Abstract
Objective
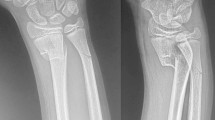
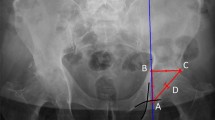
Operative treatment of an intra-articular distal radius fracture is one of the most common procedures in orthopedic and hand surgery. The intra- and interobserver agreement of common radiographical measurements of these fractures using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) and plain radiographs were evaluated.
Materials and methods
Thirty-seven patients undergoing open reduction and volar fixation for a distal radius fracture were studied. Two radiologists analyzed the preoperative radiographs and CBCT images. Agreement of the measurements was subjected to intra-class correlation coefficient and the Bland–Altman analyses.
Results
Plain radiographs provided a slightly poorer level of agreement. For fracture diastasis, excellent intraobserver agreement was achieved for radiographs and good or excellent agreement for CBCT, compared to poor interobserver agreement (ICC 0.334) for radiographs and good interobserver agreement (ICC 0.621) for CBCT images. The Bland–Altman analyses indicated a small mean difference between the measurements but rather large variation using both imaging methods, especially in angular measurements.
Conclusions
For most of the measurements, radiographs do well, and may be used in clinical practice. Two different measurements by the same reader or by two different readers can lead to different decisions, and therefore a standardization of the measurements is imperative. More detailed analysis of articular surface needs cross-sectional imaging modalities.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cummings SR, Black DM, Rubin SM. Lifetime risks of hip, Colles’, or vertebral fracture and coronary heart disease among white postmenopausal women. Arch Intern Med. 1989;149(11):2445–8.
Mattila VM, Huttunen TT, Sillanpää P, Niemi S, Pihlajamäki H, Kannus P. Significant change in the surgical treatment of distal radius fractures: a nationwide study between 1998 and 2008 in Finland. J Trauma. 2011;71(4):939–43.
Leung F, Tu YK, Chew WY, Chow SP. Comparison of external and percutaneous pin fixation with plate fixation for intra-articular distal radial fractures. A randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(1):16–22.
Arora R, Lutz M, Deml C, Krappinger D, Haug L, Gabl M. A prospective randomized trial comparing nonoperative treatment with volar locking plate fixation for displaced and unstable distal radial fractures in patients sixty-five years of age and older. J Bone Joint Surg. 2011;93(23):2146–53.
Diaz-Garcia RJ, Oda T, Shauver MJ, Chung KC. A systematic review of outcomes and complications of treating unstable distal radius fractures in the elderly. J Hand Surg Am. 2011;36(5):824–35.
Lichtman DM, Bindra RR, Boyer MI, et al. Treatment of distal radius fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18(3):180–9.
Haus BM, Jupiter JB. Intra-articular fractures of the distal end of the radius in young adults: reexamined as evidence-based and outcomes medicine. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(12):2984–91.
Arora S, Grover SB, Batra S, Sharma VK. Comparative evaluation of postreduction intra-articular distal radial fractures by radiographs and multidetector computed tomography. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(15):2523–32.
Koskinen SK, Haapamäki VV, Salo J, et al. CT arthrography of the wrist using a novel, mobile, dedicated extremity cone-beam CT (CBCT). Skeletal Radiol. 2013;42(5):649–57.
Carrino JA, Al Muhit A, Zbijewski W, et al. Dedicated cone-beam CT system for extremity imaging. Radiology. 2014;270(3):816–24.
Koivisto J, Kiljunen T, Wolff J, Kortesniemi M. Assessment of effective radiation dose of an extremity CBCT, MSCT and conventional X-ray for knee area using MOSFET dosemeters. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2013;157(4):515–24.
Hardy DC, Totty WG, Reinus WR, Gilula LA. Posteroanterior wrist radiography: importance of arm positioning. J Hand Surg Am. 1987;12(4):504–8.
Medoff RJ. Essential radiographic evaluation for distal radius fractures. Hand Clin. 2005;21(3):279–88.
Wald S, Woerter K. Measurements and classifications in musculoskeletal radiology. Stuttgart, Germany: George Thieme Verlag; 2014. p. 108–23.
Muller R, Buttner P. A critical discussion of intraclass correlation coefficients. Stat Med. 1994;13(23–24):2465–76.
Reilingh ML, Beimers L, Tuijthof GJM, Stufkens SAS, Maas M, van Dijk N. Measuring hindfoot alignment radiographically: the long axial view is more reliable than the hindfoot alignment view. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39(11):1103–8.
Rosner B. Fundamentals of biostatistics. Belmont: CA. Duxbury Press; 2005.
Sampat MP, Whitman GJ, Stephens TW, et al. The reliability of measuring physical characteristics of speculated masses on mammography. Brit J Radiol. 2006;79:S134–40.
Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet. 1986;1(8476):307–10.
Ilyas AM, Jupiter JB. Distal radius fractures—classification of treatment and indications for surgery. Hand Clin. 2010;26(1):37–42.
Ng CY, McQueen MM. What are the radiological predictors of functional outcome following fractures of the distal radius? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011;93(2):145–50.
Parker AS, Nguyen M, Minard CG, Guffey D, Willis MH, Reichel LM. Measurement of ulnar variance from the lateral radiograph: a comparison of techniques. J Hand Surg Am. 2014;39(6):1114–21.
Laino DK, Petchprapa CN, Lee SK. Ulnar variance: correlation of plain radiographs, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging with anatomic dissection. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37(1):90–7.
Biswas D, Bible JE, Bohan M, Simpson AK, Whang PG, Grauer JN. Radiation exposure from musculoskeletal computerized tomographic scans. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(8):1882–9.
Koivisto J, Kiljunen T, Kadesjö N, Shi X-Q, Wolff J. Effective radiation dose of a MSCT, two CBCT and one conventional radiography device in the ankle region. J Foot Ankle Res 2015;8, doi: 10.1186/s13047-015-0067-8 eCollection
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they gave no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suojärvi, N., Sillat, T., Lindfors, N. et al. Radiographical measurements for distal intra-articular fractures of the radius using plain radiographs and cone beam computed tomography images. Skeletal Radiol 44, 1769–1775 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2231-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2231-4