Abstract
Purpose
To compare the per-lesion sensitivity and positive predictive value (PPV) of ultrasonography (US), computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Materials and methods
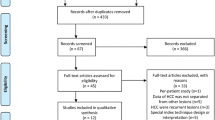
The meta-analysis of sensitivity included 242 studies (15,713 patients); 116 studies (7492 patients) allowed calculation of PPV. Pooled per-lesion sensitivity and PPV for HCC detection were compared using empirical Bayes estimates of a beta-binomial model.
Results
The pooled per-lesion sensitivity and PPV of contrast-enhanced CT (73.6%, 85.8%) and gadolinium-enhanced MRI (77.5%, 83.6%) are not significantly different (P = 0.08, P = 0.2). However, if the hepatobiliary agent gadoxetate is used, MRI has significantly higher pooled per-lesion sensitivity and PPV (85.6%, 94.2%) than CT (P < 0.0001) or than MRI with other agents (P < 0.0001). Non-contrast-enhanced US has the lowest overall sensitivity and PPV (59.3%, 77.4%). Pooled per-lesion sensitivity and PPV of contrast-enhanced US (84.4%, 89.3%) are relatively high, but no contrast-enhanced US study used the most rigorous reference standards.
Conclusion
MRI utilizing the hepatobiliary agent gadoxetate has the highest overall sensitivity and PPV, and may be the single optimal method for diagnosis of HCC. Non-contrast-enhanced US has the lowest sensitivity and PPV. More rigorous reference standards are needed to compare the performance of contrast-enhanced US with CT and MRI. Differences in sensitivity and PPV between CT and conventional gadolinium-enhanced MRI are not statistically significant overall.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CEUS:
-
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- GdMR:
-
Gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging without inclusion of hepatobiliary phase
- GxMR:
-
Gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging utilizing the hepatobiliary agent gadoxetate
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- NEUS:
-
Non-contrast-enhanced ultrasound
- PPV:
-
Positive predictive value
- SpMR:
-
Superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging
- US:
-
Ultrasound
References
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Diaz M, Cleries R (2004) Primary liver cancer: worldwide incidence and trends. Gastroenterology 127(5 Suppl 1):S5–S16
Lauer GM, Walker BD (2001) Hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med 345(1):41–52
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55(2):74–108
Cancer incidence in five continents. Volume VII. IARC scientific publications. 1997(143):i–xxxiv, 1–1240.
Cancer incidence in five continents. Volume VIII. IARC Scientific Publications. 2002(155):1–781
Wong LL (2002) Current status of liver transplantation for hepatocellular cancer. Am J Surg 183(3):309–316
Yu EW, Chie WC, Chen TH (2004) Does screening or surveillance for primary hepatocellular carcinoma with ultrasonography improve the prognosis of patients? Cancer J 10(5):317–325
Bruix J, Sherman M (2011) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology 53(3):1020–1022
Burrel M, Llovet JM, Ayuso C, et al. (2003) MRI angiography is superior to helical CT for detection of HCC prior to liver transplantation: an explant correlation. Hepatology 38(4):1034–1042
Mazzaferro V, Regalia E, Doci R, et al. (1996) Liver transplantation for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med 334(11):693–699
Hanna RF, Kased N, Kwan SW, et al. (2008) Double-contrast MRI for accurate staging of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 190(1):47–57
Hayashi PH, Trotter JF, Forman L, et al. (2004) Impact of pretransplant diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma on cadveric liver allocation in the era of MELD. Liver Transpl 10(1):42–48
Sangiovanni A, Del Ninno E, Fasani P, et al. (2004) Increased survival of cirrhotic patients with a hepatocellular carcinoma detected during surveillance. Gastroenterology 126(4):1005–1014
Wiesner RH, Freeman RB, Mulligan DC (2004) Liver transplantation for hepatocellular cancer: the impact of the MELD allocation policy. Gastroenterology 127(5 Suppl 1):S261–S267
Trevisani F, Cantarini MC, Labate AM, et al. (2004) Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma in elderly Italian patients with cirrhosis: effects on cancer staging and patient survival. Am J Gastroenterol 99(8):1470–1476
Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, et al. (1995) Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol 22(6):696–699
Freeman RB, Mithoefer A, Ruthazer R, et al. (2006) Optimizing staging for hepatocellular carcinoma before liver transplantation: a retrospective analysis of the UNOS/OPTN database. Liver Transpl 12(10):1504–1511
R-Core-Team. R (2013) A language and environment for statistical computing, 3.0.1 edn. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Vienna.
Carlin BP, Louis TA (2000) Bayes and Empirical Bayes Methods for Data Analysis, 2nd revised edn. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC
Efron B (1987) Better bootstrap confidence intervals. J Am Stat Assoc 82(397):171–200
Viechtbauer W (2010) Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J Stat Softw 36(3):1–48
OPTN (2014) Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network. Organ Distribution: Allocation of Livers. [Updated 10/31/2013; cited 2014 1/25]. http://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/PoliciesandBylaws2/policies/pdfs/policy_8.pdf.
Fung KTT, Li FTW, Raimondo ML, et al. (2004) Systematic review of radiological imaging for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients. Br J Radiol 77(920):633–640
Floriani I, D’Onofrio M, Rulli E, et al. (2012) Performance of imaging modalities in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultraschall Med 34:454–462
Xie LM, Guang Y, Ding HL, Cai AL, Huang Y (2011) Diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging for focal liver lesions: a meta-analysis. Ultrasound Med Biol 37(6):854–861
Colli A, Fraquelli M, Casazza G, et al. (2006) Accuracy of ultrasonography, spiral CT, magnetic resonance, and alpha-fetoprotein in diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol 101(3):513–523
Lee YJ, Lee JM, Lee JS, et al. (2015) Hepatocellular carcinoma: diagnostic performance of multidetector CT and MR imaging—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Radiology 275(1):97–109
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, et al. (2011) QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 155(8):529–536
Supplementary References (Forest Plots)
Kim CK, Lim JH, Lee WJ (2001) Detection of hepatocellular carcinomas and dysplastic nodules in cirrhotic liver—accuracy of ultrasonography in transplant patients. J Ultrasound Med 20(2):99–104
Lim JH, Kim SH, Lee WJ, Choi D, Lim HK (2006) Ultrasonographic detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: correlation of preoperative ultrasonography and resected liver pathology. Clin Radiol 61(2):191–197
Liu WC, Lim JH, Park CK, et al. (2003) Poor sensitivity of sonography in detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in advanced liver cirrhosis: accuracy of pretransplantation sonography in 118 patients. Eur Radiol 13(7):1693–1698
Rao ARN, Chui AKK, Shi LW, et al. (2003) Sensitivity of radiological investigations in diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic livers. Transpl Proc 35(1):348–349
Maciel AC, Cerski CT, Moreira RK, et al. (2006) Hepatocellular carcinoma in patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation: radiological findings with anatomopathological correlation in Brazil. Arq Gastroenterol 43(1):24–29
