Abstract
Purpose
Lipid nanocapsules (LNC) entrapping lipophilic complexes of 188Re (188Re(S3CPh)2(S2CPh) [188Re-SSS]) were investigated as a novel radiopharmaceutical carrier for internal radiation therapy of malignant gliomas. The present study was designed to evaluate the efficacy of intra-cerebral administration of 188Re-SSS LNC by means of convection-enhanced delivery (CED) on a 9L rat brain tumour model.
Methods
Female Fischer rats with 9L glioma were treated with a single injection of 188Re-SSS LNC by CED 6days after cell implantation. Rats were put into random groups according to the dose infused: 12, 10, 8 and 3Gy in comparison with blank LNC, perrhenate solution (4Gy) and non-treated animals. The radionuclide brain retention level was evaluated by measuring 188Re elimination in faeces and urine over 72h after the CED injection. The therapeutic effect of 188Re-SSS LNC was assessed based on animal survival.
Results
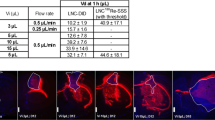
CED of 188Re perrhenate solution resulted in rapid drug clearance with a brain T 1/2 of 7h. In contrast, when administered in LNC, 188Re tissue retention was greatly prolonged, with only 10% of the injected dose being eliminated at 72h. Rat median survival was significantly improved for the group treated with 8Gy 188Re-SSS LNC compared to the control group and blank LNC-treated animals. The increase in the median survival time was about 80% compared to the control group; 33% of the animals were long-term survivors. The dose of 8Gy proved to be a very effective dose, between toxic (10–12Gy) and ineffective (3–4Gy) doses.
Conclusions
These findings show that CED of 188Re-loaded LNC is a safe and potent anti-tumour system for treating malignant gliomas. Our data are the first to show the in vivo efficacy of 188Re internal radiotherapy for the treatment of brain malignancy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nieder C, Adam M, Molls M, Grosu AL. Therapeutic options for recurrent high-grade glioma in adult patients: recent advances. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2006;60:181–93.
Behin A, Hoang-Xuan K, Carpentier AF, Delattre J-Y. Primary brain tumours in adults. Lancet 2003;361:323–31.
Mitra A, Nan A, Line BR, Ghandehari H. Nanocarriers for nuclear imaging and radiotherapy of cancer. Curr Pharm Des 2006;12:4729–49.
Barth RF, Yang W, Coderre JA. Rat brain tumor models to assess the efficacy of boron neutron capture therapy: a critical evaluation. J Neuro-Oncol 2003;62:61–74.
Ljunggren K, Liu X, Erlandsson K, Ljungberg M, Salford L, Strand SE. Absorbed dose distribution in glioma tumors in rat brain after therapeutic intratumoral injection of 201Tl-chloride. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2004;19:562–9.
Jeong JM, Chung J-K. Therapy with 188Re-labeled radiopharmaceuticals: an overview of promising results from initial clinical trials. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2003;18:707–17.
Iznaga-Escobar N. 188Re-direct labeling of monoclonal antibodies for radioimmunotherapy of solid tumors: biodistribution, normal organ dosimetry, and toxicology. Nucl Med Biol 1998;25:441–7.
Lambert B, De Klerk JMH. Clinical applications of 188Re-labelled radiopharmaceuticals for radionuclide therapy. Nucl Med Commun 2006;27:223–9.
Ballot S, Noiret N, Hindre F, Denizot B, Garin E, Rajerison H, et al. 99mTc/188Re-labelled lipid nanocapsules as promising radiotracers for imaging and therapy: formulation and biodistribution. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2006;33:602–7.
Mevellec F, Roucoux A, Noiret N, Patin H, Tisato F, Bandoli G. Synthesis and characterization of the bis(trithioperoxybenzoate)(dithiobenzoate)rhenium(III) hetero complex. Inorg Chem Commun 1999;2:230–3.
Heurtault B, Saulnier P, Pech B, Proust J-E, Benoit J-P. A novel phase inversion-based process for the preparation of lipid nanocarriers. Pharm Res 2002;19:875–80.
Mardor Y, Rahav O, Zauberman Y, Lidar Z, Ocherashvilli A, Daniels D, et al. Convection-enhanced drug delivery: increased efficacy and magnetic resonance image monitoring. Cancer Res 2005;65:6858–63.
Knapp FF Jr., Guhlke S, Beets AL, Lin WY, Stabin M, Amols H, et al. Endovascular beta irradiation for prevention of restenosis using solution radioisotopes: pharmacologic and dosimetric properties of rhenium-188 compounds. Cardiovasc Radiat Med 1999;1:86–97.
Hunt Bobo R, Laske DW, Akbasak A, Morrison PF, Dedrick RL, Oldfield EH. Convection-enhanced delivery of macromolecules in the brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994;91:2076–80.
Vogelbaum MA. Convection enhanced delivery for the treatment of malignant gliomas: symposium review. J Neuro-Oncol 2005;73:57–69.
Jestin E, Mougin-Degraef M, Faivre-Chauvet A, Remaud-Le Saec P, Hindre F, Benoit JP, et al. Radiolabeling and targeting of lipidic nanocapsules for applications in radioimmunotherapy. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2007;51:51–60.
