Abstract
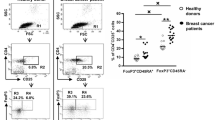
Expression levels of VEGF and Her-2, levels of T-regulatory (Treg) cells, levels of CD3+ cells, and ratios of Th (CD4+ T cells)/Tr (Treg) cells were compared between stage I, II, III, and IV breast cancer patients (n = 120) prior to chemotherapy and healthy women (n = 30). Cells from peripheral blood were counted by flow cytometry, Her-2 and VEGF expression was detected by pathological examination, and Her-2 was detected by FISH. Breast cancer patients had more Treg cells and a lower ratio of Th/Tr cells than the healthy women. Stage IV breast cancer patients had more Treg cells and a lower ratio of Th/Tr cells than stage I, II, or III breast cancer patients. Patients positive for VEGF had a lower ratio of Th/Tr cells compared with patients negative for VEGF, and those positive for both VEGF and Her-2 also had a lower ratio of Th/Tr cells compared with patients not positive for both VEGF and Her-2. The decreased Th/Tr cells ratio indicates impaired immune function, suggesting that the stage IV breast cancer and the Her-2/VEGF-positive breast cancer patients have lower immune function.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dunn GP, Old LJ, Schreiber RD (2004) The three Es of cancer immunoediting. Annu Rev Immunol 22:329–360
Croci DO, Zacarías Fluck MF, Rico MJ, Matar P, Rabinovich GA, Scharovsky OG (2007) Dynamic cross-talk between tumor and immune cells in orchestrating the immunosuppressive network at the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Immunol Immunother 56(11):1687–1700
Krupnick AS, Kreisel D, Szeto WY, Popma SH, Amin KM, Moore JS, Rosengard BR (2001) Multiparameter flow cytometric approach for simultaneous evaluation of T lymphocyte endothelial cell interactions. Cytometry 46(5):271–280
Abo-Elenein A, Elgohary S, Hashish A, El-Halaby E (2008) Significance of immunoregulatory T cells in different stages of breast cancer patients. Egyptian J Immunol/Egyptian Ass Immunologists 15(2):145
Sutmuller RP, van Duivenvoorde LM, van Elsas A, Schumacher TN, Wildenberg ME, Allison JP, Toes RE, Offringa R, Melief CJ (2001) Synergism of cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 blockade and depletion of CD25(+) regulatory T cells in antitumor therapy reveals alternative pathways for suppression of autoreactive cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses. J Exp Med 194(6):823–832
Li L, Chao QG, Ping LZ, Xue C, Xia ZY, Qian D, Shi-ang H (2009) The prevalence of FOXP3+ regulatory T-cells in peripheral blood of patients with NSCLC. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 24(3):357–367
Taneja P, Maglic D, Kai F, Zhu S, Kendig RD, Fry EA, Inoue K (2010) Classical and novel prognostic markers for breast cancer and their clinical significance. Cli Med Insights Oncol 4:15–34
Group IBCS (2006) Tamoxifen after adjuvant chemotherapy for premenopausal women with lymph node-positive breast cancer: international breast cancer study group trial 13–93. J Clin Oncol 24(9):1332–1341. doi:10.1200/jco.2005.03.0783
Erdem O, Dursun A, Coskun U, Gunel N (2005) The prognostic value of p53 and c-erbB-2 expression, proliferative activity and angiogenesis in node-negative breast carcinoma. Tumori 91(1):46–52
Blackwell KL, Dewhirst MW, Liotcheva V, Snyder S, Broadwater G, Bentley R, Lal A, Riggins G, Anderson S, Vredenburgh J (2004) HER-2 gene amplification correlates with higher levels of angiogenesis and lower levels of hypoxia in primary breast tumors. Clin Cancer Res 10(12):4083
Clere N, Bermont L, Fauconnet S, Lascombe I, Saunier M, Vettoretti L, Plissonnier ML, Mougin C (2007) The human papillomavirus type 18 E6 oncoprotein induces Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor 121 (VEGF121) transcription from the promoter through a p53-independent mechanism. Exp Cell Res 313(15):3239–3250
Tai W, Qin B, Cheng K (2010) Inhibition of breast cancer cell growth and invasiveness by dual silencing of HER-2 and VEGF. Mol Pharm 7(2):543–556
Wang Z, Meng H, Han C et al (2010) Expression of human epidermal growth factor 2 and vascular endothelial growth factor in primary or recurrent metastatic breast cancer. Zhong Guo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 32(4):403–406