Libbrecht L, Bielen D, Verslype C, et al. (2002) Focal lesions in cirrhotic explant livers: pathological evaluation and accuracy of pretransplantation imaging examinations. Liver Transpl 8(9):749–761
Rode A, Bancel B, Douek P, et al. (2001) Small nodule detection in cirrhotic livers: evaluation with US, spiral CT, and MRI and correlation with pathologic examination of explanted liver. J Comput Assist Tomogr 25(3):327–336
Compagnon P, Grandadam S, Lorho R, et al. (2008) Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma without preoperative tumor biopsy. Transplantation 86(8):1068–1076
Bennett GL, Krinsky GA, Abitbol RJ, et al. (2002) Sonographic detection of hepatocellular carcinoma and dysplastic nodules in cirrhosis: correlation of pretransplantation sonography and liver explant pathology in 200 patients. Am J Roentgenol 179(1):75–80
Snowberger N, Chinnakotla S, Lepe RM, et al. (2007) Alpha fetoprotein, ultrasound, computerized tomography and magnetic resonance imaging for detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with advanced cirrhosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 26(9):1187–1194
Teefey SA, Hildeboldt CC, Dehdashti F, et al. (2003) Detection of primary hepatic malignancy in liver transplant candidates: prospective comparison of CT, MR imaging US and PET. Radiology 226(2):533–542
Yu NC, Chaudhari V, Raman SS, et al. (2011) CT and MRI improve detection of hepatocellular carcinoma, compared with ultrasound alone, in patients with cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 9(2):161–167
Gambarin-Gelwan M, Wolf DC, Shapiro R, Schwartz ME, Min AD (2000) Sensitivity of commonly available screening tests in detecting hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients undergoing liver transplantation. Am J Gastroenterol 95(6):1535–1538
Van Thiel DH, Yong S, Li SD, Kennedy M, Brems J (2004) The development of de novo hepatocellular carcinoma in patients on a liver transplant list: frequency, size, and assessment of current screening methods. Liver Transpl 10(5):631–637
Kunishi Y (2012) Efficacy of fusion imaging combining sonography and hepatobiliary phase MRI with Gd-EOB-DTPA to detect small hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Roentgenol 198(1):106–114
Lee MW, Kim YJ, Park HS, et al. (2010) Targeted sonography for small hepatocellular carcinoma discovered by CT or MRI: factors affecting sonographic detection. Am J Roentgenol 194(5):W396–W406
Mikami S, Kubo S, Hirohashi K, et al. (2000) Computed tomography during arteriography and arterial portography in small hepatocellular carcinoma and dysplastic nodule: a prospective study. Jpn J Cancer Res 91(8):859–863
Zhang K, Kokudo N, Hasegawa K, et al. (2007) Detection of new tumors by intraoperative ultrasonography during repeated hepatic resections for hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch Surg 142(12):1170–1175
Chen LD, Xu HX, Xie XY, et al. (2010) Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma: differential diagnosis with contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Eur Radiol 20(3):743–753
Goto E, Masuzaki R, Tateishi R, et al. (2012) Value of post-vascular phase (Kupffer imaging) by contrast-enhanced ultrasonography using Sonazoid in the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol 47(4):477–485
Honda T, Kumada T, Kiriyama S, et al. (2003) Comparison of contrast-enhanced harmonic ultrasonography and power Doppler ultrasonography for depicting vascularity of hepatocellular carcinoma identified by angiography-assisted CT. Hepatol Res 27(4):314–321
Tanaka Y, Sasaki Y, Katayama K, Hiramatsu N, Ito A (2000) Probability of hepatocellular carcinoma of small hepatocellular nodules undetectable by computed tomography during arterial portography. Hepatology 31(4):890–898
Rickes S, Schulze S, Neye H, Ocran KW, Wermke W (2003) Improved diagnosing of small hepatocellular carcinomas by echo-enhanced power Doppler sonography in patients with cirrhosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 15(8):893–900
Hohmann J, Skrok J, Basilico R, et al. (2012) Characterisation of focal liver lesions with unenhanced and contrast enhanced low MI real time ultrasound: on-site unblinded versus off-site blinded reading. Eur J Radiol 81(3):E317–E324
Colagrande S, Fargnoli R, Dal Pozzo F, et al. (2000) Value of hepatic arterial phase CT versus lipiodol ultrafluid CT in the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Comput Assist Tomogr 24(6):878–883
Di Martino M, De Filippis G, De Santis A, et al. (2013) Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients: prospective comparison of US, CT and MR imaging. Eur Radiol 23(4):887–896
Tong MJ, Blatt LM, Kao VWC (2001) Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic viral hepatitis in the United States of America. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 16(5):553–559
Burns PN, Wilson SR, Simpson DH (2000) Pulse inversion imaging of liver blood flow—improved method for characterizing focal masses with microbubble contrast. Invest Radiol 35(1):58–71
Kan M, Hiraoka A, Uehara T, et al. (2010) Evaluation of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography using perfluorobutane (Sonazoid (R)) in patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with dynamic computed tomography. Oncol Lett 1(3):485–488
Kawada N, Ohkawa K, Tanaka S, Matsunaga T, Uehara H (2010) Improved diagnosis of well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma with gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and Sonazoid contrast-enhanced ultrasonography Gd-EOB-DTPA and Sonazoid for early HCC. Hepatol Res 40(9):930–936
Liu GJ, Wang W, Xie XY, et al. (2010) Real-time contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of focal liver lesions in fatty liver. Clin Imaging 34(3):211–221
Luo W, Numata K, Kondo M, et al. (2009) Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography for evaluation of the enhancement patterns of focal liver tumors in the late phase by intermittent imaging with a high mechanical index. J Ultrasound Med 28(4):439–448
Luo W, Numata K, Morimoto M, et al. (2009) Focal liver tumors: characterization with 3D perflubutane microbubble contrast agent-enhanced US versus 3D contrast-enhanced multidetector CT. Radiology 251(1):287–295
Luo W, Numata K, Morimoto M, et al. (2009) Three-dimensional contrast-enhanced sonography of vascular patterns of focal liver tumors: pilot study of visualization methods. Am J Roentgenol 192(1):165–173
Luo W, Numata K, Morimoto M, et al. (2010) Differentiation of focal liver lesions using three-dimensional ultrasonography: retrospective and prospective studies. World J Gastroenterol 16(17):2109–2119
Maruyama H, Takahashi M, Sekimoto T, et al. (2012) Heterogeneity of microbubble accumulation: a novel approach to discriminate between well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinomas and regenerative nodules. Ultrasound Med Biol 38(3):383–388
Mita K, Kim SR, Kudo M, et al. (2010) Diagnostic sensitivity of imaging modalities for hepatocellular carcinoma smaller than 2 cm. World J Gastroenterol 16(33):4187–4192
Alaboudy A, Inoue T, Hatanaka K, et al. (2011) Usefulness of combination of imaging modalities in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma using sonazoid (R)-enhanced ultrasound, gadolinium diethylene-triamine-pentaacetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging, and contrast-enhanced computed tomography. Oncology 81:66–72
Ooi CC, Low SCA, Schneider-Kolsky M, et al. (2010) Diagnostic accuracy of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in differentiating benign and malignant focal liver lesions: a retrospective study. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 54(5):421–430
