponding affiliation with a j of 50 and Y-index = (50, 0.9828) and P.V. Giannoudis from the University of Leeds in the UK with a j of 46 and Y-index = (46, 1.266). Comparing the top three authors had higher publication potential in nonunion articles: P.V. Giannoudis had higher CPP2019 of his first-author articles and corresponding-author articles than Wu and Ring, while Ring had higher CPP2019 for his single-author articles (Table 6). M.D. McKee with Y-index = (25, 1.131) and S. Rammelt with Y-index = (25, 0.9048) both had a j of 25. McKee and Rammelt are located on the same curve (j = 25) in Fig. 4, indicating that they had the same publication potential with the same value of j but different publication characteristics [18]. Similarly, T. Niikura (19, 1.138), M. Bhandari (19, 1.043), A. Moghaddam (19, 0.9420) and C.M. Robinson (19, 0.8380) are also located on the same curve (j = 19). Niikura published higher ratio of the number of corresponding-author articles to the number of first-author articles with an h of 1.138, followed by Bhandari with an h of 1.043, Moghaddam with an h of 0.9420 and Robinson with an h of 0.8380. These authors had the same publication potential with a j of 19 but the publication characteristics were also different. D. Ring with Y-index = (50, 0.9828) and M.J. Parker with Y-index = (20, 0.9828) are located on the line (h = 0.9828), indicating that they had the same publication characteristics but different publication potentials [19]. Ring had the greater publication potential with a j of 50 than Parker with a j of 20. It has been pointed out that a bias in analysis of authorship might occur when different authors had the same name, or one author used different names (e.g. maiden names) in their articles [20].
Top ten most frequently cited nonunion-related articles
The total number of citations of a document in the Web of Science Core Collection is updated from time to time. Ho’s group proposed citation indicators TCyear [21] and Cyear [7]. The advantage of using TCyear and Cyear is that they are immutable and ensure repeatability compared with the citation index of the Web of Science Core Collection [22]. Citation frequency is considered to reflect the impact of scientific publications, although this does not necessarily correlate with the paper quality [23]. The best articles can be classified as articles that most researchers can read and cite in peer-reviewed journals [24]. The 8976 nonunion articles ranked differently if sorted by TC2019 than sorted by C2019. A total of 3521 articles (39% of 8976 articles) had no citation in the most recent year (C2019 = 0) and 987 (11%) articles had no citation from their publication year to the end of 2019 (TC2019 = 0). Furthermore, among the top 100 C2019 articles, 34% of the articles were among the top 100 TC2019 articles.
The 8976 nonunion articles were searched out with search keywords on their ‘front page’: title, abstract and author keywords from SCI-EXPANDED in the last three decades. Table 7 lists the ten most frequently cited articles in nonunion research with two citation indicators [7]. Five of the ten articles were published in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery-American Volume (IF2019 = 4.578). Nine of the ten articles were single-country articles from the USA with five articles, France with two and one by Canada and Germany, respectively. The only internationally collaborative article was published by 59 authors from South Africa, the USA, Israel, Finland, the UK, Germany, France, Australia, Canada, Belgium, Netherlands and Norway. The citation history of the top ten most frequently cited articles is presented in Fig. 5. The article by Chen et al. [25] had a sharply increased citation after its publication for ten years in nonunion studies and then decreased. It ranked top on annual citation from 2007 to 2019. An article’s impact might not be always high [22]. A highly cited article published by Friedlaender et al. (2001) had a TC2019 of 723 ranked fourth but had a low impact in 2019 with a C2019 of ten (ranked 217th) indicating that with time, the significance of the article diminished. Although some recently published articles in the past few years have great potential, their TC2019 is not high. The top three cited articles in 2019 by Campana et al. (2014), Xavier et al. (2015) and Goodman et al. (2013) had a C2019 of 117 (ranked 1st), 77 (ranked 2nd) and 73 (ranked 3rd) but had a low TC2019 of 262 (ranked 24th), 220 (ranked 41st) and 387 (ranked 14th).
Five articles were ranked on both the top 10 TC2019 as the most frequently cited articles and C2019 as the most impact in the most recent year articles. These five highly cited and the most impact articles in 2019 articles were summarised as follows:
-
1.
