Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate the supportive role of molecular and structural biomarkers (CSF protein levels, FDG PET and MRI) in the early differential diagnosis of dementia in a large sample of patients with neurodegenerative dementia, and in determining the risk of disease progression in subjects with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
Methods
We evaluated the supportive role of CSF Aβ42, t-Tau, p-Tau levels, conventional brain MRI and visual assessment of FDG PET SPM t-maps in the early diagnosis of dementia and the evaluation of MCI progression.
Results
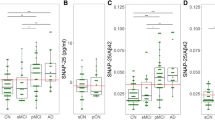
Diagnosis based on molecular biomarkers showed the best fit with the final diagnosis at a long follow-up. FDG PET SPM t-maps had the highest diagnostic accuracy in Alzheimer’s disease and in the differential diagnosis of non-Alzheimer’s disease dementias. The p-tau/Aβ42 ratio was the only CSF biomarker providing a significant classification rate for Alzheimer’s disease. An Alzheimer’s disease-positive metabolic pattern as shown by FDG PET SPM in MCI was the best predictor of conversion to Alzheimer’s disease.
Conclusion
In this clinical setting, FDG PET SPM t-maps and the p-tau/Aβ42 ratio improved clinical diagnostic accuracy, supporting the importance of these biomarkers in the emerging diagnostic criteria for Alzheimer’s disease dementia. FDG PET using SPM t-maps had the highest predictive value by identifying hypometabolic patterns in different neurodegenerative dementias and normal brain metabolism in MCI, confirming its additional crucial exclusionary role.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prince M, Bryce R, Ferri C. World Alzheimer report 2011: the benefits of early diagnosis and intervention. London: Alzheimer's Disease International; 2011.
Geldmacher DS, Kirson NY, Birnbaum HG, Eapen S, Kantor E, Cummings AK, et al. Implications of early treatment among Medicaid patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2014;10:214–24.
Gaugler JE, Ascher-Svanum H, Roth DL, Fafowora T, Siderowf A, Beach TG. Characteristics of patients misdiagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease and their medication use: an analysis of the NACC-UDS database. BMC Geriatr. 2013;13:137.
Albert MS, DeKosky ST, Dickson D, Dubois B, Feldman HH, Fox NC, et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7:270–9.
Sperling RA, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, Bennett DA, Craft S, Fagan AM, et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7:280–92.
McKeith IG, Dickson DW, Lowe J, Emre M, O’Brien JT, Feldman H, et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: third report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology. 2005;65:1863–72.
Rascovsky K, Hodges JR, Knopman D, Mendez MF, Kramer JH, Neuhaus J, et al. Sensitivity of revised diagnostic criteria for the behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia. Brain. 2011;134:2456–77.
Gorno-Tempini ML, Hillis AE, Weintraub S, Kertesz A, Mendez M, Cappa SF, et al. Classification of primary progressive aphasia and its variants. Neurology. 2011;76:1006–14.
Armstrong MJ, Litvan I, Lang AE, Bak TH, Bhatia KP, Borroni B, et al. Criteria for the diagnosis of corticobasal degeneration. Neurology. 2013;80:496–503.
Dubois B, Feldman HH, Jacova C, Hampel H, Molinuevo JL, Blennow K, et al. Advancing research diagnostic criteria for Alzheimer ’ s disease : the IWG-2 criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13(6):614–29.
Shaw LM, Korecka M, Clark CM, Lee VM-Y, Trojanowski JQ. Biomarkers of neurodegeneration for diagnosis and monitoring therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2007;6:295–303.
Herholz K, Salmon E, Perani D, Baron JC, Holthoff V, Frölich L, et al. Discrimination between Alzheimer dementia and controls by automated analysis of multicenter FDG PET. Neuroimage. 2002;17:302–16.
Anchisi D, Borroni B, Franceschi M, Kerrouche N, Kalbe E, Beuthien-Beumann B, et al. Heterogeneity of brain glucose metabolism in mild cognitive impairment and clinical progression to Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2005;62:1728–33.
Cerami C, Della Rosa PA, Magnani G, Santangelo R, Marcone A, Cappa SF, et al. Brain metabolic maps in Mild Cognitive Impairment predict heterogeneity of progression to dementia. Neuroimage Clin. 2014;7:187–94.
Ferreira D, Perestelo-Pérez L, Westman E, Wahlund LO, Sarría A, Serrano-Aguilar P. Meta-review of CSF core biomarkers in Alzheimer’s disease: the state-of-the-art after the new revised diagnostic criteria. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014;6:47.
Frisoni GB, Fox NC, Jack CR, Scheltens P, Thompson PM. The clinical use of structural MRI in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2010;6:67–77.
Nordberg A, Carter SF, Rinne J, Drzezga A, Brooks DJ, Vandenberghe R, et al. A European multicentre PET study of fibrillar amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;40:104–14.