Suzuki S, Iijima H, Moriyasu F, et al. (2004) Differential diagnosis of hepatic nodules using delayed parenchymal phase imaging of levovist contrast ultrasound: comparative study with SPIO-MRI. Hepatol Res 29(2):122–126
Takahashi M, Maruyama H, Shimada T, et al. (2013) Characterization of hepatic lesions (≤30 mm) with liver-specific contrast agents: a comparison between ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. Eur J Radiol 82(1):75–84
Tanaka S, Ioko T, Oshikawa O, Hamada Y, Yoshioka F (2001) Dynamic sonography of hepatic tumors. Am J Roentgenol 177(4):799–805
Wang WP, Wu Y, Luo Y, et al. (2009) Clinical value of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in the characterization of focal liver lesions: a prospective multicenter trial. Hepatob Pancreatic Dis Int 8(4):370–376
Wang ZL, Tang J, Weskott HP, et al. (2008) Undetermined focal liver lesions on gray-scale ultrasound in patients with fatty liver: characterization with contrast-enhanced ultrasound. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23(10):1511–1519
Wen YL, Kudo M, Zheng RQ, et al. (2003) Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: therapeutic response using contrast-enhanced coded phase-inversion harmonic sonography. Am J Roentgenol 181(1):57–63
Wen YL, Zhou P, Kudo M (2004) Detection of intratumoral vascularity in small hepatocellular carcinoma by coded phase inversion harmonics. Intervirology 47(3–5):169–178
Xu HX, Liu GJ, Lu MD, et al. (2006) Characterization of focal liver lesions using contrast-enhanced sonography with a low mechanical index mode and a sulfur hexafluoride-filled microbubble contrast agent. J Clin Ultrasound 34(6):261–272
Xu HX, Lu MD, Liu LN, et al. (1018) Discrimination between neoplastic and non-neoplastic lesions in cirrhotic liver using contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Br J Radiol 2012(85):1376–1384
Xu HX, Xie XY, Lu MD, et al. (2008) Contrast-enhanced sonography in the diagnosis of small hepatocellular carcinoma ≤2 cm. J Clin Ultrasound 36(5):257–266
Yamamoto K, Shiraki K, Nakanishi S, et al. (2005) 1.5 Harmonic Imaging Sonography with microbubble contrast agent improves characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 11(36):5607–5613
Yoshizumi H, Maruyama H, Okugawa H, et al. (2008) How to characterize non-hypervascular hepatic nodules on contrast-enhanced computed tomography in chronic liver disease: feasibility of contrast-enhanced ultrasound with a microbubble contrast agent. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23(10):1528–1534
Youk JH, Kim CS, Lee JM (2003) Contrast-enhanced agent detection—imaging value in the characterization of focal hepatic lesions. J Ultrasound Med 22(9):897–910
Arita J, Takahashi M, Hata S, et al. (2011) Usefulness of contrast-enhanced intraoperative ultrasound using sonazoid in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg 254(6):992–999
Dai Y, Chen MH, Fan ZH, et al. (2008) Diagnosis of small hepatic nodules detected by surveillance ultrasound in patients with cirrhosis: comparison between contrast-enhanced ultrasound and contrast-enhanced helical computed tomography. Hepatol Res 38(3):281–290
Furuse J, Nagase M, Ishii H, Yoshino M (2003) Contrast enhancement patterns of hepatic tumours during the vascular phase using coded harmonic imaging and Levovist to differentiate hepatocellular carcinoma from other focal lesions. Br J Radiol 76(906):385–392
Hatanaka K, Kudo M, Minami Y, et al. (2008) Differential diagnosis of hepatic tumors: value of contrast-enhanced harmonic Sonography using the newly developed contrast agent, Sonazoid. Intervirology 51:61–69
Sugimoto K, Moriyasu F, Shiraishi J, et al. (2012) Assessment of arterial hypervascularity of hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of contrast-enhanced US and gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MR imaging. Eur Radiol 22(6):1205–1213
Pei XQ, Liu LZ, Xiong YH, et al. (1023) Quantitative analysis of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography: differentiating focal nodular hyperplasia from hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Radiol 2013(86):20120536
Mandai M, Koda M, Matono T, et al. (1002) Assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma by contrast-enhanced ultrasound with perfluorobutane microbubbles: comparison with dynamic CT. Br J Radiol 2011(84):499–507
Granito A, Galassi M, Piscaglia F, et al. (2013) Impact of gadoxetic acid (Gd-EOB-DTPA)-enhanced magnetic resonance on the non-invasive diagnosis of small hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 37(3):355–363
Nicolau C, Vilana R, Catala V, et al. (2006) Importance of evaluating all vascular phases on contrast-enhanced sonography in the differentiation of benign from malignant focal liver lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186(1):158–167
Pompili M, Riccardi L, Semeraro S, et al. (2008) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound assessment of arterial vascularization of small nodules arising in the cirrhotic liver. Dig Liver Dis 40(3):206–215
Quaia E, Alaimo V, Baratella E, et al. (2009) The added diagnostic value of 64-row multidetector CT combined with contrast-enhanced US in the evaluation of hepatocellular nodule vascularity: implications in the diagnosis of malignancy in patients with liver cirrhosis. Eur Radiol 19(3):651–663
Ricci P, Cantisani V, Drudi F, et al. (2009) Is contrast-enhanced US alternative to spiral CT in the assessment of treatment outcome of radiofrequency ablation in hepatocellular carcinoma? Ultraschall Med 30(3):252–258
Seitz K, Strobel D, Bernatik T, et al. (2009) Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) for the characterization of focal liver lesions—prospective comparison in clinical practice: cEUS vs. CT (DEGUM multicenter trial). Parts of this manuscript were presented at the Ultrasound Dreilandertreffen 2008, Davos. Ultraschall Med 30(4):383–389
Vilana R, Llovet JM, Bianchi L, et al. (2003) Contrast-enhanced power Doppler sonography and helical computed tomography for assessment of vascularity of small hepatocellular carcinomas before and after percutaneous ablation. J Clin Ultrasound 31(3):119–128
von Herbay A, Haeussinger D, Gregor M, Vogt C (2007) Characterization and detection of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): comparison of the ultrasound contrast agents SonoVue (BR 1) and Levovist (SH U 508A)—comparison of SonoVue and Levovist in HCC. Ultraschall Med 28(2):168–175
Bartolotta TV, Taibbi A, Midiri M, et al. (2010) Characterisation of focal liver lesions undetermined at grey-scale US: contrast-enhanced US versus 64-row MDCT and MRI with liver-specific contrast agent. Radiol Med. 115(5):714–731
Catala V, Nicolau C, Vilana R, et al. (2007) Characterization of focal liver lesions: comparative study of contrast-enhanced ultrasound versus spiral computed tomography. Eur Radiol 17(4):1066–1073
Fracanzani AL, Burdick L, Borzio M, et al. (2001) Contrast-enhanced Doppler ultrasonography in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma and premalignant lesions in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 34(6):1109–1112
Gaiani S, Celli N, Piscaglia F, et al. (2004) Usefulness of contrast-enhanced perfusional sonography in the assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma hypervascular at spiral computed tomography. J Hepatol 41(3):421–426
Giorgio A, Calisti G, Di Sarno A, et al. (2011) Characterization of dysplastic nodules, early hepatocellular carcinoma and progressed hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis with contrast-enhanced ultrasound. Anticancer Res 31(11):3977–3982
Iavarone M, Sangiovanni A, Forzenigo LV, et al. (2010) Diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis by dynamic contrast imaging: the importance of tumor cell differentiation. Hepatology 52(5):1723–1730
