Abstract
Purpose
Increased expression of αvβ3/αvβ5 integrin is involved in angiogenesis and the inflammatory process in atherosclerotic plaques. The novel 68Ga-DOTA-RGD peptide binds with high affinity to αvβ3/αvβ5 integrin. The aim of this study was to investigate the uptake of the 68Ga-DOTA-RGD peptide in atherosclerotic plaques.
Methods
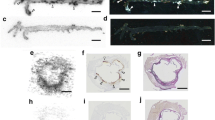
Uptake of intravenously administered 68Ga-DOTA-RGD peptide was studied ex vivo in excised tissue samples and aortic sections of LDLR−/−ApoB100/100 atherosclerotic mice. The uptake of the tracer in aortic cryosections was examined by using digital autoradiography. Subsequently, the autoradiographs were combined with histological and immunohistological analysis of the sections.
Results
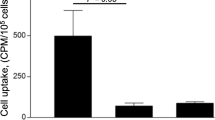
DOTA-RGD peptide was successfully labelled with the generator-produced 68Ga. The tracer had reasonably good specific radioactivity (8.7 ± 1.1 GBq/μmol) and was quite stable in vivo. According to ex vivo biodistribution results, 68Ga-DOTA-RGD was cleared rapidly from the blood circulation and excreted through the kidneys to the urine with high radioactivity in the intestine, lungs, spleen and liver. Autoradiography results showed significantly higher uptake of 68Ga-DOTA-RGD peptide in the atherosclerotic plaques compared to healthy vessel wall (mean ratio ± SD 1.4 ± 0.1, p = 0.0004).
Conclusion
We observed that 68Ga-DOTA-RGD is accumulated into the plaques of atherosclerotic mice. However, this data only shows the feasibility of the approach, while the clinical significance still remains to be proven. Further studies are warranted to assess the uptake of this tracer into human atherosclerotic plaques.






Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Libby P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature. 2002;420:868–74.
Libby P, Theroux P. Pathophysiology of coronary artery disease. Circulation. 2005;111:3481–8.
Fan J, Watanabe T. Inflammatory reactions in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2003;10:63–71.
Wintermark M, Jawadi SS, Rapp JH, Tihan T, Tong E, Glidden DV, et al. High-resolution CT imaging of carotid artery atherosclerotic plaques. Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29:875–82.
Waters EA, Wickline SA. Contrast agents for MRI. Basic Res Cardiol. 2008;103:114–21.
MacNeill BD, Jang IK, Bouma BE, Iftimia N, Takano M, Yabushita H, et al. Focal and multi-focal plaque macrophage distributions in patients with acute and stable presentations of coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44:972–9.
Schaar JA, Mastik F, Regar E, den Uil CA, Gijsen FJ, Wentzel JJ, et al. Current diagnostic modalities for vulnerable plaque detection. Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13:995–1001.
Laitinen I, Marjamäki P, Haaparanta M, Savisto N, Laine VJ, Soini SL, et al. Non-specific binding of [(18)F]FDG to calcifications in atherosclerotic plaques: experimental study of mouse and human arteries. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2006;33:1461–7.
Khurana R, Simons M, Martin JF, Zachary IC. Role of angiogenesis in cardiovascular disease: a critical appraisal. Circulation. 2005;112:1813–24.
Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Finn AV, Gold HK, Tulenko TN, et al. Atherosclerotic plaque progression and vulnerability to rupture: angiogenesis as a source of intraplaque hemorrhage. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:2054–61.
Hoshiga M, Alpers CE, Smith LL, Giachelli CM, Schwartz SM. Alpha-v beta-3 integrin expression in normal and atherosclerotic artery. Circ Res. 1995;77:1129–35.
Antonov AS, Kolodgie FD, Munn DH, Gerrity RG. Regulation of macrophage foam cell formation by alpha V beta 3 integrin: potential role in human atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol. 2004;165:247–58.
