Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate and validate the reproducibility of MR Elastography (MRE)-derived liver stiffness values on two different MR vendor platforms performed on the same subject on the same day.
Methods
This investigation was approved by the hospital IRB. MRE exams were performed twice in identical fashion in eight volunteers and in five clinical patients on two different 1.5 T MR scanners—once on a Philips MR scanner and immediately afterward in back-to-back fashion on a General Electric MR scanner, or vice versa. All scan parameters were kept identical on the two platforms to the best extent possible. After the MRE magnitude and phase images were obtained, the data were converted into quantitative images displaying the stiffness of the liver parenchyma. Mean liver stiffness values between the two platforms were compared using interclass correlation with a p value <0.05 considered statistically significant.
Results
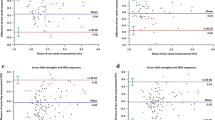
Interclass correlation coefficient (ICC) value of 0.994 was obtained for 13 subjects with p value <0.001 indicating a significantly positive correlation.
Conclusion
As MRE gains in acceptance and as its availability becomes more widespread, it is important to ascertain and confirm that liver stiffness values obtained on different MRE vendor platforms are consistent and reproducible. In this small pilot investigation, we demonstrate that liver stiffness measurement with MRE is reproducible and has very good consistency across two vendor platforms.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beath SV (1994) Liver disorders in childhood. Arch Dis Child 71(4):390
Friedman SL (2003) Liver fibrosis—from bench to bedside. J Hepatol 38(Suppl 1):S38–S53
Friedman SL (2010) Evolving challenges in hepatic fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7(8):425–436. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2010.97
Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D (2008) Autoimmune paediatric liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 14(21):3360–3367
Brunt EM (2010) Pathology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7(4):195–203. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2010.21
Bortolotti F, Guido M (2007) Reversal of liver cirrhosis: a desirable clinical outcome and its pathogenic background. J pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 44(4):401–406. doi:10.1097/MPG.0b013e318032069a
Naini BV, Lassman CR (2012) Total parenteral nutrition therapy and liver injury: a histopathologic study with clinical correlation. Hum Pathol 43(6):826–833. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2011.07.008
Castera L, Pinzani M (2010) Biopsy and non-invasive methods for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis: does it take two to tango? Gut 59(7):861–866. doi:10.1136/gut.2010.214650
Pariente D, Franchi-Abella S (2010) Paediatric chronic liver diseases: how to investigate and follow up? Role of imaging in the diagnosis of fibrosis. Pediatr Radiol 40(6):906–919. doi:10.1007/s00247-010-1600-3
Straub BK, Schirmacher P (2010) Pathology and biopsy assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig Dis 28(1):197–202. doi:10.1159/000282086
Regev A, Berho M, Jeffers LJ, et al. (2002) Sampling error and intraobserver variation in liver biopsy in patients with chronic HCV infection. Am J Gastroenterol 97(10):2614–2618. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.06038.x
Xanthakos SA, Podberesky DJ, Serai SD, et al. (2014) Use of magnetic resonance elastography to assess hepatic fibrosis in children with chronic liver disease. J Pediatr 164(1):186–188. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.07.050
Yin M, Talwalkar JA, Glaser KJ, Manduca A, Grimm RC, Rossman PJ, Fidler JL, Ehman RL (2007) Assessment of hepatic fibrosis with magnetic resonance elastography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 5 (10):1207–1213.e1202. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2007.06.012
Serai SD, Towbin AJ, Podberesky DJ (2012) Pediatric liver MR elastography. Dig Dis Sci 57(10):2713–2719. doi:10.1007/s10620-012-2196-2
Serai SD, Wallihan DB, Venkatesh SK, et al. (2014) Magnetic resonance elastography of the liver in patients status-post fontan procedure: feasibility and preliminary results. Congenit Heart Dis 9(1):7–14. doi:10.1111/chd.12144
Towbin AJ, Serai SD, Podberesky DJ (2013) Magnetic resonance imaging of the pediatric liver: imaging of steatosis, iron deposition, and fibrosis. Magn Reson Imaging Clin North Am 21(4):669–680. doi:10.1016/j.mric.2013.05.001
Wallihan DB, Podberesky DJ, Marino BS, Sticka JS, Serai S (2013) Relationship of MR elastography determined liver stiffness with cardiac function after Fontan palliation. J Magn Reson Imaging . doi:10.1002/jmri.24496
Manduca A, Oliphant TE, Dresner MA, et al. (2001) Magnetic resonance elastography: non-invasive mapping of tissue elasticity. Med Image Anal 5(4):237–254
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1(8476):307–310
Bland JM, Altman DG (2012) Agreed statistics: measurement method comparison. Anesthesiology 116(1):182–185. doi:10.1097/ALN.0b013e31823d7784
Lee Y, Lee JM, Lee JE, et al. (2014) MR elastography for noninvasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis: reproducibility of the examination and reproducibility and repeatability of the liver stiffness value measurement. J Magn Reson Imaging 39(2):326–331. doi:10.1002/jmri.24147
Shi Y, Glaser KJ, Venkatesh SK, Ben-Abraham EI, Ehman RL (2014) Feasibility of using 3D MR elastography to determine pancreatic stiffness in healthy volunteers. J Magn Reson Imaging . doi:10.1002/jmri.24572
Bota S, Sporea I, Sirli R, et al. (2012) Intra- and interoperator reproducibility of acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography–preliminary results. Ultrasound Med Biol 38(7):1103–1108. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2012.02.032
Ebinuma H, Saito H, Komuta M, et al. (2011) Evaluation of liver fibrosis by transient elastography using acoustic radiation force impulse: comparison with Fibroscan((R)). J Gastroenterol 46(10):1238–1248. doi:10.1007/s00535-011-0437-3
Rizzo L, Calvaruso V, Cacopardo B, et al. (2011) Comparison of transient elastography and acoustic radiation force impulse for non-invasive staging of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol 106(12):2112–2120. doi:10.1038/ajg.2011.341
Acknowledgements
Partial support from NIH grant EB001981 to RLE.
Conflict of interest
RLE and the Mayo Clinic hold patents and have a financial interest through royalties related to MRE technology. HW is an employee of Philips Healthcare. DJP received travel reimbursement from Philips Healthcare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serai, S.D., Yin, M., Wang, H. et al. Cross-vendor validation of liver magnetic resonance elastography. Abdom Imaging 40, 789–794 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0282-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0282-y