Celli N, Gaiani S, Piscaglia F, et al. (2007) Characterization of liver lesions by real-time contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 19(1):3–14
Giorgio A, De Stefano G, Coppola C, et al. (2007) Contrast-enhanced sonography in the characterization of small hepatocellular carcinomas in cirrhotic patients: comparison with contrast-enhanced ultrafast magnetic resonance imaging. Anticancer Res 27(6C):4263–4269
Giorgio A, Ferraioli G, Tarantino L, et al. (2004) Contrast-enhanced sonographic appearance of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: comparison with contrast-enhanced helical CT appearance. Am J Roentgenol 183(5):1319–1326
Forner A, Vilana R, Ayuso C, et al. (2008) Diagnosis of hepatic nodules 20 mm or smaller in cirrhosis: prospective validation of the noninvasive diagnostic criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 47(1):97–104
Kang BK, Lim JH, Kim SH, et al. (2003) Preoperative depiction of hepatocellular carcinoma: ferumoxides-enhanced MR imaging versus triple-phase helical CT. Radiology 226(1):79–85
Kim SH, Choi D, Lim JH, et al. (2005) Ferucarbotran-enhanced MRI versus triple-phase MDCT for the preoperative detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Roentgenol 184(4):1069–1076
Kim SH, Lee J, Kim MJ, et al. (2009) Gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI versus triple-phase MDCT for the preoperative detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Roentgenol 192(6):1675–1681
Kim SJ, Kim SH, Lee JM, et al. (2008) Ferucarbotran-enhanced 3.0-T magnetic resonance imaging using parallel imaging technique compared with triple-phase multidetector row computed tomography for the preoperative detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Comput Assist Tomogr 32(3):379–385
Lim JH, Choi D, Kim SH, et al. (2002) Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: value of adding delayed phase imaging to dual-phase helical CT. Am J Roentgenol 179(1):67–73
Lim JH, Kim CK, Lee WJ, et al. (2000) Detection of hepatocellular carcinomas and dysplastic nodules in cirrhotic livers: accuracy of helical CT in transplant patients. Am J Roentgenol 175(3):693–698
Lin MT, Chen CL, Wang CC, et al. (2011) Diagnostic sensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma imaging and its application to non-cirrhotic patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 26(4):745–750
Lu CH, Chen CL, Cheng YF, et al. (2010) Correlation between imaging and pathologic findings in explanted livers of hepatocellular carcinoma cases. Transpl Proc 42(3):830–833
Maetani YS, Ueda M, Haga H, et al. (2008) Hepatocellular carcinoma in patients undergoing living-donor liver transplantation. Intervirology 51:46–51
Hirakawa M, Yoshimitsu K, Irie H, et al. (2011) Performance of radiological methods in diagnosing hepatocellular carcinoma preoperatively in a recipient of living related liver transplantation: comparison with step section histopathology. Jpn J Radiol 29(2):129–137
Bhattacharjya S, Bhattacharjya T, Quaglia A, et al. (2004) Liver transplantation in cirrhotic patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma: an analysis of pre-operative imaging, explant histology and prognostic histologic indicators. Dig Surg 21(2):152–159
Addley HC, Griffin N, Shaw AS, et al. (2011) Accuracy of hepatocellular carcinoma detection on multidetector CT in a transplant liver population with explant liver correlation. Clin Radiol 66(4):349–356
Ronzoni A, Artioli D, Scardina R, et al. (2007) Role of MDCT in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis undergoing orthotopic liver transplantation. Am J Roentgenol 189(4):792–798
Steingruber IE, Mallouhi A, Czermak BV, et al. (2003) Pretransplantation evaluation of the cirrhotic liver with explantation correlation: accuracy of CT arterioportography and digital subtraction hepatic angiography in revealing hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Roentgenol 181(1):99–108
Valls C, Cos M, Figueras J, et al. (2004) Pretransplantation diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: value of dual-phase helical CT. Am J Roentgenol 182(4):1011–1017
de Ledinghen V, Laharie D, Lecesne R, et al. (2002) Detection of nodules in liver cirrhosis: spiral computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging? A prospective study of 88 nodules in 34 patients. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(2):159–165
Denecke T, Grieser C, Froling V, et al. (2009) Multislice computed tomography using a triple-phase contrast protocol for preoperative assessment of hepatic tumor load in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma before liver transplantation. Transpl Int 22(4):395–402
Liu YYI, Kamaya A, Jeffrey RB, Shin LK (2012) Multidetector computed tomography triphasic evaluation of the liver before transplantation: importance of equilibrium phase washout and morphology for characterizing hypervascular lesions. J Comput Assist Tomogr 36(2):213–219
Peterson MS, Baron RL, Marsh JW, et al. (2000) Pretransplantation surveillance for possible hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: epidemiology and CT-based tumor detection rate in 430 cases with surgical pathologic correlation. Radiology 217(3):743–749
Pollinger HS, Greene FL (2004) The optimal imaging modality for hepatocellular carcinoma: is there a gold standard? Curr Surg 61(2):141–146
Rizvi S, Camci C, Yong Y, et al. (2006) Is post-lipiodol CT better than IV contrast CT scan for early detection of HCC? A single liver transplant center experience. Transpl Proc 38(9):2993–2995
Yaqoob J, Bari V, Usman MU, et al. (2004) The evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma with biphasic contrast enhanced helical CT scan. J Pak Med Assoc 54(3):123–127
Kwak H-S, Lee J-M, Kim C-S (2004) Preoperative detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of combined contrast-enhanced MR imaging and combined CT during arterial portography and CT hepatic arteriography. Eur Radiol 14(3):447–457
Chung YE, Kim M-J, Kim Y-E, et al. (2013) Characterization of incidental liver lesions: comparison of multidetector CT versus Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MR imaging. PLoS ONE 8(6):e66141
Kawata S, Murakami T, Kim T, et al. (2002) Multidetector CT: diagnostic impact of slice thickness on detection of hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Roentgenol 179(1):61–66
Kim KW, Lee JM, Klotz E, et al. (2009) Quantitative CT color mapping of the arterial enhancement fraction of the liver to detect hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology 250(2):425–434
Kim SK, Kim SH, Lee WJ, et al. (2002) Preoperative detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: ferumoxides-enhanced versus mangafodipir trisodium-enhanced MR imaging. Am J Roentgenol 179(3):741–750
Kim YK, Kim CS, Han YM, et al. (2009) Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: gadoxetic acid-enhanced 3-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging versus multi-detector row computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 33(6):844–850
Kim YK, Kwak HS, Kim CS, et al. (2006) Hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease: comparison of SPIO-enhanced MR imaging and 16-detector row CT. Radiology 238(2):531–541
Kitamura T, Ichikawa T, Erturk SM, et al. (2008) Detection of hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma with multidetector-row CT: single arterial-phase imaging with computer-assisted automatic bolus-tracking technique compared with double arterial-phase imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr 32(5):724–729