Bone morphogenetic proteins [25]
C2019 of 69 (ranked 4th) and TC2019 of 1389 (ranked 1st)
In this article, Chen et al. [25] was one of the first to provide a state-of-the-art review of the advancements on basic science and clinical applications of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) research. BMPs are extremely important in embryonic development as well as in postnatal cell functions and are involved in the heart, nervous system and cartilage development, as well as postnatal bone formation with strong bone induction properties. Therefore, at that early stage, numerous potential therapeutic applications of BMPs were outlined including bone defects and fracture nonunion. In the years following this publication, BMPs were widely studied and successfully applied in the treatment of nonunions with BMP-2 and BMP-7 currently approved for use by the US Food and Drug Administration [35] and are considered critical components in the therapeutic armamentarium for nonunions [36].
-
2.
Tissue-engineered bone regeneration [26]
C2019 of 56 (ranked 5th) and TC2019 of 1056 (ranked 2nd)
In this pioneer basic science paper, the authors manufactured a combined construct of coral scaffold and marrow stromal cells (MSCs) to fill bony defects in sheep. Contrary to the failure of scaffolds used in the past, the idea was to use the naturally occurring coral exoskeleton which has adequate mechanical properties and increased porosity similar to cancellous bone, in order to better deliver the MSCs. The authors established ‘critical’-size bone defects of increasing width in sheep metatarsals and treated the defects with either coral exoskeleton alone, or in combination with fresh bone marrow or MSCs. They succeeded in bridging the defects after 16 weeks in the third group of combined coral exoskeleton and MSCs and this was the first study to effectively demonstrate replacement of a critical defect with mature bone that would have evolved into a nonunion otherwise.
-
3.
Percutaneous autologous bone-marrow grafting for nonunions: Influence of the number and concentration of progenitor cells [30]
C2019 of 49 (ranked 6th) and TC2019 of 534 (ranked 6th)
This study was the first one to provide guidelines and revive interest on the harvesting of bone marrow aspirate concentrate (BMAC) from the iliac crest and its subsequent injection in atrophic tibia nonunion sites [30]. Following bone marrow aspiration from bilateral iliac crests and its concentration via a cell separator, 20 cc of BMAC were injected into the nonunion site of 60 patients. Fifty-three patients went into union, whereas seven developed nonunion. Although the study confirmed the efficacy of the procedure from previous reports [37], it was the first to show that the number of progenitor cells as well as the need for increased concentration is critical in order to obtain union. From that point onward, BMAC in the treatment of nonunions has been widely used and the area is still under constant evolution [38].
-
4.
Non-operative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures: a multicenter, randomized clinical trial [39]
C2019 of 41 (ranked 9th) and TC2019 of 442 (ranked 8th)
Prior to this study, even the most displaced midshaft clavicle fractures, were traditionally receiving non-operative treatment based on earlier reports [40] that had inherent biases. However, some subsequent studies showed increased level of complications such as nonunion and malunion as well as lower rates of patient satisfaction [41]. This prospective randomised clinical trial coming from eight Canadian centres and published by the Canadian Orthopaedic Association looked at 132 patients divided into two groups of similar characteristics and who received either plate fixation or non-operative treatment with a sling [39]. The authors looked at time to radiographic union, constant shoulder scores, DASH scores, complications and patient satisfaction at one year. Plate fixation showed better outcomes as far as function (scores) and malunion/nonunion complications, as well as patient satisfaction. In the plate fixation group, three out of 67 patients developed a wound infection but were successfully addressed with local wound care and antibiotics, and later plate removal with formal irrigation/debridement after union. The authors concluded that primary plate fixation of those injuries is justified. Although this study significantly helped revive the debate of operative versus non-operative management of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures, it is still unclear what the best option is, and patients must be adequately informed of the pros and cons of each treatment, as outlined in a recent systematic review also from Canada [42].
-
5.
Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2 for treatment of open tibial fractures: a prospective, controlled, randomized study of four hundred and fifty patients [27]
C2019 of 39 (ranked 10th) and TC2019 of 937 (ranked 3rd)
This multi-author randomised control trial by the BMP-2 Evaluation in Surgery for Tibial Trauma (BESTT) study group evaluated the safety and efficacy of the use of recombinant BMP-2 (rhBMP-2) in the treatment of open tibial shaft fractures compared to the standard of care [27]. Τhe authors looked at 121 patients with a 12-month follow-up receiving either intramedullary nail alone with routine wound care or intramedullary nailing with addition of an implant consisting of an absorbable collagen sponge containing rhBMP-2 of 6 or 12 mg over the fracture site. The study found that the patients who received the 12-mg dose rhBMP-2 implant had lower rates of hardware failure and infections and demonstrated faster wound healing and required fewer number of secondary interventions than the other two groups. Since then, there have been several clinical studies showing that rhBMP-2 (as well as rhBMP-7) enhances bone defect regeneration in adults and as stated earlier they have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for specific clinical indications [35].
