Abstract
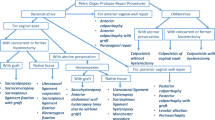
Pelvic floor dysfunction is a relatively common but often complex condition, presenting with a variety of clinical symptoms, especially when it involves multiple compartments. Clinical exam alone is often inadequate and requires a complementary imaging study. Magnetic resonance defecography (MRD) is an excellent noninvasive diagnostic study with its multiplanar capability, lack of ionizing radiation and excellent soft tissue resolution. It can identify both anatomic and functional abnormalities in the pelvic floor and specifically excels in its ability to simultaneously detect multicompartmental pathology and help with vital pre-operative assessment. This manuscript reviews the relevant anatomical landmarks, describes the optimal technique, highlights an approach to the interpretation of MRD, and provides an overview of the various pelvic floor disorders in the different anatomical compartments.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hallock JL and Handa VL. The epidemiology of pelvic floor disorders and childbirth: an update. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2016 March; 1-13.
Wu JM, Vaughan CP, Goode PS, Redden DT, Burgio KL, Richter HE, Markland AD. Prevelance and trends of symptomatic pelvic floor disorders in U.S. women. Obstet Gynecol. 2014 January; 123(1): 141-148.
Sung VW, Washington B, Raker CA. Costs of ambulatory care related to female pelvic floor disorders in the United States. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2010; 202(5): 483.e1–483.e4.
Wu JM, Kawasaki A, Hundley AF, Dieter AA, Myers ER, Sung VW. Predicting the number of women who will undergo incontinence and prolapse surgery, 2010 to 2050. American journal of Obstetrics and gynecology. 2011; 205(3):230.el-330.e5.
García del Salto L, de Miguel Criado J, Aguilera del Hoyo LF, Gutiérrez Velasco L, Fraga Rivas P, Manzano Paradela M, Díez Pérez de las Vacas MI, Marco Sanz AG, Fraile Moreno E. MR imaging–based assessment of the female pelvic floor. Radiographics. 2014;34(5);1417-39.
Mortele KJ and Fairhurst J. Dynamic MR defecography of the posterior compartment: indications, techniques and MRI features. Clinical Imaging, 2007;31(5): p.371.
Maglinte DD, Kelvin FM, Fitzgerald K, Hale DS, Benson JT. Association of compartment defects in pelvic floor dysfunction. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999 Feb;172(2):439-444.
Kelvin FM, Hale DS, Maglinte DD, Patten BJ, Benson JT. Female pelvic organ prolapse: diagnostic contribution of dynamic cystoproctography and comparison with physical examination. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999 Jul;173(1):31-37.
Nygaard I, Barber MD, Burgio KL, Kenton K, Meikle S, Schaffer J, Spino C, Whitehead WE, Wu J, Brody DJ; Pelvic Floor Disorders Network. Prevalence of symptomatic pelvic floor disorders in US women. JAMA, 2008; 300(11): p.1311-1316.
Halligan S, Spence-Jones C, Kamm MA, Bartram CI. Dynamic cystoproctography and physiological testing in women with urinary stress incontinence and urogenital prolapse. Clin Radiol, 1996;51:785-790.
Altringer WE, Saclarides TJ, Dominguez JM, Brubaker LT, Smith CS Four-contrast defecography: pelvic “floor-oscopy”. Dis Colon Rectum 1995; 38:695-699.
Kelvin FM, Maglinte D, Hornback JA, Benson JT. Pelvic prolopase: assessment with evacuation proctography (defecography). Radiology 1992; 184:547-551.
Colaiacomo MC, Masselli G, Polettini E, Lanciotti S, Casciani E, Bertini L, Gualdi G. Dynamic MR imaging of the pelvic floor: a pictorial review. Radiographics 2009; 10:1148/rg.e.35.
Hetzer FH, Andreisek G, Tsagari C, Sahrbacher U, Weishaupt D. MR defecography in patients with fecal incontinence: imaging findings and their effect on surgical management. Radiology, 2006; 240(2): p. 449-457.
Kelvin FM, Maglinte DD, hale DS, Benson JT. Female pelvic organ prolapse: a comparison of triphasic dynamic MR imaging and triphasic fluoroscopic cystocolpoproctography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000 Jan; 174(1):81-88.
Lienemann A, Anthuber C, Baron A, Kohz P, Reiser M. Dynamic MR colpocystorectography assessing pelvic floor descent. Eur Radiol 1997;7:1309-1317.
Pizzoferrato AC, Nyangoh Timoh K, Fritel X, Zareski E, Bader G, Fauconnier A. Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging and pelvic floor disorders: how and when? Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2014;181;259-266.
