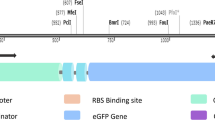
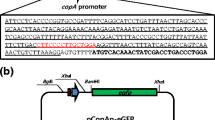
Abstract
Owing to the prevalence of cadmium contamination and its serious hazards, it is important to establish an efficient and low-cost monitoring technique for the detection of the heavy metal cadmium. In this study, we first designed 30 cadmium whole-cell biosensors (WCBs) using different combinations of detection elements, reporting elements, and the host. The best performing WCB KT-5-R with Pseudomonas putida KT2440 as the host and composed of CadR and mCherry was selected for further analysis and engineering. In order to enhance its sensitivity, a positive feedback amplifier was added or the gene dosage of the reporter gene was increased. The WCB with the T7RNAP amplification module, p2T7RNAPmut-68, had the best performance and improved tolerance to cadmium with a detection limit of 0.01 μM, which is the WHO standard. It also showed excellent specificity toward cadmium when assayed with mixed metal ions. This study demonstrated the power of circuit engineering in WCB design and provided valuable insights for the development of other WCBs.
Key points
• KT-5-R was selected after prescreening and engineered for better performance.
• Using multi-copy reporters and the T7RNAP amplifier greatly improved the performance.
• p2T7RNAPmut-68 had a detection limit of 0.01 μM and improved tolerance to cadmium.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Supplementary Information is available.
References
Abbas SZ, Rafatullah M, Hossain K, Ismail N, Tajarudin HA, Khalil H (2018) A review on mechanism and future perspectives of cadmium-resistant bacteria. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15(1):243–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1400-5
Akerstrom M, Barregard L, Lundh T, Sallsten G (2013) The relationship between cadmium in kidney and cadmium in urine and blood in an environmentally exposed population. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 268(3):286–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2013.02.009
Bereza-Malcolm LT, Mann G, Franks AE (2015) Environmental sensing of heavy metals through whole cell microbial biosensors: a synthetic biology approach. ACS Synth Biol 4(5):535–546. https://doi.org/10.1021/sb500286r
Bereza-Malcolm L, Aracic S, Kannan R, Mann G, Franks AE (2017) Functional characterization of Gram-negative bacteria from different genera as multiplex cadmium biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 94:380–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.03.029
Bhattacharyya MH (2009) Cadmium osteotoxicity in experimental animals: mechanisms and relationship to human exposures. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 238(3):258–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2009.05.015
de Angelis C, Galdiero M, Pivonello C, Salzano C, Gianfrilli D, Piscitelli P, Lenzi A, Colao A, Pivonello R (2017) The environment and male reproduction: the effect of cadmium exposure on reproductive function and its implication in fertility. Reprod Toxicol 73:105–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2017.07.021
Feng L, Liu J (2010) Solid sampling graphite fibre felt electrothermal atomic fluorescence spectrometry with tungsten coil atomic trap for the determination of cadmium in food samples. J Anal At Spectrom 25(7):1072–1078. https://doi.org/10.1039/b924270h
Guo MZ, Du RX, Xie ZX, He XY, Huang KL, Luo YB, Xu WT (2019) Using the promoters of MerR family proteins as "rheostats" to engineer whole-cell heavy metal biosensors with adjustable sensitivity. J Biol Eng 13(1):9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13036-019-0202-3
He M-Y, Lin Y-J, Kao Y-L, Kuo P, Grauffel C, Lim C, Cheng Y-S, Chou H-HD (2021) Sensitive and specific cadmium biosensor developed by reconfiguring metal transport and leveraging natural gene repositories. ACS sensors 6:995–1002. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c02204
Hou J, Chen GS, Wang ZP (2001) Simultaneous determination of trace cadmium and arsenic in grains using atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Spectrosc Spectr Anal 21(3):387–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-2031(02)00007-3
Hou QH, Ma AZ, Wang T, Lin JQ, Wang HL, Du BH, Zhuang XL, Zhuang GQ (2015) Detection of bioavailable cadmium, lead, and arsenic in polluted soil by tailored multiple Escherichia coli whole-cell sensor set. Anal Bioanal Chem 407(22):6865–6871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8830-z
Hu BF, Jia XL, Hu J, Xu DY, Xia F, Li Y (2017) Assessment of heavy metal pollution and health risks in the soil-plant-human system in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14(9):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14091042
Hynninen A, Virta M (2010) Whole-cell bioreporters for the detection of bioavailable metals. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 118:31–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/10_2009_9
Hynninen A, Tonismann K, Virta M (2010) Improving the sensitivity of bacterial bioreporters for heavy metals. Bioengineered bugs 1(2):132–138. https://doi.org/10.4161/bbug.1.2.10902
Iu KL, Pulford ID, Duncan HJ (1979) Determination of cadmium, cobalt, copper, nickel and lead in soil extracts by dithizone extraction and atomic absorption spectrometry with electrothermal atomization. Anal Chim Acta 106(2):319–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0003-2670(01)85015-7
Jain CK, Ali I (2000) Arsenic: occurrence, toxicity and speciation techniques. Water Res 34(17):4304–4312. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0043-1354(00)00182-2
Jia XQ, Bu RR, Zhao TT, Wu K (2019) Sensitive and specific whole-cell biosensor for arsenic detection. Appl Environ Microbiol 85(11):10. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00694-19
Jia X, Ma Y, Bu R, Zhao T, Wu K (2020) Directed evolution of a transcription factor PbrR to improve lead selectivity and reduce zinc interference through dual selection. AMB Express 10(1):67. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-020-01004-8
Kim HJ, Lim JW, Jeong H, Lee SJ, Lee DW, Kim T, Lee SJ (2016) Development of a highly specific and sensitive cadmium and lead microbial biosensor using synthetic CadC-T7 genetic circuitry. Biosens Bioelectron 79:701–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.12.101