Dufourcq P, Louis H, Moreau C, Daret D, Boisseau MR, Lamaziere JMD, et al. Vitronectin expression and interaction with receptors in smooth muscle cells from human atheromatous plaque. Arterioscl Throm Vas. 1998;18:168–76.
Beer AJ, Schwaiger M. Imaging of integrin alphavbeta3 expression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008;27:631–44.
Burtea C, Laurent S, Murariu O, Rattat D, Toubeau G, Verbruggen A, et al. Molecular imaging of alpha v beta3 integrin expression in atherosclerotic plaques with a mimetic of RGD peptide grafted to Gd-DTPA. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;78:148–57.
Indrevoll B, Kindberg GM, Solbakken M, Bjurgert E, Johansen JH, Karlsen H, et al. NC-100717: a versatile RGD peptide scaffold for angiogenesis imaging. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006;16:6190–3.
Heinonen SE, Leppänen P, Kholova I, Lumivuori H, Hakkinen SK, Bosch F, et al. Increased atherosclerotic lesion calcification in a novel mouse model combining insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and hypercholesterolemia. Circ Res. 2007;101:1058–67.
Laitinen I, Marjamäki P, Någren K, Laine VJ, Wilson I, Leppänen P, et al. Uptake of inflammatory cell marker [11C]PK11195 into mouse atherosclerotic plaques. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009;36:73–80.
Decristoforo C, Hernandez GI, Carlsen J, Rupprich M, Huisman M, Virgolini I, et al. 68Ga- and 111In-labelled DOTA-RGD peptides for imaging of alphavbeta3 integrin expression. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008;35:1507–15.
Jeong JM, Hong MK, Chang YS, Lee YS, Kim YJ, Cheon GJ, et al. Preparation of a promising angiogenesis PET imaging agent: 68Ga-labeled c(RGDyK)-isothiocyanatobenzyl-1, 4, 7-triazacyclononane-1, 4, 7-triacetic acid and feasibility studies in mice. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:830–6.
Li ZB, Chen K, Chen X. (68)Ga-labeled multimeric RGD peptides for microPET imaging of integrin alpha(v)beta (3) expression. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008;35:1100–8.
Horton MA. The alpha v beta 3 integrin ''vitronectin receptor''. Int J Biochem Cell B. 1997;29:721–5.
Hillis GS, Flapan AD. Cell adhesion molecules in cardiovascular disease: a clinical perspective. Heart. 1998;79:429–31.
Dijkgraaf I, Kruijtzer JA, Liu S, Soede AC, Oyen WJ, Corstens FH, et al. Improved targeting of the alpha(v)beta (3) integrin by multimerisation of RGD peptides. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2007;34:267–73.
Paulhe F, Racaud-Sultan C, Ragab A, Albiges-Rizo C, Chap H, Iberg N, et al. Differential regulation of phosphoinositide metabolism by alpha(V)beta(3) and alpha(V)beta(5) integrins upon smooth muscle cell migration. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:41832–40.
Veniant MM, Zlot CH, Walzem RL, Pierotti V, Driscoll R, Dichek D, et al. Lipoprotein clearance mechanisms in LDL receptor-deficient "Apo-B48-only" and "Apo-B100-only" mice. J Clin Invest. 1998;102:1559–68.
Acknowledgements
This study was conducted within the Finnish Centre of Excellence in Molecular Imaging in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Research, supported by the Academy of Finland, University of Turku, Turku University Hospital and Åbo Akademi University. The work was funded by the Finnish Foundation for Cardiovascular Research and Drug Discovery Graduate School of the University of Turku. The authors would like to thank Erja Mäntysalo for excellent assistance in animal experiments, Erica Nyman for performing tissue sectioning and immunostainings, Irina Lisinen for providing expertise in statistical tests, Sanna Hellberg for image processing, and Henri Sipilä for assistance in 68Ga-labelling and HPLC analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haukkala, J., Laitinen, I., Luoto, P. et al. 68Ga-DOTA-RGD peptide: biodistribution and binding into atherosclerotic plaques in mice. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 36, 2058–2067 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-009-1220-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-009-1220-z