Kumano S, Uemura M, Haraikawa T, et al. (2009) Efficacy of double arterial phase dynamic magnetic resonance imaging with the sensitivity encoding technique versus dynamic multidetector-row helical computed tomography for detecting hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma. Jpn J Radiol 27(6):229–236
Lee JM, Kim IH, Kwak HS, et al. (2003) Detection of small hypervascular hepatocellular carcinomas in cirrhotic patients: comparison of superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced MR imaging with dual-phase spiral CT. Korean J Radiol 4(1):1–8
Lv PJ, Lin XZ, Chen KM, Gao JB (2012) Spectral CT in patients with small HCC: investigation of image quality and diagnostic accuracy. Eur Radiol 22(10):2117–2124
Monzawa S, Ichikawa T, Nakajima H, et al. (2007) Dynamic CT for detecting small hepatocellular carcinoma: usefulness of delayed phase imaging. Am J Roentgenol 188(1):147–153
Murakami T, Kim T, Kawata S, et al. (2003) Evaluation of optimal timing of arterial phase imaging for the detection of hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma by using triple arterial phase imaging with multidetector-row helical computed tomography. Invest Radiol 38(8):497–503
Murakami T, Kim T, Takamura M, et al. (2001) Hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma: detection with double arterial phase multi-detector row helical CT. Radiology 218(3):763–767
Noguchi Y, Murakami T, Kim T, et al. (2003) Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of dynamic MR imaging with dynamic double arterial phase helical CT. Am J Roentgenol 180(2):455–460
Noguchi Y, Murakami T, Kim T, et al. (2002) Detection of hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma by dynamic magnetic resonance imaging with double-echo chemical shift in-phase and opposed-phase gradient echo technique: comparison with dynamic helical computed tomography imaging with double arterial phase. J Comput Assist Tomogr 26(6):981–987
Akai H, Kiryu S, Matsuda I, et al. (2011) Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma by Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced liver MRI: comparison with triple phase 64 detector row helical CT. Eur J Radiol 80(2):310–315
Onishi H, Kim T, Imai Y, et al. (2012) Hypervascular hepatocellular carcinomas: detection with gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MR imaging and multiphasic multidetector CT. Eur Radiol 22(4):845–854
Sano K, Ichikawa T, Motosugi U, et al. (2011) Imaging study of early hepatocellular carcinoma: usefulness of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 261(3):834–844
Sun HY, Lee JM, Shin CI, et al. (2010) Gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for differentiating small hepatocellular carcinomas (≤2 cm in diameter) from arterial enhancing pseudolesions special emphasis on hepatobiliary phase imaging. Invest Radiol 45(2):96–103
Yoo HJ, Lee JM, Lee JY, et al. (2009) Additional value of SPIO-enhanced MR imaging for the noninvasive imaging diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic liver. Invest Radiol 44(12):800–807
Yukisawa S, Okugawa H, Masuya Y, et al. (2007) Multidetector helical CT plus superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced MR imaging for focal hepatic lesions in cirrhotic liver: a comparison with multi-phase CT during hepatic arteriography. Eur J Radiol 61(2):279–289
Zhao H, Yao JL, Wang Y, Zhou KR (2007) Detection of small hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of dynamic enhancement magnetic resonance imaging and multiphase multirow-detector helical CT scanning. World J Gastroenterol 13(8):1252–1256
Zhao H, Zhou KR, Yan FH (2003) Role of multiphase scans by multirow-detector helical CT in detecting small hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 9(10):2198–2201
Zheng XH, Guan YS, Zhou XP, et al. (2005) Detection of hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of multi-detector CT with digital subtraction angiography and Lipiodol CT. World J Gastroenterol 11(2):200–203
Zhou JS, Huan Y, Wei MQ, Jiang XQ (2010) Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma with multi-slice spiral CT by using double-arterial phase and portal venous phase enhanced scanning: effect of iodine concentration of contrast material. Afr J Biotechnol 9(23):3443–3447
Baek CK, Choi JY, Kim KA, et al. (2012) Hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease: a comparison of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI and multiphasic MDCT. Clin Radiol 67(2):148–156
Higashihara H, Osuga K, Onishi H, et al. (2012) Diagnostic accuracy of C-arm CT during selective transcatheter angiography for hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with intravenous contrast-enhanced, biphasic, dynamic MDCT. Eur Radiol 22(4):872–879
Hwang J, Kim SH, Lee MW, Lee JY (1015) Small (≤2 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease: comparison of gadoxetic acid-enhanced 3.0 T MRI and multiphasic 64-multirow detector CT. Br J Radiol 2012(85):E314–E322
Ichikawa T, Kitamura T, Nakajima H, et al. (2002) Hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma: can double arterial phase imaging with multidetector CT improve tumor depiction in the cirrhotic liver? Am J Roentgenol 179(3):751–758
Ichikawa T, Saito K, Yoshioka N, et al. (2010) Detection and characterization of focal liver lesions A japanese phase III, multicenter comparison between gadoxetic acid disodium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and contrast-enhanced computed tomography predominantly in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic liver disease. Invest Radiol 45(3):133–141
Iwazawa J, Ohue S, Hashimoto N, et al. (2010) Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of angiographic C-arm CT and MDCT. Am J Roentgenol 195(4):882–887
Jang HJ, Lim JH, Lee SJ, et al. (2000) Hepatocellular carcinoma: are combined CT during arterial portography and CT hepatic arteriography in addition to triple-phase helical CT all necessary for preoperative evaluation? Radiology 215(2):373–380
Choi D, Kim SH, Lim JH, et al. (2001) Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: combined T2-weighted and dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MRI versus combined CT during arterial portography and CT hepatic arteriography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 25(5):777–785
Choi D, Kim S, Lim J, et al. (2001) Preoperative detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: ferumoxides-enhanced mr imaging versus combined helical CT during arterial portography and CT hepatic arteriography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 176(2):475–482
Inoue T, Kudo M, Komuta M, et al. (2012) Assessment of Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI for HCC and dysplastic nodules and comparison of detection sensitivity versus MDCT. J Gastroenterol 47(9):1036–1047
Hatanaka K, Kudo M, Minami Y, Maekawa K (2008) Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography for diagnosis of hepatic malignancies: comparison with contrast-enhanced CT. Oncology 75(Suppl 1):42–47
Tanimoto A, Kuribayashi S (2006) Application of superparamagnetic iron oxide to imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Radiol 58(2):200–216
Tanaka Y, Sasaki Y, Katayama K, et al. (2000) Probability of hepatocellular carcinoma of small hepatocellular nodules undetectable by computed tomography during arterial portography. Hepatology 31(4):890–898
Schima W, Hammerstingl R, Catalano C, et al. (2006) Quadruple-phase MDCT of the liver in patients with suspected hepatocellular carcinoma: effect of contrast material flow rate. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186(6):1571–1579
Laghi A, Iannaccone R, Rossi P, et al. (2003) Hepatocellular carcinoma: detection with triple-phase multi-detector row helical CT in patients with chronic hepatitis. Radiology 226(2):543–549