Research focuses and their development trends
Ho’s group proposed distribution of words in article titles, abstracts, author keywords and KeyWords Plus in different periods as information to evaluate main research focuses and find their development trends in research topics [43]. The results of keyword analyses provide information about the main and possible research foci as each word cluster comprised several supporting words. Thus, the development of the seven possible main research foci in nonunion-related research is presented. Figure 6 shows the development of the seven topics.
-
Topic 1: Epidemiology
Supporting words—epidemiology, incidence, incidences, prevalence and prevalences
-
Topic 2: Aetiology (or etiology, or cause)
Supporting words—aetiology, cause, causes, caused, factor, factors, heal, heals, infection, infections, infectious, infected and etiology
-
Topic 3: Classification
Supporting words—classification and classifications
-
Topic 4: Diagnosis and prediction of nonunion
Supporting words—predict, predictable, predictably, predicting, prediction, predictive, predictor, predictors, predicts, score, scoring, scores, diagnose, diagnoses, diagnosing, diagnosis, diagnostic, diagnostics, radiographic, radiographs, radiography, radiologic, radiological, radiotherapy, radioulnar, biomarkers, mark, markedly, marker and markers
-
Topic 5: Treatment modalities
Supporting words—treat, treating, treatment, treatments, management, manage and managing
-
Topic 6: Functional outcomes
Supporting words—outcome and outcomes
-
Topic 7: Health economics
Supporting words—cost, costs, economic, economical, economically, economics, burden and burdens
These seven topics identified support the efforts of clinicians over the years to understand better the characteristics, aetiology, diagnosis, prediction and treatment options that can be applied successfully to treat this difficult complication. Moreover, the burden of this condition, on the physiological and mental state of patients, has received a lot of attention. Finally, the cost-related implications of treatment have also been explored. All of the above themes represent the spectrum of research activities that have taken place up to now. It is envisaged that in the future, the same themes of research on nonunion will continue to dominate the activities of the scientific and clinical community.
Limitations
Bibliometrics represents a quantitative method of publications, allowing researchers and scientists to assess numerous, unlimited peer-reviewed publications in a specific field of science. It is based on the citation number of existing publications. Interestingly, it should be emphasised that there is no correlation between the frequency of citations and the quality of the research published. In addition, due the inherent delays between publishing an articles and breakthroughs and innovations in treatment modalities, high-cited papers identified in bibliometric analysis may not represent the latest technological advances applied in the clinical setting. While bibliometric analysis can identify trends of research, specific institutions with focused research programmes and outputs in a topic of interest, it cannot provide evidence in terms of guidelines of treatment. Strengths of bibliometrics include mapping of the literature, identifying key opinion leaders and development of networking for collaborative research.
Conclusions
A bibliometric analysis of the literature was carried out on fracture nonunion which is the most common fracture fixation complication in the field of orthopaedic trauma. Overall, over a 30-year period, 10,064 nonunion-related publications were published. Such information was generated as number of citations, publications outputs, journals published the articles, institutions and countries involved and focus of topics related to fracture nonunion (epidemiology, classification, diagnosis, prediction, treatment modalities, functional outcomes and cost of treatment). It is envisaged that the information contained in this study will assist clinicians and scientist to shape their research focus in the future and by having identified prominent researchers and institutions and help stimulate international team collaborative efforts.