Lehmann M, Ghosh PM, Madison C, Laforce R, Corbetta-Rastelli C, Weiner MW, et al. Diverging patterns of amyloid deposition and hypometabolism in clinical variants of probable Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 2013;136:844–58.
Murray J, Tsui WH, Li Y, Mchugh P, Williams S, Pirraglia E, et al. FDG and amyloid PET in cognitively normal individuals at risk for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Adv J Mol Imaging. 2014;4:15–26.
McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman BT, Jack Jr CR, Kawas CH, et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7:263–9.
Coppi E, Ferrari L, Santangelo R, Caso F, Pinto P, Passerini G, et al. Further evidence about the crucial role of CSF biomarkers in diagnosis of posterior cortical atrophy. Neurol Sci. 2014;35:785–7.
Santangelo R, Coppi E, Ferrari L, Bernasconi MP, Pinto P, Passerini G, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers can play a pivotal role in the diagnostic work up of primary progressive aphasia. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;43:1429–40.
Ferreira D, Rivero-Santana A, Perestelo-Pérez L, Westman E, Wahlund L-O, Sarría A, et al. Improving CSF biomarkers’ performance for predicting progression from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease by considering different confounding factors: a meta-analysis. Front Aging Neurosci. 2014;6:287.
Blennow K, Dubois B, Fagan AM, Lewczuk P, de Leon MJ, Hampel H. Clinical utility of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in the diagnosis of early Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2015;11:58–69.
Jack CR, Dickson DW, Parisi JE, Xu YC, Cha RH, O’Brien PC, et al. Antemortem MRI findings correlate with hippocampal neuropathology in typical aging and dementia. Neurology. 2002;58:750–7.
Barkhof F, Polvikoski TM, Van Straaten EC, Kalaria RN, Sulkava R, Aronen HJ, et al. The significance of medial temporal lobe atrophy: a postmortem MRI study in the very old. Neurology. 2007;69:1521–7.
Hodges JR. Alzheimer’s disease and the frontotemporal dementias: contributions to clinico-pathological studies, diagnosis, and cognitive neuroscience. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;33:S211–7.
Raji CA, Lopez OL, Kuller LH, Becker JT. Age, Alzheimer disease, and brain structure. Neurology. 2009;73(22):1899–905.
Perani D. Functional neuroimaging of cognition. Handb Clin Neurol. 2008;88:61–111.
Perani D. FDG-PET and amyloid-PET imaging: the diverging paths. Curr Opin Neurol. 2014;27:405–13.
Weiner MW, Veitch DP, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, Cairns NJ, Green RC, et al. The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: a review of papers published since its inception. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9:e111–94.
Sánchez-Juan P, Ghosh PM, Hagen J, Gesierich B, Henry M, Grinberg LT, et al. Practical utility of amyloid and FDG-PET in an academic dementia center. Neurology. 2014;82:230–8.
Perani D, Della Rosa PA, Cerami C, Gallivanone F, Fallanca F, Vanoli EG, et al. Validation of an optimized SPM procedure for FDG-PET in dementia diagnosis in a clinical setting. Neuroimage. 2014;6:445–54.
Ossenkoppele R, Prins ND, Pijnenburg YAL, Lemstra AW, van der Flier WM, Adriaanse SF, et al. Impact of molecular imaging on the diagnostic process in a memory clinic. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9:414–21.
Cerami C, Crespi C, Della Rosa PA, Dodich A, Marcone A, Magnani G, et al. Brain changes within the visuo-spatial attentional network in posterior cortical atrophy. J Alzheimers Dis. 2015;43:385–95.
Frisoni GB, Bocchetta M, Chételat G, Rabinovici GD, de Leon MJ, Kaye J, et al. Imaging markers for Alzheimer disease: which vs how. Neurology. 2013;81:487–500.
Frisoni GB, Perani D, Bastianello S, Bernardi G, Cappa SF, Trabucchi M. A roadmap to the use of biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease in clinical practice: the Italian inter-societal consensus. Document based on a workshop held at the 3rd National Health Research Conference, Cernobbio, Como, 12 November 2012, organized by the Directorate for Research of the Italian Ministry of Health. http://www.centroalzheimer.org/iw/pdf/italian_roadmap.pdf. Accessed 14 August 2015.
Li Y, Rinne JO, Mosconi L, Pirraglia E, Rusinek H, DeSanti S, et al. Regional analysis of FDG and PIB-PET images in normal aging, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008;35:2169–81.
Edison P, Archer HA, Hinz R, Hammers A, Pavese N, Tai YF, et al. Amyloid, hypometabolism, and cognition in Alzheimer disease: an [11C]PIB and [18F]FDG PET study. Neurology. 2007;68:501–8.
