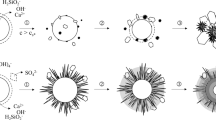
Abstract
The deterioration of buildings and monuments by gypsum is the result of crystallization cycles of this salt. Although gypsum can dehydrate to a hemihydrate, the mineral bassanite, and to an anhydrate, the mineral anhydrite, this reaction occurs in nature on a geological time scale and therefore it is unlikely to occur when gypsum is found on and in building materials. The CaSO4–H2O system appears deceptively simple, however there are still discrepancies between the experimental and thermodynamically calculated data. The reason for the latter can be attributed to the slow crystallization kinetics of anhydrite. Apart from this, the large numbers of studies carried out on this system have focused on industrially important metastable phases, such as the hemihydrate and soluble anhydrite. The paper presents a review of the studies dealing with the phase equilibria of the CaSO4–H2O system as well as the influence of other salts on the solubility of gypsum. It tries to glean out the relevant information that will serve to explain the deterioration observed on building materials by the crystallization of gypsum and thus allows developing improved conservation methods.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrate-Zohar MA, Zezza U, Veniale F, Setti M (1985) Decay stage and causes of the terra-cotta ornaments (Cloister of the Carthusian Monastery, Pavia. Italy. In: 5th International congress on deterioration and conservation of stone. Presses Polytechniques Romandes, Lausanne, pp 443–451
Archer DG (1992) Thermodynamic properties of NaCl + H2O system. II. Thermodynamic properties of NaCl (aq), NaCl 2H2O (cr), and phase equilibria. J Phys Chem Ref Data 21:793–821
Arnold A, Kueng A (1985) Crystallization and habits of salt efflorescences on walls. I. Methods of investigation and habits. In: 5th International congress on deterioration and conservation of stone. Presses Polytechniques Romandes, Lausanne, pp 255–277
Ausset P, Lefèvre RA, Del Monte M (2000) Early mechanisms of development of sulphated black crusts on carbonate stone. In: Fassina V (ed) 9th Intl. Congress on Deterioration and Conservation of Stone (Venice), vol 1. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 329–337
Baboian R (1986) Materials degradation caused by acid rain. ACS Symposium Series 318, American Chemical Society, Washington, DC 1986
Badan B, Bacelle G, Marchesini L (1976) Surface reactivity of marble and stone: Quarry and Altered Samples. In: Rossi-Manaresi R (ed) The conservation of stone I. Centro per la Conservazione delle Sculture all’aperto, Bologna, pp 89–101
Bayer K (2006) Gypsum—An overlooked corrosive factor for some types of silicate sandstones in Bohemia. In: Proceedings of the SALTeXPERT Workshop ARIADNE 13, Prague, ARCCHIP and GCI, 2002 (in press)
Begohna A, Teles M (2000) Study of stone deterioration in the Palácio do Freixo in Oporto. In: Fassina V (ed.) 9th Intl. Congress on Deterioration and Conservation of Stone (Venice), Vol.2. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 593–601
Bläuer C (1985) Weathering of Bernese sandstone. In: 5th Intl. Congress on Deterioration and Conservation of Stone. Presses Polytechniques Romandes, Lausanne, pp 381–409
Block J, Waters OB (1968) The CaSO4-Na2SO4-NaCl-H2O system at 25° to 100°. J Chem Eng Data 13:336–344
Bock E (1961) On the solubility of anhydrous calcium sulphate and of gypsum in concentrated solutions of sodium chloride at 25°C, 30°C, 40°C and 50°C. Can J Chem 39:1746–1751
Bortolaso G, Lazzarini L, Mengazzo Vitturi L, Rampazzo G (1988) The deterioration of “Rosso Ammonitico Veronese” nodular limestone: Comparison between a quarry and a Venetian monument. In: 6th Intl. Congress on Deterioration and Conservation of Stone. Nicholas Copernicus University Press Department, Torun, pp 97–109