References
Chloros GD, Howard A, Giordano V, Giannoudis PV (2020) Radiographic long bone fracture healing scores: can they predict non-union? Injury 51:1693–1695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2020.07.024
Brinker MR, Hanus BD, Sen M, O'Connor DP (2013) The devastating effects of tibial nonunion on health-related quality of life. J Bone Joint Surg Am 95:2170–2176. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.L.00803
Li Y, Xu G, Long X, Ho Y-S (2019) A bibliometric analysis of classic publications in web of science category of orthopedics. J Orthop Surg Res 14:1–11
Ho Y-S (2018) Comments on “Mapping the scientific research on non-point source pollution: A bibliometric analysis” by Yang et al.(2017). Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:30737–30738
Garfield E (1990) KeyWords Plus-ISI's breakthrough retrieval method. 1. Expanding your searching power on current-contents on diskette. Curr Contents 32:5–9
Li Y, Wang X, Thomsen JB, Nahabedian MY, Ishii N, Rozen WM, Long X, Ho Y-S (2020) Research trends and performances of breast reconstruction: a bibliometric analysis. Ann Transl Med 8
Ho Y-S (2012) Top-cited articles in chemical engineering in Science Citation Index Expanded: a bibliometric analysis. Chin J Chem Eng 20:478–488
Chuang K, Wang M, Ho Y (2011) High-impact papers presented in the subject category database of the institute for scientific information. Scientometrics 87:551–562
Ho YS (2021) Comments on: Tang et al. (2020) ‘Bibliometric review of research trends on disinfection by-products in drinking water during 1975-2018’ (In Press). Sep Purif Technol 241
Hsuly Y-H, Ho Y-S (2014) Highly cited articles in health care sciences and services field in science citation index expanded a bibliometric analysis for 1958-2012. Methods Inf Med 53:446–458
Monge-Nájera J, Ho Y-S (2017) El Salvador publications in the Science Citation Index Expanded: subjects, authorship, collaboration and citation patterns. Rev Biol Trop 65:1428–1436
Chuang K-Y, Huang Y-L, Ho Y-S (2007) A bibliometric and citation analysis of stroke-related research in Taiwan. Scientometrics 72:201–212
Vega-Arce M, Salas G, Núñez-Ulloa G, Pinto-Cortez C, Fernandez IT, Ho Y-S (2019) Research performance and trends in child sexual abuse research: a Science Citation Index Expanded-based analysis. Scientometrics 121:1505–1525
Ho Y-S (2013) Comments on “a bibliometric study of earthquake research: 1900–2010”. Scientometrics 96:929–931
Mattsson P, Sundberg CJ, Laget P (2011) Is correspondence reflected in the author position? A bibliometric study of the relation between corresponding author and byline position. Scientometrics 87:99–105
Burman KD (1982) "Hanging from the masthead": reflections on authorship. Ann Intern Med 97:602–605. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-97-4-602
Brown T, Gutman SA, Ho YS, Fong KNK (2018) A bibliometric analysis of occupational therapy publications. Scand J Occup Ther 25:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/11038128.2017.1329344
Ho Y-S, Hartley J (2016) Classic articles published by American scientists (1900–2014): a bibliometric analysis. Curr Sci 1156–1165
Chuang K-Y, Ho Y-S (2015) An evaluation based on highly cited publications in Taiwan. Curr Sci 933–941
Zhang J, Wang M-H, Ho Y-S (2012) Bibliometric analysis of aerosol research in meteorology and atmospheric sciences. Int J Environ Pollut 49:16–35
Ming HW, Hui ZF, Yuh SH (2011) Comparison of universities’ scientific performance using bibliometric indicators. Malays J Libr Inf Sci 16:1–19
Fu H-Z, Wang M-H, Ho Y-S (2012) The most frequently cited adsorption research articles in the Science Citation Index (Expanded). J Colloid Interface Sci 379:148–156
Brandt JS, Downing AC, Howard DL, Kofinas JD, Chasen ST (2010) Citation classics in obstetrics and gynecology: the 100 most frequently cited journal articles in the last 50 years. Am J Obstet Gynecol 203:355.e351–355.e357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2010.07.025
Robinson JK, Callen JP (2010) The best of the best: a new section led by Henry W. Lim, MD. Arch Dermatol 146:554–554
Chen D, Zhao M, Mundy GR (2004) Bone morphogenetic proteins. Growth Factors 22:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1080/08977190412331279890
Petite H, Viateau V, Bensaid W, Meunier A, de Pollak C, Bourguignon M, Oudina K, Sedel L, Guillemin G (2000) Tissue-engineered bone regeneration. Nat Biotechnol 18:959–963
