Abstract
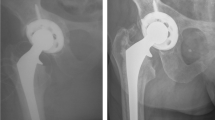
We reviewed 81 consecutive ABG I primary total hip replacements implanted in 72 patients between January 1993 and December 1998. The mean follow-up was 8.2 (range 7–12) years. There was significant polyethylene wear and osteolysis associated with the acetabular cup .The cumulative survival of the cup with revision being the end point at 8.2 years was 95.1% (95% CI: 92–97.6%). However, the cumulative survival of the cup with revision and aseptic loosening together was 72% (95% CI: 61–78%) and survival of the acetabular liner for wear was 62% (95% CI: 48–74%). Stem survival with revision being the end point was 100%. In spite of significant radiological failures of the cups, most patients remained asymptomatic. Though results of the ABG stems in this series were good, we advocate a regular follow-up of all these hips in view of the poor outcome of the cups.
Résumé
Nous avons examiné 81 prothèses totales primaires consécutives de la hanche de type ABG I chez 72 malades opérés entre janvier 1993 et décembre 1998. Le suivi moyen était de 8,2 ans (7–12 ans). Il y avait une usure notable du polyéthylène avec ostéolyse cotyloidienne . La survie à 8,2 ans de la cupule acétabulaire avec une révision comme événement final est de 95,1% (95% CI:92–97.6). Cependant la survie cumulative de la cupule acétabulaire avec révision ou descellement aseptique est de 72% (95% CI:61–78%) et la survie des inserts acétabulaires pour usure est de 62% (95% CI:48–74%). La survie de la tige avec révision comme événement final est de 100%. Malgré les échecs radiologiques des cupules, la plupart des malades sont restées asymptomatiques. Bien que les résultats des tiges ABG dans cette série soient bons, nous préconisons une surveillance régulière de ces prothèses vu le résultat médiocre des cupules cotyloidiennes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali MS, Kumar A (2003) Hydroxiapatite coated RM cup in primary hip arthroplasty 27:90–93
Araujo CG, Gonzales FJ, Tonino A (1998) International ABG study group. Rheumatoid Arthritis and hydroxyapatite coated hip prosthesis: five year results. J Arthroplasty 6:660–667
Blacha J (2004) High Osteolysis and revision rate with hydroxyapatite coated ABG hip prosthesis. 65 hips in 56 patients followed for 6–9 years. Acta Orthop Scand 75(3):276–282
Bruijn JD, Seelen RM, Feenstra RM, Hansen BE, Bernoski FP (1995) Failure of Mecring screw-ring acetabular component in total hip arthroplasty. A 3 to 7-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77:760–766
DeLee JG, Charnley J (1976) Radiological demarcation of cemented sockets in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop 121:20–32
Duffy P, Sher JL, Partington PF (2004) Premature wear and Osteolysis in HA coated uncemented total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86:36–38
Effenberger H Ramsaver T, Dorn U, Imhof M (2004) Factors influencing the revision rate of Zweymuller acetabular cup. Int Orthop 28:155–158
Fernandez-Gonzalez J, Canosa Sevillano R, Garcia Araujo C (1997) Cementless total hip arthroplasty with threaded cup. Int Orthop 21:327–331
Gallo J, Kaminek P, Zapletalova J (2003) Early failure of polyethylene liner in ABG I total hip prosthesis. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech 70:343–349
Giannikas KA, Din R, Sadiq S, Dunningham TH (2002) Medium term results of ABG total hip arthroplasty in young patients. J Arthroplasty 17:184–188
Gruen TA, McNeice GM, Amstutz HC (1979) "Modes of failure" of cemented stem-type femoral components: a radiographic analysis of loosening. Clin Orthop 141:17–27
Harris WH (1969) Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures. Treatment by mould arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 51:737–755
Heekin RD, Callaghan JJ, Hopkinson WJ (1993) The porous coated anatomic total hip prosthesis inserted without cement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 75:77–91
Hendrix RW, Wixon RL, Rana NA, Rogers LF (1983) Arthrography after total hip arthroplasty. A modified technique used in the diagnosis of pain. Radiology 148:647–652
Hernandez-Vaquero D, Suarez Vazquez A, Fernandez-Corona C, Menendez-Vinvela G, Alegre-Matio R, Garcia-Sandoval MA (1996) Loosening of threaded acetabular cups in arthroplasty of the hip. The association with different types of coxarthrosis. Int Orthop 20:70–74
Johnston RC, Fitzgerald RH, Harris WH (1990) Clinical and Radiological evaluation of total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 72:161–168
Martell JM, Pierson RH 3rd, Jacobs JJ (1993) Primary total hip reconstruction with titanium fibre coated prosthesis inserted without cement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 75:554–571
Mckellop H, Shen FW, Lu B, Campbell P, Salovey R (2000) Effect of sterilization method and other modifications on the wear resistance of acetabular cups made of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. A hip-simulator study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82:1708–1725
Owen TD, Moran CG, Smith SR, Pinder IM (1994) Results of uncemented porous-coated anatomic total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 76:258–262
Rogers A, Kulkarni R, Downes EM (2003) The ABG hydroxyapatite-coated hip prosthesis: one hundred consecutive operations with average 6-year follow-up. J Arthroplasty 18:619–625
Salvati E, Lieberman J, Huko, Evans B (1995) Complications of femoral and acetabular modularity. Clin Orthop Relat Res 319:85–93
Schmalzried TP, Guttmann D, Grecula M, Amstutz HC (1994) The relationship between the design, position, and articular wear of acetabular components inserted without cement and the development of pelvic osteolysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 76:677–688
Schmalzried T, Shepherd EF, Dorey FJ (2000) The John Charnley Award. Wear is a function of use, not time. Clin Orthop Relat Res 381:36–46
Shih CH, Lee PC, Chen JH (1997) Measurement of polyethylene wear in cementless total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br 79:361–365
Spicer DD, Scharper LA, Pomeroy DL, Badenhausen We Jr, Curry JI, Suthers KE, Smith MW (2001) Cementless cup fixation in total hip arthroplasty after 5–8 years. Int Orthop 25:286–289
Tompkins GS, Jacobs JJ, Kull LR (1997) Primary total hip arthroplasty with a porous-coated acetabular component. Seven-to-ten-year results. J Bone Joint Surg Am 79:169–176
Tonino AJ, Rahmy AI (2000) The hydroxyapatite–ABG hip system: 5- to 7-year results from an international multicentre study. The International ABG Study Group. J Arthroplasty 15:274–282
Von Schewelow T, Sanzen L, Onsten I, Carlsson A (2004) Catastrophic failure of an uncemented acetabular component due to high wear and osteolysis: an analysis of 154 omnifit prostheses with mean 6-year followup. Acta Orthop Scand 75:283–294
Wilkinson JM, Gordan A, Stockley I (2003) Experiences with the Plasmacup—early stability, wear, remodelling and outcome. Int Orthop 27 (Suppl 1):16–19
Zicat B, Engh CA, Gokcen E (1995) Patterns of osteolysis around total hip components inserted with and without cement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77:432–439
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badhe, S., Livesley, P. Early polyethylene wear and osteolysis with ABG acetabular cups (7- to 12-year follow-up). International Orthopaedics (SICO 30, 31–34 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-005-0021-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-005-0021-7