Gupta S, Sharma JB, Hari S, Kumar S, Roy KK, Singh N. Study of dynamic magnetic resonance imagining in diagnosis of pelvic organ prolapse. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2012;286(4);953-958.
Van Iersel JJ, Formijne Jonkers HA, Verheijen PM, Broeders IA, Heggelman BG, Sreetharan V, Fütterer JJ, Somers I, van der Leest M, Consten EC. Comparison of dynamic magnetic resonance defecography with rectal contrast and conventional defecography for posterior pelvic floor compartment prolapse. Colorectal Dis. 2017;19(1):O46-O53.
Kobi M, Flusberg M, Paroder V, Chernyak V. Practical guide to dynamic pelvic floor MRI. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging: JMRI 2018;47(5): p.1155-1170.
Pannu HK, Javitt MC, Glanc P, Bhosale PR, Harisinghani MG, Khati NJ, Mitchell DG, Nyberg DA, Pandharipande PV, Shipp TD, Siegel CL, Simpson L, Wall DJ, Wong-You-Cheong JJ. ACR Appropriateness Criteria pelvic floor dysfunction. J Am Coll Radiol, 2015;12(2): p.134-142.
Bitti GT, Argiolas GM, Ballicu N, Caddeo E, Cecconi M, Demurtas G, Matta G, Peltz MT, Secci S, Siotto P. Pelvic floor failure: MR Imaging evaluation of anatomic and functional abnormalities. Radiographics 2014; 34:429-448.
Woodfield CA, Krishnamoorthy S, Hampton BS, Brody JM. Imaging pelvic floor disorders: Trend toward comprehensive MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010 June;194:1640-1649.
Felt-Bersma RJ, Tiersma ES, Cuesta MA. Rectal prolapse, rectal intussusception, rectocele, solitary rectal ulcer syndrome and enterocele. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2008. 37(3): p. 645-668, ix.
Strohbehn K. Normal pelvic floor anatomy. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 1998;25(4):683-705.
Dobben AC, Felt-Bersma RJ, ten Kate FJ, Stoker J. Cross-sectional imaging of the anal sphincter in fecal incontinence. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008 Mar;190(3):671-682.
Lalwani N, Khatri G, El Sayed RF, Ram R, Jambhekar K, Chernyak V, Kamath A, Lewis S, Flusberg M, Scholz F, Arif-Tiwari H, Palmer SL, Lockhart ME, Fielding JR. MR defecography technique: recommendations of the society of abdominal radiology’s disease-focused panel on pelvic floor imaging. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2019 Aug 5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02160-7. [Epub ahead of print]
Bernstein MA, Huston III J, Ward HA. Imaging artifacts at 3.0T. J Magn Reson Imaging 2006;24(4):735-746.
Grob ATM, Olde Heuvel J, Futterer JJ, Massop D, Veenstra van Nieuwenhoven AL, Simonis FFJ, van der Vaart CH. Underestimation of pelvic organ prolapse in the supine straining position, based on magnetic resonance imaging findings. Int Urogynecol J. 2019 Jan 17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00192-018-03862-0. [Epub ahead of print]
Bertschinger KM, Hetzer FH, Roos JE, Treiber K, Marincek B, Hilfiker PR. Dynamic MR imaging of the pelvic floor performed with patient sitting in an open-magnet unit versus with patient supine in a closed-magnet unit. Radiology. 2002;223:501–508.
Pannu HK, Scatarige JC, Eng J. Comparison of supine MRI with and without rectal contrast to fluoroscopic cystocolpoproctography for the diagnosis of pelvic organ prolapse. J Comput Assit Tomogr 2009;33:125-130.
Gufler H, Ohde A, Grau G, Grossmann A. Colpocystoproctography in the upright and supine positions correlated with dynamic MRI of the pelvic floor. Eur J Radiol 2004;51:41-47.
Tumbarello JA, Hsu Y, Leicky-Gaupp C, Rohrer S, deLancey JO. Do repetitive valsalva maneuvers change maximum prolapse on dynamic MRI? Int urogynecol J 2010;21:1247-1251
Flusberg M, Sahni VA, Erturk SM, Mortele KJ. Dynamic MR defecography: assessment of the usefulness of the defecation phase. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011 Apr;196(4):W394-399.
Khatri G, Bailey AA, Bacsu C, Christie AL, Kumar N, Pedrosa I, Zimmern P. Influence of rectal gel volume on defecation during dynamic pelvic floor magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Imaging. 2015 Nov-Dec;39(6):1027-1031.
Solopova AE, Hetzer FH, Marincek B, Weishaupt D. MR defecography: prospective comparison of two rectal enema compositions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008 Feb;190(2):W118-124.
Law MY, Fielding JR. MRI of Pelvic Floor Dysfunction: Review. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;191: S45-53.