Govender S, Csimma C, Genant HK, Valentin-Opran A, Amit Y, Arbel R, Aro H, Atar D, Bishay M, Börner MG, Chiron P, Choong P, Cinats J, Courtenay B, Feibel R, Geulette B, Gravel C, Haas N, Raschke M, Hammacher E, van der Velde D, Hardy P, Holt M, Josten C, Ketterl RL, Lindeque B, Lob G, Mathevon H, McCoy G, Marsh D, Miller R, Munting E, Oevre S, Nordsletten L, Patel A, Pohl A, Rennie W, Reynders P, Rommens PM, Rondia J, Rossouw WC, Daneel PJ, Ruff S, Rüter A, Santavirta S, Schildhauer TA, Gekle C, Schnettler R, Segal D, Seiler H, Snowdowne RB, Stapert J, Taglang G, Verdonk R, Vogels L, Weckbach A, Wentzensen A, Wisniewski T (2002) Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 for treatment of open tibial fractures: a prospective, controlled, randomized study of four hundred and fifty patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84:2123–2134. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-200212000-00001
Friedlaender GE, Perry CR, Cole JD, Cook SD, Cierny G, Muschler GF, Zych GA, Calhoun JH, LaForte AJ, Yin S (2001) Osteogenic protein-1 (bone morphogenetic protein-7) in the treatment of tibial nonunions: a prospective, randomized clinical trial comparing rhOP-1 with fresh bone autograft. J Bone Jt Surg 83:S151
Bruder SP, Kraus KH, Goldberg VM, Kadiyala S (1998) The effect of implants loaded with autologous mesenchymal stem cells on the healing of canine segmental bone defects. J Bone Joint Surg Am 80:985–996. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-199807000-00007
Hernigou P, Poignard A, Beaujean F, Rouard H (2005) Percutaneous autologous bone-marrow grafting for nonunions. Influence of the number and concentration of progenitor cells. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87:1430–1437. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.D.02215
Zhang X, Schwarz EM, Young DA, Puzas JE, Rosier RN, O'Keefe RJ (2002) Cyclooxygenase-2 regulates mesenchymal cell differentiation into the osteoblast lineage and is critically involved in bone repair. J Clin Invest 109:1405–1415. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci15681
Society COT (2007) Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:1
Claes L, Heigele C (1999) Magnitudes of local stress and strain along bony surfaces predict the course and type of fracture healing. J Biomech 32:255–266
Hill JM, McGuire MH, Crosby LA (1997) Closed treatment of displaced middle-third fractures of the clavicle gives poor results. J Bone Joint Surg Br 79:537–539. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.79b4.7529
Barcak EA, Beebe MJ (2017) Bone morphogenetic protein: is there still a role in orthopedic trauma in 2017? Orthop Clin 48:301–309
Zhou Y-Q, Tu H-L, Duan Y-J, Chen X (2020) Comparison of bone morphogenetic protein and autologous grafting in the treatment of limb long bone nonunion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res 15:288. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-020-01805-4
Connolly JF, Guse R, Tiedeman J, Dehne R (1991) Autologous marrow injection as a substitute for operative grafting of tibial nonunions. Clin Orthop Relat Res 259–270
Imam MA, Holton J, Ernstbrunner L, Pepke W, Grubhofer F, Narvani A, Snow M (2017) A systematic review of the clinical applications and complications of bone marrow aspirate concentrate in management of bone defects and nonunions. Int Orthop 41:2213–2220. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-017-3597-9
Society COT (2007) Nonoperative treatment compared with plate fixation of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures. A multicenter, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg-Am Vol 89:1
Neer CS 2nd (1960) Nonunion of the clavicle. J Am Med Assoc 172:1006–1011. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1960.03020100014003
McKee M, Schemitsch E, Stephen DJ, Kreder H, Yoo D, Harrington J (1999) Functional outcome following clavicle fractures in polytrauma patients. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 47:616
Axelrod DE, Ekhtiari S, Bozzo A, Bhandari M, Johal H (2020) What is the best evidence for management of displaced midshaft clavicle fractures? A systematic review and network meta-analysis of 22 randomized controlled trials. Clin Orthop Relat Res 478:392–402. https://doi.org/10.1097/corr.0000000000000986
Wang C-C, Ho Y-S (2016) Research trend of metal–organic frameworks: a bibliometric analysis. Scientometrics 109:481–513
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors satisfy the four ICMJE criteria as follows:
1. Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis or interpretation of data for the work
2. Drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content
3. Final approval of the version to be published
4. Agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Giannoudis, P.V., Chloros, G.D. & Ho, YS. A historical review and bibliometric analysis of research on fracture nonunion in the last three decades. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 45, 1663–1676 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-021-05020-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-021-05020-6