Building Effects review group report (1989) The effects of acid deposition on buildings and building materials. Her Majesty’s Stationary Office, London
Calaforra Chordi JM (1998) Caracterización geomorfológica del karst en yeso (Geomorphological characterization of gypsum karsts). In: Karstología de yesos (Karst formation in gypsum deposits). Universidad de Almería, Servicio de Publicaciones. Instituto de Estudios Almerienses, Almería, 69–195
Charola AE (2000) Salts in the deterioration of porous materials: an overview. J Am Inst Conserv 39:332–343
Charola AE (2001) Acidic deposition on stone: a literature survey. US/ICOMOS Sci J 3:19–58
Charola AE (2003) Salt deterioration: open questions. In: Mauersalze und Architekturoberflächen (Salts in walls and architectural surfaces). Leitner H, Laue S and Siedel H (eds). Hochschule für Bildende Künste, Dresden: 10–24
Charola AE, Lewin SZ (1979) Efflorescences on building stones—SEM in the characterization and elucidation of the mechanisms of formation. Scanning Electron Microscopy/1979/I:378–386
Charola AE, Koestler RJ (1985/86) SEM Study of the deterioration of monumental stones in Vienna. In: Vendl A, Pichler B, Weber J, Banik G (eds) Wiener Berichte über Naturwissenschaft in der Kunst. Vol.2/3. Orac,Vienna, pp 176–186
Charola AE, Weber J (1992) The hydration-dehydration mechanism of sodium sulphate. In: Delgado Rodrigues J, Enriques F, Telmo Jeremias F (eds) 7th International congress on deterioration and conservation of stone. Laboratório Nacional de Engenharia Civil, Lisbon, pp 581–590
Charola AE, Centeno SA (2002) Analysis of gypsum-containing lime mortars: Possible errors due to the use of different drying conditions. J Am Inst Conserv 41:269–278
Charola AE, Ware R (2002) Acid deposition and the deterioration of stone: a brief review of a broad topic. In: Siegesmund S, Weiss R and Vollbrecht A (eds) Natural stone, weathering phenomena, conservation strategies and case studies. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 205:393–406
Charola AE, Pühringer J (2005) Salts in the deterioration of porous materials: a call for the right questions. Restor Build Monum 11:433–42
Clegg SL, Rard JA, Pitzer KS (1994) Thermodynamic properties of 0–6 mol kg–1 aqueous sulfuric acid from 273.15 to 328.15 K. J Chem Eng Data 90:1875–1894
D’Ans (1968) Der Übergangspunkt Gips→Anhydrit (The transition point gypsum→anhydrite). Kali Steinsalz 5:109–111
D’Ans J, Bredtschneider D, Eick H, Freund H-E (1955) Untersuchungen über die Calciumsulphate (Investigations on the sulfates of calcium). Kali Steinsalz 1:17–38
Davis WA (1907) The nature of the changes involved in the production and setting of plaster of paris. J Soc Chem Ind 26:727–738
Deer WA, Howie RA, Zussman J (1975) Rock-Forming Minerals Vol. 5 Non-Silicates. Longman, London (1962) 7th impression: 202–218
Dudnikova KT, Samoilov OYa (1963) Solubility of gypsum in aqueous solutions of salting-out agents. Sov Radiochem 5:644–646
Fassina V, Lazzarini, Biscontin G, Calogero S (1979) Influenza del materiale particellare atmosférico sui processi di degradazione della pietra a Venezia (Influence of atmospheric particulates on the deterioration process of the stones in Venice). In: 3rd International congress on deterioration and conservation of stone (Venice). Università degli Studi di Padova, Padua, pp 43–53
Franchi R, Manganelli Del Fà C (1979) Ricerche sulla degradazione delle “Pietre”: IX. Il Cristo del Sansovino. In: 3rd Intl. Congress on Deterioration and Conservation of Stone (Venice). Università delgi Studi di Padova, Padua, pp 481–490
Franke L, Grabau J (1998) Influence of salt content on the drying behavior of brick. In: Baer NS, Fitz S, Livingston RA (eds) Conservation of historic brick structures. Donhead, Shaftesbury, pp 59–68