CS Reiner, D Weishaupt. Dynamic pelvic floor imaging: MRI techniques and imaging parameters. Abdom Imaging, 38 (2013), pp.903-911.
Arif-Tiwari H, Twiss CO, Lin FC, Funk JT, Vedantham S, Martin DR, Kalb BT. Improved detection of pelvic organ prolapse: Comparative utility of defecography phase sequence to nondefecography valsalva maneuvers in dynamic pelvic floor magnetic resonance imaging. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2019 Jul - Aug;48(4):342-347.
Bharucha AE, Fletcher JG, Harper CM, Hough D, Daube JR, Stevens C, Seide B, Riederer SJ, Zinsmeister AR. Relationship between symptoms and disordered continence mechanisms in women with idiopathic faecal incontinence. Gut, 2005. 54(4): p.546-555.
Fielding JR. Practical MR imaging of female pelvic floor weakness. Radiographics 2002;22:295-304.
Bhan SN, Mnatzakanian GN, Nisenbaum R. MRI for pelvic floor dysfunction: can the strain phase be eliminated? Abdom Radiol (NY). 2016;41:215-220.
Halligan S, Bartram CI, Park HJ, Kamm MA. Proctographic features of anismus. Radiology, 1995. 197(3): p.679-682.
Reiner CS, Tutuian R, Solopova AE, Pohl D, Marincek B, Weishaupt D. MR defecography in patients with dyssynergic defecation: spectrum of imaging findings and diagnostic value. Br J Radiol, 2011. 84(998): p.136-144.
Haya N, Segev E, Younes G, Glodschmidt E, AuslendeR, Abramov Y. The effect of bladder fullness on evaluation of pelvic organ prolapse. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2012;118:24-26.
Broekhuis SR, Fütterer JJ, Barentsz JO, Vierhout ME, Kluivers KB. A systematic review of clinical studies on dynamic magnetic resonance imaging of pelvic organ prolapse: the use of reference lines and anatomical landmarks. Int Urogynecol J pelvic floor dysfunct 2009;(6):721-729.
Singh K, Reid Wm, berger LA. Assessment and grading of pelvic organ prolapse by use of dynamic pelvic floor in women: quantification of muscle mass. American Journal of Roentgenology. 2000;174(3):657-660.
Bergman A, McCarthy TA, Ballard CA, Yanai J. Role of the Q-tip test in evaluating stress urinary incontinence. J reprod Med 1987;32:273-275.
Bennett GL, Hecht EM, Tanpitukpongse TP, Babb JS, Taouli B, Wong S, Rosenblum N, Kanofsky JA, Lee VS. MRI of the urethra in women with lower urinary tract symptoms: Spectrum of findings at static and dynamic imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009:193:1708-1715.
Yaşar L, Telci SO, Doğan K, Kaya E, Ekin M. Predictive role of measurement of pelvic floor muscle thickness with static MRI in stress and mixed urinary incontinence. Int Urogynecol J. 2019 Feb;30(2):271-277.
Dierick F, Galtsova E, Lauer C, Buisseret F, Bouché AF, Martin L. Clinical and MRI changes of puborectalis and iliococcygeus after a short period of intensive pelvic floor muscles training with or without instrumentation: A prospective randomized controlled trial. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2018 Aug;118(8):1661-1671.
Woodfield CA, Hampton BS, Sung V, Brody JM. Magnetic resonance imaging of pelvic organ prolapse: comparing pubococcygeal and midpubic lines with clinical staging. Int Urogynecol J pelvic floor dysfunct 2009;20:695-701.
Novellas S, Mondot L, Bafghi A, Fournol M, Baudin G, Coco L, Bongain A, Chevallier P. Evaluation of two classifications systems for pelvic prolapse on dynamic MRI. J Radiol 2009; 90(11 pt 1):1717-1724.
Kim JK1, Kim YJ, Choo MS, Cho KS. The urethra and its supporting structures in women with stress urinary incontinence: MR imaging using an endovaginal coil. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2003 Apr;180(4):1037-1044.
Macura KF, Genadry RR, Bluemke DA. MR imaging of the female urethra and supporting ligaments in assessment of urinary incontinence: spectrum of abnormalities. RadioGraphics 2006;26:1135-1149.
Summers A, Winkel LA, Hussain HK, DeLancey JOL. The relationship between anterior and apical compartment support. Am J obstet Gynecol. 2006 May; 194(5):1438-1443.
Funk MJ, Levin PJ, Wu JM. Trends in the surgical management of stress urinary incontinence. Obstet Gynecol. 2012 Apr; 119(4): 845-851.