Leoni S, Piscaglia F, Golfieri R, et al. (2010) The impact of vascular and nonvascular findings on the noninvasive diagnosis of small hepatocellular carcinoma based on the EASL and AASLD criteria. Am J Gastroenterol 105(3):599–609
Marin D, Catalano C, De Filippis G, et al. (2009) Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: added value of coronal reformations from isotropic voxels with 64-MDCT. Am J Roentgenol 192(1):180–187
Marin D, Di Martino M, Guerrisi A, et al. (2009) Hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis: qualitative comparison of gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced MR imaging and multiphasic 64-section CT. Radiology 251(1):85–95
Pitton MB, Kloeckner R, Herber S, et al. (2009) MRI versus 64-row MDCT for diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 15(48):6044–6051
Sutcliffe RP, Lewis D, Kane PA, et al. (2011) Manganese-enhanced MRI predicts the histological grade of hepatocellular carcinoma in potential surgical candidates. Clin Radiol 66(3):237–243
Bartolozzi C, Donati F, Cioni D, Crocetti L, Lencioni R (2000) MnDPDP-enhanced MRI vs dual-phase spiral CT in the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. Eur Radiol 10(11):1697–1702
Golfieri R, Marini E, Bazzocchi A, et al. (2009) Small (≤3 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: the role of double contrast agents in MR imaging vs. multidetector-row CT. Radiol Med 114(8):1239–1266
Iannaccone R, Laghi A, Catalano C, et al. (2005) Hepatocellular carcinoma: role of unenhanced and delayed phase multi-detector row helical CT in patients with cirrhosis. Radiology 234(2):460–467
Stoker J, Romijn MG, de Man RA, et al. (2002) Prospective comparative study of spiral computer tomography and magnetic resonance imaging for detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 51(1):105–107
Bluemke DA, Sahani D, Amendola M, et al. (2005) Efficacy and safety of MR imaging with liver-specific contrast agent: US multicenter phase III study. Radiology 237(1):89–98
Balci NC, Befeler AS, Leiva P, Pilgram TK, Havlioglu N (2008) Imaging of liver disease: comparison between quadruple-phase multidetector computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 23(10):1520–1527
Di Martino M, Marin D, Guerrisi A, et al. (2010) Intraindividual comparison of gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MR imaging and 64-section multidetector CT in the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Radiology 256(3):806–816
Doyle DJ, O’Malley ME, Jang HJ, Jhaveri K (2007) Value of the unenhanced phase for detection of hepatocellular carcinomas 3 cm or less when performing multiphase computed tomography in patients with cirrhosis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 31(1):86–92
Semelka RC, Martin DR, Balci C, Lance T (2001) Focal liver lesions: comparison of dual-phase CT and multisequence multiplanar MR imaging including dynamic gadolinium enhancement. J Magn Reson Imaging 13(3):397–401
Haradome H, Grazioli L, Tinti R, et al. (2011) Additional value of gadoxetic acid-DTPA-enhanced hepatobiliary phase MR imaging in the diagnosis of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with dynamic triple-phase multidetector CT imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 34(1):69–78
Kondo H, Kanematsu M, Itoh K, et al. (2005) Does T2-weighted MR imaging improve preoperative detection of malignant hepatic tumors? Observer performance study in 49 surgically proven cases. Magn Reson Imaging 23(1):89–95
Park MS, Kim S, Patel J, et al. (2012) Hepatocellular carcinoma: detection with diffusion-weighted versus contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in pretransplant patients. Hepatology 56(1):140–148
Choi SH, Lee JM, Yu NC, et al. (2008) Hepatocellular carcinoma in liver transplantation candidates: detection with gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced MRI. Am J Roentgenol 191(2):529–536
Ouedraogo W, Tran-Van Nhieu J, Baranes L, et al. (2011) Evaluation of noninvasive diagnostic criteria for hepatocellular carcinoma on pretransplant MRI (2010): correlation between MR imaging features and histological features on liver specimen. J Radiol 92(7–8):688–700
Becker-Weidman DJS, Kalb B, Sharma P, et al. (2011) Hepatocellular Carcinoma lesion characterization: single-institution clinical performance review of multiphase gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging-comparison to prior same-center results after MR systems improvements. Radiology 261(3):824–833
Krinsky GA, Lee VS, Theise ND, et al. (2001) Hepatocellular carcinoma and dysplastic nodules in patients with cirrhosis: prospective diagnosis with MR imaging and explantation correlation. Radiology 219(2):445–454
Lauenstein TC, Salman K, Morreira R, et al. (2007) Gadolinium-enhanced MRI for tumor surveillance before liver transplantation: center-based experience. Am J Roentgenol 189(3):663–670
Hardie AD, Kizziah MK, Rissing MS (2011) Can the patient with cirrhosis be imaged for hepatocellular carcinoma without gadolinium? Comparison of combined T2-weighted, T2*-weighted, and diffusion-weighted MRI with gadolinium-enhanced MRI using liver explantation standard. J Comput Assist Tomogr 35(6):711–715
Hecht EM, Holland AE, Israel GM, et al. (2006) Hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic liver: gadolinium-enhanced 3D T1-weighted MR imaging as a stand-alone sequence for diagnosis. Radiology 239(2):438–447
Petruzzi N, Mitchell D, Guglielmo F, et al. (2013) Hepatocellular carcinoma likelihood on MRI exams: evaluation of a standardized categorization system. Acad Radiol 20(6):694–698
Kwak HS, Lee JM, Kim YK, Lee YH, Kim CS (2005) Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of ferumoxides-enhanced and gadolinium-enhanced dynamic three-dimensional volume interpolated breath-hold MR imaging. Eur Radiol 15(1):140–147
Kim JI, Lee JM, Choi JY, et al. (2008) The value of gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced delayed phase MR imaging for characterization of hepatocellular nodules in the cirrhotic liver. Invest Radiol 43(3):202–210
Kim MJ, Kim JH, Chung JJ, et al. (2003) Focal hepatic lesions: detection and characterization with combination gadolinium- and superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 228(3):719–726
Kim YK, Kim CS, Kwak HS, Lee JM (2004) Three-dimensional dynamic liver MR imaging using sensitivity encoding for detection of hepatocellular carcinomas: comparison with superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 20(5):826–837
Kim YK, Kim CS, Lee YH, Kwak HS, Lee JM (2004) Comparison of superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced and gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced dynamic MRI for detection of small hepatocellular carcinomas. Am J Roentgenol 182(5):1217–1223
Kim YK, Kwak HS, Han YM, Kim CS (2007) Usefulness of combining sequentially acquired gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and resovist-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with computed tomography hepatic arteriography and computed tomography arterioportography using 16-slice multidetector computed tomography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 31(5):702–711
Kim YK, Lee YH, Kim CS, Han YM (2008) Added diagnostic value of T2-weighted MR imaging to gadolinium-enhanced three-dimensional dynamic MR imaging for the detection of small hepatocellular carcinomas. Eur J Radiol 67(2):304–310
Kim YK, Lee YH, Kim CS, Han YM, Hwang SB (2008) Double-dose 1.0-M gadobutrol versus standard-dose 0.5-M gadopentetate dimeglumine in revealing small hypervascular hepatocellular carcinomas. Eur Radiol 18(1):70–77