Kasanuki K, Iseki E, Fujishiro H, Yamamoto R, Higashi S, Minegishi M, et al. Neuropathological investigation of the hypometabolic regions on positron emission tomography with [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose in patients with dementia with Lewy bodies. J Neurol Sci. 2012;314:111–9.
Landau SM, Harvey D, Madison CM, Reiman EM, Foster NL, Aisen PS, et al. Comparing predictors of conversion and decline in mild cognitive impairment. Neurology. 2010;75:230–8.
Prestia A, Caroli A, van der Flier WM, Ossenkoppele R, Van Berckel B, Barkhof F, et al. Prediction of dementia in MCI patients based on core diagnostic markers for Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 2013;80:1048–56.
Zhang D, Wang Y, Zhou L, Yuan H, Shen D. Multimodal classification of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Neuroimage. 2011;55:856–67.
Morinaga A, Ono K, Ikeda T, Ikeda Y, Shima K, Noguchi-Shinohara M, et al. A comparison of the diagnostic sensitivity of MRI, CBF-SPECT, FDG-PET and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for detecting Alzheimer’s disease in a memory clinic. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2010;30:285–92.
Shaffer JL, Petrella JR, Sheldon FC, Choudhury KR, Calhoun VD, Coleman RE, et al. Predicting cognitive decline in subjects at risk for Alzheimer disease by using combined cerebrospinal fluid, MR imaging, and PET biomarkers. Radiology. 2013;266:583–91.
Choo IH, Ni R, Schöll M, Wall A, Almkvist O, Nordberg A. Combination of (18)F-FDG PET and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers as a better predictor of the progression to Alzheimer’s disease in mild cognitive impairment patients. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;33:929–39.
Alexopoulos P, Kriett L, Haller B, Klupp E, Gray K, Grimmer T, et al. Limited agreement between biomarkers of neuronal injury at different stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2014;10:684–9.
Della Rosa PA, Cerami C, Gallivanone F, Prestia A, Caroli A, Castiglioni I, et al. A standardized [18F]-FDG-PET template for spatial normalization in statistical parametric mapping of dementia. Neuroinformatics. 2014;12:575–93.
Petersen RC, Roberts RO, Knopman DS, Boeve BF, Geda YE, Ivnik RJ, et al. Mild cognitive impairment: ten years later. Arch Neurol. 2009;66:1447–55.
Tapiola T, Alafuzoff I, Herukka SK, Parkkinen L, Hartikainen P, Soininen H, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid {beta}-amyloid 42 and tau proteins as biomarkers of Alzheimer-type pathologic changes in the brain. Arch Neurol. 2009;66:382–9.
Jack Jr CR, Albert MS, Knopman DS, McKhann GM, Sperling RA, Carrillo MC, et al. Introduction to the recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7:257–62.
Salmon E, Garraux G, Delbeuck X, Collette F, Kalbe E, Zuendorf G, et al. Predominant ventromedial frontopolar metabolic impairment in frontotemporal dementia. Neuroimage. 2003;20:435–40.
Foster NL, Heidebrink JL, Clark CM, Jagust WJ, Arnold SE, Barbas NR, et al. FDG-PET improves accuracy in distinguishing frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain. 2007;130:2616–35.
Gorno-Tempini ML, Dronkers NF, Rankin KP, Ogar JM, Phengrasamy L, Rosen HJ, et al. Cognition and anatomy in three variants of primary progressive aphasia. Ann Neurol. 2004;55:335–46.
Fellgiebel A, Scheurich A, Bartenstein P, Müller MJ. FDG-PET and CSF phospho-tau for prediction of cognitive decline in mild cognitive impairment. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. 2007;155:167–71.
Walhovd KB, Fjell AM, Brewer J, McEvoy LK, Fennema-Notestine C, Hagler DJ, et al. Combining MR imaging, positron-emission tomography, and CSF biomarkers in the diagnosis and prognosis of Alzheimer disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010;31:347–54.
Kaerst L, Kuhlmann A, Wedekind D, Stoeck K, Lange P, Zerr I. Using cerebrospinal fluid marker profiles in clinical diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;38:63–73.
Van de Pol LA, Hensel A, Barkhof F, Gertz HJ, Scheltens P, van der Flier WM. Hippocampal atrophy in Alzheimer disease: age matters. Neurology. 2006;66:236–8.
Compliance with ethical standards
Funding
This research was funded by EU FP7 INMIND Project (FP7-HEALTH-2013, grant agreement no. 278850), the Italian Ministry of Health (Ricerca Finalizzata Progetto Reti Nazionale AD NET-2011-02346784), and Fondazione Eli-Lilly (Eli-Lilly grant 2011 "Imaging of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in prodromal and presymptomatic Alzheimer's disease phases”).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Ethical approval
For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perani, D., Cerami, C., Caminiti, S.P. et al. Cross-validation of biomarkers for the early differential diagnosis and prognosis of dementia in a clinical setting. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 43, 499–508 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-015-3170-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-015-3170-y