Lacoeuille F, Hindre F, Moal F, Roux J, Passirani C, Couturier O, et al. In vivo evaluation of lipid nanocapsules as a promising colloidal carrier for paclitaxel. Int J Pharm 2007;344:143–9.
Bao A, Goins B, Klipper R, Negrete G, Mahindaratne M, Phillips WT. A novel liposome radiolabeling method using 99mTc-“SNS/S” complexes: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Pharm Sci 2003;92:1893–904.
Judge LM, O'Leary DJ, Fujii G, Skenes C, Paquette T, Proffitt RT. A hydrazino nicotinamide derivative of cholesterol for radiolabelling liposomes with 99mTc. J Labelled Compd Radiopharm 1999;42:23–8.
Sendelbeck SL, Urquhart J. Spatial distribution of dopamine, methotrexate and antipyrine during continuous intracerebral microperfusion. Brain Res 1985;328:251–58.
MacKay JA, Deen DF, Szoka FC Jr. Distribution in brain of liposomes after convection enhanced delivery: modulation by particle charge, particle diameter, and presence of steric coating. Brain Res 2005;1035:139–53.
Beduneau A, Saulnier P, Hindre F, Clavreul A, Leroux JC, Benoit JP. Design of targeted lipid nanocapsules by conjugation of whole antibodies and antibody Fab¢ fragments. Biomaterials 2007;28:4978–90.
Garcion E, Lamprecht A, Heurtault B, Paillard A, Aubert-Pouessel A, Denizot B, et al. A new generation of anticancer, drug-loaded, colloidal vectors reverses multidrug resistance in glioma and reduces tumor progression in rats. Mol Cancer Ther 2006;5:1710–22.
Hsieh BT, Hsieh JF, Tsai SC, Lin WY, Huang HT, Ting G, et al. Rhenium-188-Labeled DTPA: a new radiopharmaceutical for intravascular radiation therapy. Nucl Med Biol 1999;26:967–72.
Noble CO, Krauze MT, Drummond DC, Yamashita Y, Saito R, Berger MS, et al. Novel nanoliposomal CPT-11 infused by convection-enhanced delivery in intracranial tumors: pharmacology and efficacy. Cancer Res 2006;66:2801–6.
Barth RF. Rat brain tumor models in experimental neuro-oncology: the 9L, C6, T9, F98, RG2 (D74), RT-2 and CNS-1 gliomas. J Neurooncol 1998;36:91–102.
Kimler BF. The 9L rat brain tumor model for pre-clinical investigation of radiation-chemotherapy interactions. J Neurooncol 1994;20:103–9.
Vonarbourg A, Sapin A, Lemaire L, Franconi F, Menei P, Jallet P, et al. Characterization and detection of experimental rat gliomas using magnetic resonance imaging. MAGMA 2004;17:133–9.
Vavra M, Ali MJ, Kang EW, Navalitloha Y, Ebert A, Allen CV, et al. Comparative pharmacokinetics of 14C-sucrose in RG-2 rat gliomas after intravenous and convection-enhanced delivery. Neuro Oncol 2004;6:104–12.
Kimler BF, Martin DF, Evans RG, Morantz RA, Vats TS. Combination of radiation therapy and intracranial bleomycin in the 9L rat brain tumor model. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1990;18:1115–21.
Lemaire L, Roullin VG, Franconi F, Venier-Julienne MC, Menei P, Jallet P, et al. Therapeutic efficacy of 5-fluorouracil-loaded microspheres on rat glioma: a magnetic resonance imaging study. NMR Biomed 2001;14:360–6.
Li Y, Owusu A, Lehnert S. Treatment of intracranial rat glioma model with implant of radiosensitizer and biomodulator drug combined with external beam radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2004;58:519–27.
Schlemmer H-P, Bachert P, Herfarth KK, Zuna I, Debus J, Van Kaick G. Proton MR spectroscopic evaluation of suspicious brain lesions after stereotactic radiotherapy. Am J Neuroradiol 2001;22:1316–24.
Zeng Q-S, Li C-F, Liu H, Zhen J-H, Feng D-C. Distinction between recurrent glioma and radiation injury using magnetic resonance spectroscopy in combination with diffusion-weighted imaging. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2007;68:151–58.
Lamprecht A, Benoit J-P. Etoposide nanocarriers suppress glioma cell growth by intracellular drug delivery and simultaneous P-glycoprotein inhibition. J Control Release 2006;112:208–13.
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to Sandrine Vinchon-Petit for CED experiences and to Myriam Moreau for her help in LNC formulation (INSERM U646, Angers, France) for her help in LNC formulation. We are also grateful to Pierre Legras and Jérome Roux (Service Commun d’Animalerie Hospitalo—Universitaire, Angers, France) for their technical assistance in animal experiments. This work was supported by a ‘Région des Pays de la Loire’ grant and by the county committee of Maine et Loire of ‘La ligue contre le cancer.’ Animal care was carried out in strict accordance to French Ministry of Agriculture regulations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allard, E., Hindre, F., Passirani, C. et al. 188Re-loaded lipid nanocapsules as a promising radiopharmaceutical carrier for internal radiotherapy of malignant gliomas. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 35, 1838–1846 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-008-0735-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-008-0735-z