Lee HY, Lee JM, Kim SH, et al. (2008) Detection and characterization of focal hepatic lesions: comparative study of MDCT and gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced MR imaging. Clin Imaging 32(4):287–295
Li CS, Chen RC, Lii JM, et al. (2006) Magnetic resonance imaging appearance of well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma. J Comput Assist Tomogr 30(4):597–603
Matsuo M, Kanematsu M, Itoh K, et al. (2001) Detection of malignant hepatic tumors: comparison of gadolinium- and ferumoxide-enhanced MR imaging. Am J Roentgenol 177(3):637–643
Mori K, Yoshioka H, Takahashi N, et al. (2005) Triple arterial phase dynamic MRI with sensitivity encoding for hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of the diagnostic accuracy among the early, middle, late, and whole triple arterial phase imaging. Am J Roentgenol 184(1):63–69
Nakamura H, Ito N, Kotake F, Mizokami Y, Matsuoka T (2000) Tumor-detecting capacity and clinical usefulness of SPIO-MRI in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol 35(11):849–855
Park G, Kim YK, Kim CS, Yu HC, Hwang SB (2010) Diagnostic efficacy of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI in the detection of hepatocellular carcinomas: comparison with gadopentetate dimeglumine. Br J Radiol 83(996):1010–1016
Park Y, Kim SH, Jeon YH, et al. (2010) Gadoxetic acid (Gd-EOB-DTPA)-enhanced MRI versus gadobenate dimeglumine (Gd-BOPTA)-enhanced MRI for preoperatively detecting hepatocellular carcinoma: an initial experience. Korean J Radiol 11(4):433–440
Sugihara E, Murakami T, Kim T, et al. (2003) Detection of hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma with dynamic magnetic resonance imaging with simultaneously obtained in-phase and opposed-phase echo images. J Comput Assist Tomogr 27(2):110–116
Takahashi N, Yoshioka H, Yamaguchi M, Saida Y, Itai Y (2003) Accelerated dynamic MR imaging with a parallel imaging technique for hypervascular hepatocellular carcinomas: usefulness of a test bolus in examination and subtraction imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 18(1):80–89
Tanaka O, Ito H, Yamada K, et al. (2005) Higher lesion conspicuity for SENSE dynamic MRI in detecting hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma: analysis through the measurements of liver SNR and lesion-liver CNR comparison with conventional dynamic MRI. Eur Radiol 15(12):2427–2434
Tomemori T, Yamakado K, Nakatsuka A, et al. (2001) Fast 3D dynamic MR imaging of the liver with MR SmartPrep: comparison with helical CT in detecting hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Imaging 25(5):355–361
Xu PJ, Yan FH, Wang JH, et al. (2010) Contribution of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the characterization of hepatocellular carcinomas and dysplastic nodules in cirrhotic liver. J Comput Assist Tomogr 34(4):506–512
Yoshioka H, Takahashi N, Yamaguchi M, et al. (2002) Double arterial phase dynamic MRI with sensitivity encoding (SENSE) for hypervascular hepatocellular carcinomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 16(3):259–266
Youk JH, Lee JM, Kim CS (2004) MRI for detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of mangafodipir trisodium and gadopentetate dimeglumine contrast agents. Am J Roentgenol 183(4):1049–1054
Yu JS, Kim KW, Lee JT, Yoo HS (2000) Focal lesions in cirrhotic liver: comparing MR imaging during arterial portography with gd-enhanced dynamic MR imaging. Yonsei Med J 41(5):546–555
Guo L, Liang C, Yu T, et al. (2012) 3 T MRI of hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with cirrhosis: does T2-weighted imaging provide added value? Clin Radiol 67(4):319–328
Ishigami K, Yoshimitsu K, Nishihara Y, et al. (2009) Hepatocellular carcinoma with a pseudocapsule on gadolinium-enhanced MR images: correlation with histopathologic findings. Radiology 250(2):435–443
Choi D, Kim SH, Lim JH, et al. (2001) Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: combined T2-weighted and dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MRI versus combined CT during arterial portography and CT hepatic arteriography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 25(5):777–785
Chou CT, Chen RC, Chen WT, Lii JM (2011) Characterization of hyperintense nodules on T1-weighted liver magnetic resonance imaging: comparison of Ferucarbotran-enhanced MRI with accumulation-phase FS-T1WI and gadolinium-enhanced MRI. J Chin Med Assoc 74(2):62–68
Chung J, Yu JS, Kim DJ, et al. (2011) Hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic liver: diffusion-weighted imaging versus superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced MRI. Magn Reson Imaging 29(9):1235–1243
Kim YK, Kim CS, Chung GH, et al. (2006) Comparison of gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced dynamic MRI and 16-MDCT for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186(1):149–157
Kim DJ, Yu JS, Kim JH, Chung JJ, Kim KW (1018) Small hypervascular hepatocellular carcinomas: value of diffusion-weighted imaging compared with “washout” appearance on dynamic MRI. Br J Radiol 2012(85):e879–e886
Le Moigne F, Durieux M, Bancel B, et al. (2012) Impact of diffusion-weighted MR imaging on the characterization of small hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic liver. Magn Reson Imaging 30(5):656–665
Pauleit D, Textor J, Bachmann R, et al. (2002) Hepatocellular carcinoma: detection with gadolinium- and ferumoxides-enhanced MR imaging of the liver. Radiology 222(1):73–80
Piana G, Trinquart L, Meskine N, et al. (2011) New MR imaging criteria with a diffusion-weighted sequence for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic liver diseases. J Hepatol 55(1):126–132
Pirovano G, Vanzulli A, Marti-Bonmati L, et al. (2000) Evaluation of the accuracy of gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced MR imaging in the detection and characterization of focal liver lesions. Am J Roentgenol 175(4):1111–1120
Seitz K, Bernatik T, Strobel D, et al. (2010) Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) for the characterization of focal liver lesions in clinical practice (DEGUM Multicenter Trial): cEUS vs. MRI—a prospective comparison in 269 patients. Ultraschall Med 31(5):492–499
Vandecaveye V, De Keyzer F, Verslype C, et al. (2009) Diffusion-weighted MRI provides additional value to conventional dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Radiol 19(10):2456–2466
Castoldi MC, Fauda V, Scaramuzza D, Vergnaghi D (2000) Hepatic and hepatocarcinoma magnetic resonance: comparison of the results obtained with paramagnetic (gadolinium) and superparamagnetic (iron oxide particles) contrast media. Radiol Med 100(3):160–167
Kim TK, Lee KH, Jang HJ, et al. (2011) Analysis of gadobenate dimeglumine-enhanced MR findings for characterizing small (1–2-cm) hepatic nodules in patients at high risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology 259(3):730–738
Tahir B, Sandrasegaran K, Ramaswamy R, et al. (2011) Does the hepatocellular phase of gadobenate dimeglumine help to differentiate hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients according to histological grade? Clin Radiol 66(9):845–852
Nakamura Y, Tashiro H, Nambu J, et al. (2013) Detectability of hepatocellular carcinoma by gadoxetate disodium-enhanced hepatic MRI: tumor-by-tumor analysis in explant livers. J Magn Reson Imaging 37(3):684–691
Kim AY, Kim YK, Lee MW, et al. (2012) Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI and diffusion-weighted MRI with respect to the severity of liver cirrhosis. Acta Radiol 53(8):830–838
Lee JY, Kim SH, Jeon YH, et al. (2010) Ferucarbotran-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging versus gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the preoperative detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: initial experience. J Comput Assist Tomogr 34(1):127–134
