Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this study was to determine whether SWE can detect biomechanical changes in the supraspinatus muscle that occur with increasing supraspinatus tendon abnormality prior to morphologic gray-scale changes.
Materials and methods
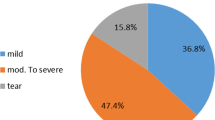
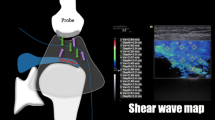
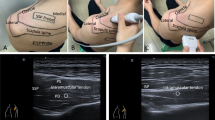
An IRB approved, HIPAA compliant retrospective study of shoulder ultrasounds from 2013–2018 was performed. The cohort consisted of 88 patients (mean age 55 ± 15 years old) with 110 ultrasounds. Images were acquired in longitudinal orientation to the supraspinatus muscle with shear wave velocity (SWV) point quantification. The tendon and muscle were graded in order of increasing tendinosis/tear (1–4 scale) and increasing fatty infiltration (0–3 scale). Mixed model analysis of variance, analysis of covariance, and Spearman rank correlation were used for statistical analysis.
Results
There was no statistically significant age or sex dependence for supraspinatus muscle SWV (p = 0.314, 0.118, respectively). There was no significant correlation between muscle SWV and muscle or tendon grade (p = 0.317, 0.691, respectively). In patients with morphologically normal muscle on gray-scale ultrasound, there were significant differences in muscle SWV when comparing tendon grade 3 with grades 1, 2, and 4 (p = 0.018, 0.025, 0.014, respectively), even when adjusting for gender and age (p = 0.044, 0.028, 0.018, respectively). Pairwise comparison of tendon grades other than those mentioned did not achieve statistical significance (p > 0.05).
Conclusion
SWE can detect biomechanical differences within the supraspinatus muscle that are not morphologically evident on gray-scale ultrasound. Specifically, supraspinatus tendon partial tears with moderate to severe tendinosis may correspond to biomechanically distinct muscle properties compared to both lower grades of tendon abnormality and full-thickness tears.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- US:
-
Ultrasound
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- SWE:
-
Shear wave elastography
- SWV:
-
Shear wave velocity
- ARFI:
-
Acoustic radiation force impulse
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
References
Gladstone JN, Bishop JY, Lo IK, Flatow EL. Fatty infiltration and atrophy of the rotator cuff do not improve after rotator cuff repair and correlate with poor functional outcome. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35(5):719–28.
Goutallier D, Postel JM, Lavau L, Bernageau J. Influence of muscular degeneration of the supra- and infraspinatus on the prognosis of surgical repair of the rotator cuff. Acta Orthop Belg. 1998;64(Suppl 2):42–5.
Mellado JM, Calmet J, Olona M, Esteve C, Camins A, Perez Del Palomar L, et al. Surgically repaired massive rotator cuff tears: MRI of tendon integrity, muscle fatty degeneration, and muscle atrophy correlated with intraoperative and clinical findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;184(5):1456–63.
Strobel K, Hodler J, Meyer DC, Pfirrmann CW, Pirkl C, Zanetti M. Fatty atrophy of supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles: accuracy of US. Radiology. 2005;237(2):584–9.
Khoury V, Cardinal E, Brassard P. Atrophy and fatty infiltration of the supraspinatus muscle: sonography versus MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;190(4):1105–11.
Wall LB, Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Dahiya N, Steger-May K, Kim HM, et al. Diagnostic performance and reliability of ultrasonography for fatty degeneration of the rotator cuff muscles. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(12):e83.
de Jesus JO, Parker L, Frangos AJ, Nazarian LN. Accuracy of MRI, MR arthrography, and ultrasound in the diagnosis of rotator cuff tears: a meta-analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;192(6):1701–7.
Carpenter EL, Lau HA, Kolodny EH, Adler RS. Skeletal muscle in healthy subjects versus those with GNE-related myopathy: evaluation with shear-wave US--a pilot study. Radiology. 2015;277(2):546–54.
Hou SW, Merkle AN, Babb JS, McCabe R, Gyftopoulos S, Adler RS. Shear wave ultrasound elastographic evaluation of the rotator cuff tendon. J Ultrasound Med. 2017;36(1):95–106.
Rosskopf AB, Ehrmann C, Buck FM, Gerber C, Fluck M, Pfirrmann CW. Quantitative shear-wave US elastography of the supraspinatus muscle: reliability of the method and relation to tendon integrity and muscle quality. Radiology. 2016;278(2):465–74.
Eby SF, Song P, Chen S, Chen Q, Greenleaf JF, An KN. Validation of shear wave elastography in skeletal muscle. J Biomech. 2013;46(14):2381–7.
Gennisson JL, Deffieux T, Mace E, Montaldo G, Fink M, Tanter M. Viscoelastic and anisotropic mechanical properties of in vivo muscle tissue assessed by supersonic shear imaging. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2010;36(5):789–801.
Merkle A AB, Lin D, Babb J, Adler R. Shear wave ultrasound evaluation of the supraspinatus muscle: anisotropy and age considerations. Radiological Society of North America 2017 Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting, November 26 - December 1, 2017. Chicago IL.
Meng C, Adler R, Peterson M, Kagen L. Combined use of power Doppler and gray-scale sonography: a new technique for the assessment of inflammatory myopathy. J Rheumatol. 2001;28(6):1271–82.
Silldorff MD, Choo AD, Choi AJ, Lin E, Carr JA, Lieber RL, et al. Effect of supraspinatus tendon injury on supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscle passive tension and associated biochemistry. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(20):e175.
Kim HM, Dahiya N, Teefey SA, Keener JD, Galatz LM, Yamaguchi K. Relationship of tear size and location to fatty degeneration of the rotator cuff. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(4):829–39.
Liu X, Ning AY, Chang NC, Kim H, Nissenson R, Wang L, et al. Investigating the cellular origin of rotator cuff muscle fatty infiltration and fibrosis after injury. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2016;6(1):6–15.
Davis ME, Korn MA, Gumucio JP, Harning JA, Saripalli AL, Bedi A, et al. Simvastatin reduces fibrosis and protects against muscle weakness after massive rotator cuff tear. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2015;24(2):280–7.
Choo A, McCarthy M, Pichika R, Sato EJ, Lieber RL, Schenk S, et al. Muscle gene expression patterns in human rotator cuff pathology. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(18):1558–65.
Sato EJ, Killian ML, Choi AJ, Lin E, Esparza MC, Galatz LM, et al. Skeletal muscle fibrosis and stiffness increase after rotator cuff tendon injury and neuromuscular compromise in a rat model. J Orthop Res. 2014;32(9):1111–6.
Laron D, Samagh SP, Liu X, Kim HT, Feeley BT. Muscle degeneration in rotator cuff tears. J Shoulder Elb Surg. 2012;21(2):164–74.
Barton ER, Gimbel JA, Williams GR, Soslowsky LJ. Rat supraspinatus muscle atrophy after tendon detachment. J Orthop Res. 2005;23(2):259–65.
Gigliotti D, Xu MC, Davidson MJ, Macdonald PB, Leiter JRS, Anderson JE. Fibrosis, low vascularity, and fewer slow fibers after rotator-cuff injury. Muscle Nerve. 2017;55(5):715–26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
“All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.”
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, D.J., Burke, C.J., Abiri, B. et al. Supraspinatus muscle shear wave elastography (SWE): detection of biomechanical differences with varying tendon quality prior to gray-scale morphologic changes. Skeletal Radiol 49, 731–738 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-019-03334-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-019-03334-6