Abstract
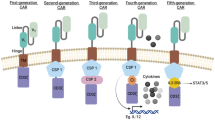
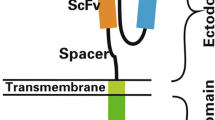
Redirecting T cell effector functions towards pre-defined target cells represents an attractive concept in the adoptive immunotherapy of malignant diseases. Our understanding of the mechanisms of T cell activation and costimulation as well as the design of recombinant T cell receptors have made major progress in the last years. Translating recent concepts of T cell stimulation into recombinant protein design provides the basis to engineer T cells with both pre-defined specificity and costimulatory capacity in order to enhance anti-tumor immunity and to break tolerance. Dual signaling immunoreceptors providing the CD3ζ signal simultaneously with an appropriate costimulatory signal moreover allows to modulate the quality of the anti-tumor T cell response in a predicted fashion.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boon T, Cerottini JC, Van den Eynde B, van der Bruggen P, Van Pel A (1994) Tumor antigens recognized by T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol 12:337–365
Lee PP, Yee C, Savage PA, Fong L, Brockstedt D, Weber JS, Johnson D, Swetter S, Thompson J, Greenberg PD, Roederer M, Davis MM (1999) Characterization of circulating T cells specific for tumor-associated antigens in melanoma patients. Nat Med 5:677–685
Schumacher TN (2002) T-cell-receptor gene therapy. Nat Rev Immunol 2:512–519
Morgan RA, Dudley ME, Wunderlich JR, Hughes MS, Yang JC, Sherry RM, Royal RE, Opalian SL, Kammula US, Restifo NP, Zheng Z, Nahvi A., de Vries CR, Rogers-Freezer LJ, Maroukakis SA, Rosenberg SA (2006) Cancer regression in patients after transfer of genetically engineered lymphocytes. Science 314:126–129
Gross G, Gorochov G, Waks T, Eshhar Z (1989) Generation of effector T cells expressing chimeric T cell receptor with antibody type-specificity. Transplant Proc 21:127–130
Eshhar Z, Waks T, Gross G, Schindler DG (1993) Specific activation and targeting of cytotoxic lymphocytes through chimeric single chains consisting of antibody-binding domains and the gamma or zeta subunits of the immunoglobulin and T-cell receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:720–724
Abken H, Hombach A, Heuser C (2003) Immune response manipulation: recombinant immunoreceptors endow T-cells with predefined specificity. Curr Pharm Des 9:1992–2001
Hombach A, Heuser C, Abken H (2002) The recombinant T cell receptor strategy: insights into structure and function of recombinant immunoreceptors on the way towards an optimal receptor design for cellular immunotherapy. Curr Gene Ther 2:211–226
Hombach A, Heuser C, Sircar R, Tillmann T, Diehl V, Kruis W, Pohl C, Abken H (1997) T cell targeting of TAG72 + tumor cells by a chimeric receptor with antibody-like specificity for a carbohydrate epitope. Gastroenterology 113:1163–1170
Westwood JA, Smyth MJ, Teng MW, Moeller M, Trapani JA, Scott AM, Smyth FE, Cartwright GA, Power BE, Honemann D, Prince HM, Darcy PK, Kershaw MH (2005) Adoptive transfer of T cells modified with a humanized chimeric receptor gene inhibits growth of Lewis-Y-expressing tumors in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:19051–19056
Altenschmidt U, Kahl R, Moritz D, Schnierle BS, Gerstmayer B, Wels W, Groner B (1996) Cytolysis of tumor cells expressing the Neu/erbB-2, erbB-3, and erbB-4 receptors by genetically targeted naive T lymphocytes. Clin Cancer Res 2:1001–1008
Haynes NM, Trapani JA, Teng MW, Jackson JT, Cerruti L, Jane SM, Kershaw MH, Smyth MJDarcy PK (2002) Rejection of syngeneic colon carcinoma by CTLs expressing single-chain antibody receptors codelivering CD28 costimulation. J Immunol 169:5780–5786
Hombach A, Schlimper C, Sievers E, Frank S, Schild HH, Sauerbruch T, Schmidt-Wolf IG, Abken H (2006) A recombinant anti-carcinoembryonic antigen immunoreceptor with combined CD3ζ-CD28 signalling targets T cells from colorectal cancer patients against their tumour cells. Gut 55:1156–1164
Hombach A, Muche JM, Gerken M, Gellrich S, Heuser C, Pohl C, Sterry W, Abken H (2001) T cells engrafted with a recombinant anti-CD30 receptor target autologous CD30+ cutaneous lymphoma cells. Gene Ther 8:891–895
Hombach A, Heuser C, Marquardt T, Wieczarkowiecz A, Groneck V, Pohl C, Abken H (2001) CD4+ T cells engrafted with a recombinant immunoreceptor efficiently lyse target cells in a MHC antigen- and Fas-independent fashion. J Immunol 167:1090–1096
Hombach A, Köhler H, Rappl G, Abken H (2006) Human CD4+ T cells lyse tumor cells via granzyme/perforin upon circumvention of MHC restriction by grafting with a recombinant, antibody-derived immunoreceptor. J Immunol 177:5668-675