Olsen AL, Smith VJ, Bergstrom JO, Colling JC, Clark AL. Epidemiology of surgically managed pelvic organ prolapse and urinary incontinence. Obstet Gynecol, 1997. 89(4): p. 501-506.
Salvador JC, Coutinho MP, Venâncio JM, Viamonte B. Dynamic magnetic resonance imaging of the female pelvic floor-a pictorial review. Insights Imaging. 2019 Jan 28;10(1):4.
Bartram, C.I., G.K. Turnbull, and J.E. Lennard-Jones, Evacuation proctography: an investigation of rectal expulsion in 20 subjects without defecatory disturbance. Gastrointest Radiol, 1988.13(1): p.72-80.
Bernier, P., G.W. Stevenson, and P. Shorvon, Defecography commode. Radiology, 1988. 166(3): p. 891-2.
Maglinte DD, Kelvin FM, Hale DS, Benson JT. Dynamic cystoproctography: a unifying diagnostic approach to pelvic floor and anorectal dysfunction. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997 Sep;169(3):759-767.
Mustain WC. Functional Disorders: Rectocele. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2017 Feb;30(1):63-75.
Lefevre R, Davila GW. Functional disorders: rectocele. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2008 May;21(2):129-137.
Dvorkin LS, Hetzer F, Scott SM, Williams NS, Gedroyc W, Lunniss PJ. Open-magnet MR defaecography compared with evacuation proctography in the diagnosis and management of patients with rectal intussusception. Colorectal Dis. 2004 Jan;6(1):45-53.
Elshazly WG, El Nekady Ael A, Hassan H. Role of dynamic magnetic resonance imaging in management of obstructed defecation case series. Int J Surg. 2010;8(4):274-282.
Tsiaoussis J, Chrysos E, Glynos M, Vassilakis JS, Xynos E. Pathophysiology and treatment of anterior rectal mucosal prolapse syndrome. Br J Surg. 1998 Dec;85(12):1699-1702.
Collinson R, Cunningham C, D’Costa H, Lindsey I. Rectal intussusception and unexplained faecal incontinence: findings of a proctographic study. Colorectal Dis. 2009 Jan;11(1):77-83.
Rao SS. Advances in diagnostic assessment of fecal incontinence and dyssynergic defecation. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Nov;8(11):910-919.
Rao SS, Bharucha AE, Chiarioni G, Felt-Bersma R, Knowles C, Malcolm A, Wald A. Functional Anorectal Disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016 Mar 25. pii: S0016-5085(16)00175-X.
Whitehead WE, Borrud L, Goode PS, Meikle S, Mueller ER, Tuteja A, Weidner A, Weinstein M, Ye W; Pelvic Floor Disorders Network. Fecal incontinence in US adults: epidemiology and risk factors. Gastroenterology. 2009 Aug;137(2):512-7, 517.e1-2
Lunniss PJ, Gladman MA, Hetzer FH, Williams NS, Scott SM. Risk factors in acquired faecal incontinence. J R Soc Med. 2004 Mar;97(3):111-6.
Erlichman DB, Kanmaniraja D, Kobi M, Chernyak V. MRI anatomy and pathology of the anal canal. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2019 May 22.
Terra MP, Beets-Tan RG, van der Hulst VP, Deutekom M, Dijkgraaf MG, Bossuyt PM, Dobben AC, Baeten CG, Stoker J. MRI in evaluating atrophy of the external anal sphincter in patients with fecal incontinence. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006 Oct;187(4):991-999.
Gilliland R, Altomare DF, Moreira H Jr, Oliveira L, Gilliland JE, Wexner SD. Pudendal neuropathy is predictive of failure following anterior overlapping sphincteroplasty. Dis Colon Rectum. 1998 Dec;41(12):1516-1522.
Prichard D, Harvey DM, Fletcher JG, Zinsmeister AR, Bharucha AE. Relationship Among Anal Sphincter Injury, Patulous Anal Canal, and Anal Pressures in Patients With Anorectal Disorders. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015 Oct;13(10):1793-1800.
Chiarioni G, Whitehead WE. Biofeedback therapy for constipation. GI Motility Testing: A Laboratory and Office Handbook, ed. M.R. Parkman HP, Rao SSC. 2011, Thorofare, NJ:: Slack Inc.
Attenberger UI, Morelli JN, Budjan J, Herold A, Kienle P, Kleine W, Häcker A, Baumann C, Heinzelbecker J, Schoenberg SO, Michaely HJ. The value of dynamic magnetic resonance imaging in interdisciplinary treatment of pelvic floor dysfunction. Abdom Imaging. 2015 Oct;40(7):2242-2247.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanmaniraja, D., Arif-Tiwari, H., Palmer, S.L. et al. MR defecography review. Abdom Radiol 46, 1334–1350 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02228-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02228-4