Freyer D, Voigt W (2003) Crystallization and phase stability of CaSO4 and CaSO4-based salts. Monatsh Chem 134:693–719
Goudie A, Viles H (1997) Salt weathering hazards. Wiley, Chichester
Grassegger G (2002) Restoration of the sarcophagus of Duke Melchior von Hatzfeld—the accompanying scientific and technical investigations. Otto Graf J 13:141–154
Grimm WD, Schwarz U (1985) Naturwerksteine und ihre Verwitterung an Münchner Bauten und Dankmälern (Natural stone and their deterioration in buildings and monuments in Munich). In: Natursteinkonservierung. Arbeitsheft 31. Bayerisches Landesamt für Denkmalpflege, Munich, pp 28–118
Haber J, Haber H, Kozlowski R, Magiera J, Pluska I (1988) Air pollution and decay of architectural monuments in the city of Cracow. In: Rosvall J, Aleby S (eds) Air pollution and conservation. Safeguarding our cultural heritage. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 499–547
Hardie LA (1967) The gypsum–anhydrite equilibrium at one atmosphere pressure. Am Mineral 52:171–200
Heusinger von Waldegg E (1906) Der Gips (Gypsum). In: Moye A (ed) 2nd edn. Theod. Thomas Verlag, Leipzig
Hill AE (1934) Ternary systems. XIX. Calcium sulfate, potassium sulfate and water. J Am Chem Soc 56:1071–1078
Hill AE (1937) The transition temperature of gypsum to anhydrite. J Am Chem Soc 59:2242–2244
Hill AE, Yanick NS (1935) Ternary system. XX. Calcium sulfate, ammonium sulfate and water. J Am Chem Soc 57:645–651
Hill AE, Wills JH (1938) Ternary systems. XXIV. Calcium sulfate, sodium sulfate and water. J Am Chem Soc 60:1647–1655
Hulett GA (1905) The solubility of gypsum as affected by size of particles and by different crystallographic surfaces. J Am Chem Soc 27:49–56
Hulett GA, Allen LE (1902) The solubility of gypsum. J Am Chem Soc 24:667–679
Kelley KK, Southard JC, Anderson CT (1941) Thermodynamic properties of gypsum and its dehydration products. US Bur Mines Tech Pap 625
Knacke O, Gans W (1977) The thermodynamics of the system CaSO4–H2O. Z Phys Chem NF 104:41–48
Lazzarini L, Fassina V (1979) Studio scientifico sullo stato di conservazione delle pietre e dei marmi della Porta della Carta di Venezia (Scientific study on state of conservation of the stones and marbles of the Porta della Carta in Venice). In: 3rd Intl. Congress on Deterioration and Conservation of Stone (Venice). Università delgi Studi di Padova, Padua, pp 647–660
Lazzarini L, Laurenzi Tabasso M (1986) Il restauro della pietra (The restoration of stone) Cedam, Padua: 22
Le Chatelier H (1887) Recherches expérimentales sur la constitution des mortier hydrauliques (Experimental research on the composition of hydraulic mortars). Dunod, Paris
Leitner H (2005) The treatment of wall paintings affected by salts: an interdisciplinary task as seen from a conservator’s perspective. Restor Build Mon 11:365–380
Madgin WM, Swayles DA (1956) Solubilities in the system CaSO4-NaCl-H2O at 25° and 35°. J Appl Chem 6:482–487
Marshall WL, Slusher R (1966) Thermodynamics of calcium sulfate dihydrate in aqueous sodium chloride solutions, 0–110°. J Phys Chem 70:4015–4027
Neumann HH, Steiger M, Wassmann A, Dannecker W (1993) Aufbau und Ausbildung schwarzer Gipskrusten und damit zusammenhängender Gefügeschäden von Naturwerksteinen am Beispiel des Leineschlosses, Hannover (Formation and development of black gypsum crusts and related deterioration of the structure of natural stones as exemplified by the Leineschloss in Hanover). In: Snethlage R (ed) Steinzerfall-Steinkonservierung, Vol. 3–1991, Verlag Ernst & Sohn, Berlin, pp 51–167
Neumann HH, Lork A, Steiger M, Juling H (1997) Decay patterns of weathered quartz sandstones: evidence of gypsum induced structural changes. In: Sveinsdottir EL (ed) Proceedings of the 6th Euroseminar on microscopy applied to building materials, Icelandic Building Research Institute, Reykjavic, pp 238–249
