Abstract.
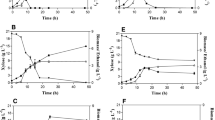
Batch xylitol production from concentrated sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate by Candida guilliermondii was performed by progressively adapting the cells to the medium. Samples were analyzed to monitor sugar and acetic acid consumption, xylitol, arabitol, ethanol, and carbon dioxide production, as well as cell growth. Both xylitol yield and volumetric productivity remarkably increased with the number of adaptations, demonstrating that the more adapted the cells, the better the capacity of the yeast to reduce xylose to xylitol in hemicellulose hydrolysates. Substrate and product concentrations were used in carbon material balances to study in which way the different carbon sources were utilized by this yeast under microaerobic conditions, as well as to shed light on the effect of the progressive adaptation to the medium on its fermentative activity. Such a theoretical means allowed estimation for the first time of the relative contribution of each medium component to the formation of the main products of this fermentation system.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sene, .L., Converti, .A., Zilli, .M. et al. Metabolic study of the adaptation of the yeast Candida guilliermondii to sugarcane bagasse hydrolysate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57, 738–743 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530100816
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530100816