Friedmann-Morvinski D, Bendavid A, Waks T, Schindler D, Eshhar Z (2005) Redirected primary T cells harboring a chimeric receptor require costimulation for their antigen-specific activation. Blood 105:3087–3093
Brocker T, Riedinger M, Karjalainen K (1996) Redirecting the complete T cell receptor/CD3 signaling machinery towards native antigen via modified T cell receptor. Eur J Immunol 26:1770–1774
Hombach A, Sent D, Schneider C, Heuser C, Koch D, Pohl C, Seliger B, Abken H (2001) T-cell activation by recombinant receptors: CD28 costimulation is required for interleukin 2 secretion and receptor-mediated T-cell proliferation but does not affect receptor-mediated target cell lysis. Cancer Res 61:1976–1982
Weijtens ME, Willemsen RA, van Krimpen BA, Bolhuis RL (1998) Chimeric scFv/gamma receptor-mediated T-cell lysis of tumor cells is coregulated by adhesion and accessory molecules. Int J Cancer 77:181–187
Alvarez-Vallina L, Hawkins RE (1996) Antigen-specific targeting of CD28-mediated T cell co-stimulation using chimeric single-chain antibody variable fragment-CD28 receptors. Eur J Immunol 26:2304–2309
Finney HM, Lawson AD, Bebbington CR, Weir AN (1998) Chimeric receptors providing both primary and costimulatory signaling in T cells from a single gene product. J Immunol 161:2791–2797
Eshhar Z, Waks T, Bendavid A, Schindler DG (2001) Functional expression of chimeric receptor genes in human T cells. J Immunol Methods 248:67–76
Maher J, Brentjens RJ, Gunset G, Riviere I, Sadelain M (2002) Human T-lymphocyte cytotoxicity and proliferation directed by a single chimeric TCRzeta /CD28 receptor. Nat Biotechnol 20:70–75
Haynes NM, Trapani JA, Teng MW, Jackson JT, Cerruti L, Jane SM, Kershaw MH, Smyth MJ, Darcy PK (2002) Single-chain antigen recognition receptors that costimulate potent rejection of established experimental tumors. Blood 100:3155–3163
Hombach A, Wieczarkowiecz A, Marquardt T, Heuser C, Usai L, Pohl C, Seliger B, Abken H (2001) Tumor specific T cell activation by recombinant immunoreceptors: CD3zeta signaling and CD28 costimulation are simultaneously required for efficient IL-2 secretion and can be integrated into one combined CD28/CD3ζ signaling receptor molecule. J Immunol 167:6123–6131
Moeller M, Haynes NM, Trapani JA, Teng MW, Jackson JT, Tanner JE, Cerutti L, Jane SM, Kershaw MH, Smyth MJ, Darcy PK (2004) A functional role for CD28 costimulation in tumor recognition by single-chain receptor-modified T cells. Cancer Gene Ther 11:371–379
Geiger TL, Nguyen P, Leitenberg D, Flavell RA (2001) Integrated src kinase and costimulatory activity enhances signal transduction through single-chain chimeric receptors in lymphocytes. Blood 98:2364–2371
Finney HM, Akbar AN, Lawson AD (2004) Activation of resting human primary T cells with chimeric receptors: costimulation from CD28, inducible costimulator, CD134, and CD137 in series with signals from the TCR zeta chain. J Immunol 172:104–113
Zhong XS, Matsushita M, Saudemont A, Santos E, Sadelain M (2006) Integrated CD28 and 4-1BB signals strongly potentiate CD8+ T cell mediated eradication of metastatic prostate cancer. Mol Ther 13(Suppl1):S103
Weinberg AD (2002) OX40: targeted immunotherapy–implications for tempering autoimmunity and enhancing vaccines. Trends Immunol 23:102–109
Huard B, Schneider P, Mauri D, Tschopp J, French LE (2001) T cell costimulation by the TNF ligand BAFF. J Immunol 167:6225–6231
Mestas J, Hughes CC (2001) Endothelial cell costimulation of T cell activation through CD58-CD2 interactions involves lipid raft aggregation. J Immunol 167:4378–4385
Lamers CH, Sleijfer S., Vulto AG, Kruit WH, Kliffen M, Debets R, Gratama JW, Stoter G, Oosterwijk E (2006) Treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma with autologous T-lymphocytes genetically retargeted against carbonic anhydrase IX: first clinical experience. J Clin Oncol 24:e20–e22
Acknowledgments
Our work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Deutsche Krebshilfe, Wilhelm Sander-Stiftung, the European Commission through the ATTACK consortium and the Köln Fortune Program of the University of Cologne.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is a symposium paper from the conference “Cancer Immunotherapy 2006 Meets Strategies for Immune Therapy- held in Mainz, Germany, on 4- May 2006.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hombach, A., Abken, H. Costimulation tunes tumor-specific activation of redirected T cells in adoptive immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 56, 731–737 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-006-0249-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-006-0249-0