Nunberg S, Charola AE (2001) Salts in Ceramic Bodies II: deterioration due to minimal changes in relative humidity. Int J Restor Build Mon 7:131–146
Ottemann J (1952) Baustoff Anhydrit. (Construction material anhydrite) Verlag Technik, Berlin
Partridge EP, White AH (1929) The solubility of calcium sulfate from 0 to 200°. J Am Chem Soc 51:360–370
Posnjak E (1938) The system CaSO4–H2O. Am J Sci 35A:247–272
Posnjak E (1940) Deposition of calcium sulfate from sea water. Am J Sci 238:559–568
Power WH, Fabuss BM, Satterfield CN (1964) Transient solubilities in the calcium sulfate-water system. J Chem Eng Data 9:437–442
Power WH, Fabuss BM, Satterfield CN (1966) Transient solute concentrations and phase changes of calcium sulfate in aqueous sodium chloride. J Chem Eng Data 11:149–154
Pühringer J (1983a) Salt disintegration: salt migration and degration by salt—a hypothesis. D15:1983 Swedish Council for Building Research, Stockholm
Pühringer J (1983b) Salzwanderungen und Verwitterung durch Salze (Salt migration and weathering through salts). In: Wittmann FH (ed) Materials Science and Restoration. Edition Lack + Chemie, Filderstadt, pp 361–366
Robie RA, Russel-Robinson S, Hemingway BS (1989) Heat capacities and entropies from 8 to 1000 K of langbeinite (K2Mg2(SO4)3), anhydrite (CaSO4) and of gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O) to 325 K. Thermochim Acta 139:67–81
Rossi-Manaresi R, Alessandrini G, Fuzzi S, Peruzzi R (1979) Assessment of the Effectiveness of Some Preservatives for Marble and Limestones. In: 3rd Intl. Congress on Deterioration and Conservation of Stone (Venice). Università degli Studi di Padova, Padua, pp 357–376
Rosval J, Aleby S (1986) Air pollution and conservation. Safeguarding our architectural heritage. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Shternina EB (1949) Solubility of gypsum in salt solutions. Izvest Sektora Fiz-Khim Anal, Inst Obshchei Neorg Khim, Akad Nauk S.S.S.R. 17:351–369 (in Russian)
Shternina EB (1957) Maximums on the solubility isotherms for calcium sulfate and calcium carbonate. Zh Neorg Khim 2:933–937 (in Russian)
Seidell A, Smith JG (1904) The solubility of calcium sulphate in solutions of nitrates. J Phys Chem 8:493–499
Smykatz-Kloss W, Istrate G, Hötzl H, Wohnlich S (1985) Vorkommen und Entstehung von Bassanit, CaSO4·0.5H2O), im Gipskarstgebiet von Foum Tatahouine, Südtunesien. (Occurrence and formation of bassanite in the gypsum karst region of Foum Tatahouine, South Tunesia). Chem Erde 44:67–77
Snethlage R (1984) Steinkonservierung 1979–1983 (Stone conservation 1979–1983) Arbeitsheft 22, Bayerisches Landesamt für Denkmalpflege. Munich: 13–83
Snethlage R, Wendler E (1997) Moisture cycles and sandstone degradation. In: Baer NS, Snethlage R (eds) Saving our architectural heritage: the conservation of historic stone structures. Wiley, Chichester, pp 7–24
Snethlage R, Wendler E, Klemm DD (1996) Tenside im Gesteinschutz—Bisherige Resultate mit einem neuen Konzept zur Erhaltung von Denkmälern aus Naturstein (Tensides in the protection of stone—Results from a new concept for the conservation of monuments in natural stone). In: Snethlage R (ed) Denkmalpflege und Naturwissenschaft. Natursteinkonservierung I. Ernst & Sohn, Berlin, pp 127–146
Steiger M (2003) Crusts and salts. In: Brimblecombe P (ed) The effects of air pollution on the built environment. Air pollution reviews, vol 2. Imperial College Press, London, pp 133–181
Steiger M (2005) Crystal growth in porous materials: I. The crystallization pressure of large crystals. J Cryst Growth 282:455–469
Tucci A, Koestler RJ, Charola AE, Rossi-Manaresi R (1985) The influence of acid rain and UV radiation on the ageing of acrylic and silicone resins. In: 5th International congress on deterioration and conservation of stone. Presses Polytechniques Romandes, Lausanne, pp 891–898