Baird AJ, Amos GJ, Saad NF, Benson MD (2013) Retrospective audit to determine the diagnostic accuracy of Primovist-enhanced MRI in the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis with explant histopathology correlation. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol 57(3):314–320
Ooka Y, Kanai F, Okabe S, et al. (2013) Gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI compared with CT during angiography in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Magn Reson Imaging 31(5):748–754
Chou CT, Chen YL, Su WW, Wu HK, Chen RC (2010) Characterization of cirrhotic nodules with gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging: the efficacy of hepatocyte-phase imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 32(4):895–902
Kim YK, Kim CS, Han YM, Lee YH (2011) Detection of liver malignancy with gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI: is addition of diffusion-weighted MRI beneficial? Clin Radiol 66(6):489–496
Kim YK, Kim CS, Han YM, Park G (2010) Detection of small hepatocellular carcinoma can gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging replace combining gadopentetate dimeglumine-enhanced and superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging? Invest Radiol 45(11):740–746
Kim YK, Kim CS, Han YM, et al. (2010) Comparison of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI and superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced MRI for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Radiol 65(5):358–365
Kim YK, Kim CS, Han YM, Yu HC, Choi D (2011) Detection of small hepatocellular carcinoma intraindividual comparison of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI at 3.0 and 1.5 T. Invest Radiol 46(6):383–389
Kim YK, Kwak HS, Kim CS, Han YM (2009) Detection and characterization of focal hepatic tumors: a comparison of T2-weighted MR images before and after the administration of gadoxectic acid. J Magn Reson Imaging 30(2):437–443
Lee CH, Kim KA, Lee J, et al. (2012) Using low tube voltage (80 kVp) quadruple phase liver CT for the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: two-year experience and comparison with Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced liver MRI. Eur J Radiol 81(4):E605–E611
Lee MH, Kim SH, Park MJ, Park CK, Rhim H (2011) Gadoxetic acid-enhanced hepatobiliary phase MRI and high-b-value diffusion-weighted imaging to distinguish well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinomas from benign nodules in patients with chronic liver disease. Am J Roentgenol 197(5):W868–W875
Motosugi U, Ichikawa T, Sou H, et al. (2009) Dilution method of gadolinium ethoxybenzyl diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (Gd-EOB-DTPA)-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). J Magn Reson Imaging 30(4):849–854
Ahn SS, Kim MJ, Lim JS, et al. (2010) Added value of gadoxetic acid-enhanced hepatobiliary phase MR imaging in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology 255(2):459–466
Park MJ, Kim YK, Lee MW, et al. (2012) Small hepatocellular carcinomas: improved sensitivity by combining gadoxetic acid-enhanced and diffusion-weighted MR imaging patterns. Radiology 264(3):761–770
Rhee H, Kim MJ, Park MS, Kim KA (1018) Differentiation of early hepatocellular carcinoma from benign hepatocellular nodules on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI. Br J Radiol 2012(85):E837–E844
Takahashi M, Maruyama H, Shimada T, et al. (2013) Characterization of hepatic lesions (≤30 mm) with liver-specific contrast agents: a comparison between ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging. Eur J Radiol 82(1):75–84
Watanabe H, Kanematsu M, Goshima S, et al. (2012) Is gadoxetate disodium-enhanced MRI useful for detecting local recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation therapy? Am J Roentgenol 198(3):589–595
Chung SH, Kim MJ, Choi JY, Hong HS (2010) Comparison of two different injection rates of gadoxetic acid for arterial phase MRI of the liver. J Magn Reson Imaging 31(2):365–372
Saito K, Kotake F, Ito N, et al. (2005) Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced MRI for hepatocellular carcinoma: quantitative evaluation of tumor enhancement in hepatobiliary phase. Magn Reson Med Sci. 4(1):1–9
Golfieri R, Renzulli M, Lucidi V, et al. (2011) Contribution of the hepatobiliary phase of Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI to dynamic MRI in the detection of hypovascular small (≤2 cm) HCC in cirrhosis. Eur Radiol 21(6):1233–1242
Bashir MR, Gupta RT, Davenport MS, et al. (2013) Hepatocellular carcinoma in a North American population: does hepatobiliary MR imaging with Gd-EOB-DTPA improve sensitivity and confidence for diagnosis? J Magn Reson Imaging 37(2):398–406
Tsang LLC, Chen CL, Huang TL, et al. (2011) Superparamagnectic iron oxide-enhanced magnetic resonance for tumor surveillance in cirrhotic liver before liver transplantation with explanted liver correlation. Transpl Proc 43(5):1674–1677
Macarini L, Milillo P, Cascavilla A, et al. (2009) MR characterisation of dysplastic nodules and hepatocarcinoma in the cirrhotic liver with hepatospecific superparamagnetic contrast agents: pathological correlation in explanted livers. Radiol Med 114(8):1267–1282
Mori K, Scheidler J, Helmberger T, et al. (2002) Detection of malignant hepatic lesions before orthotopic liver transplantation: accuracy of ferumoxides-enhanced MR imaging. Am J Roentgenol 179(4):1045–1051
Kim MJ, Kim JH, Lim JS, et al. (2004) Detection and characterization of focal hepatic lesions: mangafodipir vs. superparamagnetic iron oxide-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 20(4):612–621
Choi D, Kim SH, Lim JH, et al. (2001) Preoperative detection of hepatocellular carcinoma: ferumoxides-enhanced MRI imaging versus combined helical CT during arterial portography and CT hepatic arteriography. Am J Roentgenol 176(2):475–482
Nishie A, Tajima T, Ishigami K, et al. (2010) Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) using super paramagnetic iron oxide (SPIO)-enhanced MRI: added value of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI). J Magn Reson Imaging 31(2):373–382
Macarini L, Marini S, Milillo P, Vinci R, Ettorre GC (2006) Double-contrast MRI (DC-MRI) in the study of the cirrhotic liver: utility of administering Gd-DTPA as a complement to examinations in which SPIO liver uptake and distribution alterations (SPIO-LUDA) are present and in the identification and characterisation of focal lesions. Radiol Med 111(8):1087–1102
Ward J, Guthrie JA, Scott DJ, et al. (2000) Hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic liver: double-contrast MR imaging for diagnosis. Radiology 216(1):154–162
Qayyum A, Thoeni RF, Coakley FV, et al. (2006) Detection of hepatocellular carcinoma by ferumoxides-enhanced MR imaging in cirrhosis: incremental value of dynamic gadolinium-enhancement. J Magn Reson Imaging 23(1):17–22
Acknowledgments
Funding support and acknowledgments of individuals and institutions that have provided personal assistance are withheld from this section to preserve blinding to the submitting authors and their institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Robert F. Hanna and Vesselin Z. Miloushev have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanna, R.F., Miloushev, V.Z., Tang, A. et al. Comparative 13-year meta-analysis of the sensitivity and positive predictive value of ultrasound, CT, and MRI for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma. Abdom Radiol 41, 71–90 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-015-0592-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-015-0592-8