Greene F, Page D, Fleming I, Fritz A, Balch C, Haller D, Morrow M (2002) AJCC cancer staging man. Springer, NY
Wolff AC, Hammond MEH, Schwartz JN, Hagerty KL, Allred DC, Cote RJ, Dowsett M, Fitzgibbons PL, Hanna WM, Langer A (2007) American society of clinical oncology/college of American pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med 131(1):18–43
Al-Dissi AN, Haines DM, Singh B, Kidney BA (2010) Immunohistochemical expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 in canine simple mammary gland adenocarcinomas. Can Vet J 51(10):1109
Xu L, Yang W (1996) Standardization of immunohistochemistry result. China Oncology 6(4):229–231
Lan C, Liu JM, Liu TW, Hsu DH, Liang S, Chen JR, Peng JW (2005) erb-b2 amplification by fluorescence in situ hybridization in breast cancer specimens read as 2+ in immunohistochemical analysis. Am J Clin Pathol 124(1):97
Horlock C, Stott B, Dyson P, Morishita M, Coombes R, Savage P, Stebbing J (2009) The effects of trastuzumab on the CD4+ CD25+ FoxP3+ and CD4+ IL17A+ T-cell axis in patients with breast cancer. Br J Cancer 100(7):1061
Tan W, Zhang W, Strasner A, Grivennikov S, Cheng JQ, Hoffman RM, Karin M (2011) Tumour-infiltrating regulatory T cells stimulate mammary cancer metastasis through RANKL-RANK signalling. Nature 470(7335):548–553
Bates GJ, Fox SB, Han C, Leek RD, Garcia JF, Harris AL, Banham AH (2006) Quantification of regulatory T cells enables the identification of high-risk breast cancer patients and those at risk of late relapse. J Clin Oncol 24(34):5373
Wolf AM, Rumpold H, Wolf D, Gastl G, Reimer D, Jenewein N, Marth C, Zeimet AG (2007) Role of forkhead box protein 3 expression in invasive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 25(28):4499
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X, Cheng P, Mottram P, Evdemon-Hogan M, Conejo-Garcia JR, Zhang L, Burow M (2004) Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat Med 10(9):942–949
Wada J, Yamasaki A, Nagai S, Yanai K, Fuchino K, Kameda C, Tanaka H, Koga K, Nakashima H, Nakamura M, Tanaka M, Katano M, Morisaki T (2008) Regulatory T-cells are possible effect prediction markers of immunotherapy for cancer patients. Anticancer Res 28(4C):2401–2408
Perez SA, Karamouzis MV, Skarlos DV, Ardavanis A, Sotiriadou NN, Iliopoulou EG, Salagianni ML, Orphanos G, Baxevanis CN, Rigatos G (2007) CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T-cell frequency in HER-2/neu (HER)-positive and HER-negative advanced-stage breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 13(9):2714
Rech AJ, Mick R, Kaplan DE, Chang KM, Domchek SM, Vonderheide RH (2010) Homeostasis of peripheral FoxP3+ CD4+ regulatory T cells in patients with early and late stage breast cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 59(4):599–607
Brivio F, Fumagalli L, Parolini D, Messina G, Rovelli F, Rescaldani R, Vigore L, Vezzo R, Vaghi M, Di Bella S (2008) T-helper/T-regulator lymphocyte ratio as a new immunobiological index to quantify the anticancer immune status in cancer patients. In Vivo 22(5):647
Lissoni P, Brivio F, Fumagalli L, Messina G, Meregalli S, Porro G, Rovelli F, Vigore L, Tisi E, D’amico G (2009) Effects of the conventional antitumor therapies surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and immunotherapy on regulatory T lymphocytes in cancer patients. Anticancer Res 29(5):1847
Characiejus D, Jacobs JJL, Pasukoniene V, Kazlauskaite N, Danileviciute V, Mauricas M, Den Otter W (2011) Prediction of response in cancer immunotherapy. Anticancer Res 31(2):639–647
Ohwada S, Iino Y, Nakamura S, Takeyoshi I, Tanahashi Y, Izumi M, Kawashima Y, Arai M, Kobayashi I, Sato Y (1994) Peripheral blood T cell subsets as a prognostic factor in gastric cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 24(1):7
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Innovation Fund from the Chinese PLA General Hospital (No. 06LN14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Zk., Yang, B., Liu, H. et al. Regulatory T cells increase in breast cancer and in stage IV breast cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 61, 911–916 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-011-1158-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-011-1158-4