Kumar S, Verma N, Singh AK (2017) Development of cadmium specific recombinant biosensor and its application in milk samples. Sens Actuator B-Chem 240:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.08.160
Liao VHC, Chien MT, Tseng YY, Ou KL (2006) Assessment of heavy metal bioavailability in contaminated sediments and soils using green fluorescent protein-based bacterial biosensors. Environ Pollut 142(1):17–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.09.021
Liu XC, Hu QY, Yang JM, Huang SQ, Wei TB, Chen WZ, He YF, Wang D, Liu ZJ, Wang K, Gan JH, Chen H (2019) Selective cadmium regulation mediated by a cooperative binding mechanism in CadR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 116(41):20398–20403. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1908610116
Martelli A, Rousselet E, Dycke C, Bouron A, Moulis JM (2006) Cadmium toxicity in animal cells by interference with essential metals. Biochimie 88(11):1807–1814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2006.05.013
Nachman KE, Graham JP, Price LB, Silbergeld EK (2005) Arsenic: a roadblock to potential animal waste management solutions. Environ Health Perspect 113(9):1123–1124. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.7834
Nistala GJ, Wu K, Rao CV, Bhalerao KD (2010) A modular positive feedback-based gene amplifier. J Biol Eng 4:4–4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-1611-4-4
Pola-Lopez LA, Camas-Anzueto JL, Martinez-Antonio A, Lujan-Hidalgo MC, Anzueto-Sanchez G, Ruiz-Valdiviezo VM, Grajales-Coutino R, Gonzalez JHC (2018) Novel arsenic biosensor "POLA" obtained by a genetically modified E-coli bioreporter cell. Sens Actuator B-Chem 254:1061–1068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.08.006
Rosolina SM, Chambers JQ, Lee CW, Xue Z-L (2015) Direct determination of cadmium and lead in pharmaceutical ingredients using anodic stripping voltammetry in aqueous and DMSO/water solutions. Anal Chim Acta 893:25–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.07.010
Santos IC, Mesquita RBR, Rangel ASS (2015) Micro solid phase spectrophotometry in a sequential injection lab-on-valve platform for cadmium, zinc, and copper determination in freshwaters. Anal Chim Acta 891:171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.08.021
Shaner NC, Campbell RE, Steinbach PA, Giepmans BNG, Palmer AE, Tsien RY (2004) Improved monomeric red, orange and yellow fluorescent proteins derived from Discosoma sp red fluorescent protein. Nat Biotechnol 22(12):1567–1572. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1037
Shaner NC, Steinbach PA, Tsien RY (2005) A guide to choosing fluorescent proteins. Nat Methods 2(12):905–909. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth819
Tani C, Inoue K, Tani Y, Harun-ur-Rashid M, Azuma N, Ueda S, Yoshida K, Maeda I (2009) Sensitive fluorescent microplate bioassay using recombinant Escherichia coli with multiple promoter-reporter units in tandem for detection of arsenic. J Biosci Bioeng 108(5):414–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2009.05.014
Tao HC, Peng ZW, Li PS, Yu TA, Su J (2013) Optimizing cadmium and mercury specificity of CadR-based E-coli biosensors by redesign of CadR. Biotechnol Lett 35(8):1253–1258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1216-4
Ure AM, Hernandezartiga MP, Mitchell MC (1978) A carbon-rod atomizer for the determination of cadmium and lead in plant materials and soil extracts: part III. Simultaneous determination of cadmium by atomic fluorescence and lead by atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 96(1):37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0003-2670(01)93393-8
van der Meer JR, Belkin S (2010) Where microbiology meets microengineering: design and applications of reporter bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 8(7):511–522. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2392
Wang BJ, Barahona M, Buck M (2015) Amplification of small molecule-inducible gene expression via tuning of intracellular receptor densities. Nucleic Acids Res 43(3):1955–1964. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1388
WHO (1992) Cadmium : environmental aspects. World Heal. Organ.
WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality. World Heal. Organ.
Wongsasuluk P, Chotpantarat S, Siriwong W, Robson M (2014) Heavy metal contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from shallow groundwater wells in an agricultural area in Ubon Ratchathani province, Thailand. Environ Geochem Health 36(1):169–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-013-9537-8
Wu CH, Le D, Mulchandani A, Chen W (2009) Optimization of a whole-cell cadmium sensor with a toggle gene circuit. Biotechnol Prog 25(3):898–903. https://doi.org/10.1002/btpr.203
Zhou MH, Wu YX, Zhang JQ, Zhang Y, Chen X, Ye J, Wang SX (2019) Development and collaborative study of a diluted acid mild extraction method for determination of cadmium in grain by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Sci 35(3):283–287. https://doi.org/10.2116/analsci.18P321
Code availability
Not applicable
Funding
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support provided by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Project No. 2018YFA0902100), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21576197), and Tianjin Research Program of Application Foundation and Advanced Technology (No. 18JCYBJC23500).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J XQ and W K conceived and designed study. M YB collected data. J XQ, L T, M YB, and W K analyzed data. L T wrote the manuscript and created the figures.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
The authors agree to participate.
Consent for publication
The authors agree to submit the article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 901 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, X., Liu, T., Ma, Y. et al. Construction of cadmium whole-cell biosensors and circuit amplification. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 5689–5699 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11403-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11403-x