van’t Hoff JH (1909), Zur Bildung der ozeanischen Salzablagerungen (On the formation of the oceanic salt deposits). Zweites Heft. Vieweg und Sohn, Braunschweig
van’t Hoff JH, Armstrong EF, Hinrichsen W, Weigert F, Just G (1903) Gips und Anhydrit (Gypsum and anhydrite). Z Phys Chem 45:257–306
von Konow T (2001) Mechanisms of brick deterioration due to salts: new results on salt behaviour from in-situ studies at the Suomenlinna Fortress in Finland. Int J Restor Build Monum 7:675–688
Weber J (1993) Salt-induced deterioration of Romanesque wall paintings in the church of St. Georgen, Styria, Austria. In: Biscontin G, Graziano L (eds) Conservation of architectural surfaces: stones and wall coverings. Il Cardo, Venice, pp 97–103
Weber J, Leitner H, Gaggl W and Szambelan R (1996) Crystallization of sulphate salts induced by selective salt extraction by poultices: results from a case study. In: Preprints of the european research workshop on origin, mechanisms and effects of salts on degradation of monuments in marine and continental environments, Bari, pp 169–170
Weiser HB, Millligan WO, Ekholm WC (1936) The mechanism of the dehydration of calcium sulfate hemihydrate. J Amer Chem Soc 58:1261–1265
Winkler EM (1975) Stone: properties, durability in man’s environment, 2nd edn. Springer, Vienna and New York
Yeatts LB, Marshall WL (1969) Apparent invariance of activity coefficients of calcium sulfate at constant ionic strength and temperature in the system CaSO4–Na2SO4–NaNO3–H2O to the critical temperature of water. Association equilibria. J Phys Chem 73:81–90
Yeatts LB, Marshall WL (1972) Solubility of calcium sulfate dihydrate and association equilibria in several aqueous mixed electrolyte salt systems at 25 °C. J Chem Eng Data 17:163–168
Young ME, Jones MS, MacDonald J, Urquhart DCM, Nicholson K, McHardy WJ (1996) Investigations on the soiling and cleaning of some Scottish granites. Degradation and conservation of granitic rocks in monuments. Research report No.5. Environmental Protection and Conservation of the European Cultural Heritage. European Commission, Brussels, pp 429–434
Zdanovskii AB, Vlasov GA (1968) Determination of the boundaries of the reciprocal transformations CaSO4·2H2O and γ-CaSO4 in H2SO4 solutions. Russ J Inorg Chem 13:1318–1319
Zen E-an (1965) Solubility measurements in the system CaSO4–NaCl–H2O at 35°, 50°, and 70°C and one atmosphere pressure. J Petrol 6:124–164
Zehnder K (1982) Verwitterung von Molassensandsteinen an Bauwerken und in Naturaufschlüssen (Weathering of Molasse sandstones in buildings and in natural occurrences) Beiträge zur Geologie der Schweiz, Geotechnische Serie 61:86
Zehnder, K (1993) New aspects of decay caused by crystallization of gypsum. In: Thiel M-J (ed) Conservation of stone and other materials. Vol 1 E & FN Spon, London, pp 107–114
Zehnder, K (1996) Gyspsum efflorescences in the zone of rising damp. Monitoring of slow decay processes caused by crystallizing salts on wall paintings. In: Riederer J (ed) Proceedings 8th International congress on deterioration and conservation of stone. Möller Druck, Berlin, pp 1669–1678
Zehnder K, Arnold A (1989) Crystal growth in salt efflorescence. J Cryst Growth 97:513–521
Zhang Y, Muhammed M (1989) Solubility of calcium sulfate dihydrate in nitric acid solutions containing calcium nitrate and phosphoric acid. J Chem Eng Data 34:121–124
Acknowlegments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Christine Bläuer Böhm, Konrad Zehnder and Andreas Kueng for providing information on the natural occurrence of bassanite on building materials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Charola, A.E., Pühringer, J. & Steiger, M. Gypsum: a review of its role in the deterioration of building materials. Environ Geol 52, 339–352 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0566-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-006-0566-9