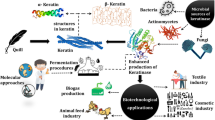
Abstract
Keratinase is an important enzyme that can degrade recalcitrant keratinous wastes to form beneficial recyclable keratin hydrolysates. Keratinase is not only important as an alternative to reduce environmental pollution caused by chemical treatments of keratinous wastes, but it also has industrial significance. Currently, the bioproduction of keratinase from native keratinolytic host is considered low, and this hampers large-scale usage of the enzyme. Straightforward approaches of cloning and expression of recombinant keratinases from native keratinolytic host are employed to elevate the amount of keratinase produced. However, this is still insufficient to compensate for the lack of its large-scale production to meet the industrial demands. Hence, this review aimed to highlight the various sources of keratinase and the strategies to increase its production in native keratinolytic hosts. Molecular strategies to increase the production of recombinant keratinase such as plasmid selection, promoter engineering, chromosomal integration, signal peptide and propeptide engineering, codon optimization, and glycoengineering were also described. These mentioned strategies have been utilized in heterologous expression hosts, namely, Escherichia coli, Bacillus sp., and Pichia pastoris, as they are most widely used for the heterologous propagations of keratinases to further intensify the production of recombinant keratinases adapted to better suit the large-scale demand for them.
Key points
• Molecular strategies to enhance keratinase production in heterologous hosts.
• Construction of a prominent keratinolytic host from a native strain.
• Patent analysis of keratinase production shows rapid high interest in molecular field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Fattah AM, El-Gamal MS, Ismail SA, Emran MA, Hashem AM (2018) Biodegradation of feather waste by keratinase produced from newly isolated Bacillus licheniformis ALW1. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 16(2):311–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2018.05.005
Abdul Gafar A, Khayat ME, Ahmad SA, Yasid NA, Shukor MY (2020) Response surface methodology for the optimization of keratinase production in culture medium containing feathers by Bacillus sp. UPM-AAG1. Catalysts:10–848. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080848
Adelere IA, Lateef A (2016) Keratinases: Emerging trends in production and applications as novel multifunctional biocatalysts. Kuwait J Sci 43:118–127
Aggarwal S, Mishra S (2020) Differential role of segments of α - mating factor secretion signal in Pichia pastoris towards granulocyte colony - stimulating factor emerging from a wild type or codon optimized copy of the gene. Microb Cell Factories 19:199. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-020-01460-8
Ahmad M, Schwab H, Winkler CM, Kolmbauer M, Pichler H, Augustin AE (2019) Pichia pastoris protease - deficient and auxotrophic strains generated by a novel, user-friendly vector toolbox for gene deletion. Yeast 36:557–570. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.3426
Akhter M, Wal Marzan L, Akter Y, Shimizu K (2020) Microbial bioremediation of feather waste for keratinase production: an outstanding solution for leather dehairing in tanneries. Microbiol Insights 28:1178636120913280. https://doi.org/10.1177/1178636120913280
Anitha TS, Palanivelu P (2013) Purification and characterization of an extracellular keratinolytic protease from a new isolate of Aspergillus parasiticus. Protein Expr Purif 88(2):214–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2013.01.007
Awad GEA, Esawy MA, Salam WA, Salama BM, Abdelkader AF, El-Diwany A (2011) Keratinase production by Bacillus pumilus GHD in solid-state fermentation using sugar cane bagasse: optimisation of culture conditions using a Box-Behnken experimental design. Ann Microbiol 61(3):663–672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-010-0187-0
Baghban R, Farajnia S, Rajabibazl M, Ghasemi Y, Mafi A (2019) Yeast expression systems: overview and recent advances. Mol Biotechnol 61:365–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-019-00164-8
Bakhtiar S, Estiveira RJ, Hatti-Kaul R (2005) Substrate specificity of alkaline protease from alkaliphilic feather-degrading Nesterenkonia sp. AL20. Enzym Microb Technol 37(5):534–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.04.003
Baumgardt K, Gilet L, Figaro S, Condon C (2018) The essential nature of YqfG, a YbeY homologue required for 3′ maturation of Bacillus subtilis 16S ribosomal RNA is suppressed by deletion of RNase R. Nucleic Acids Res 46(16):8605–8615. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky488
Ben-Elhoul M, Zaraî JN, Rekik H, Omrane BM, Mechri S, Moujehed E, Kourdali S, El HM, Badis A, Bejar S, Jaouadi B (2016) Biochemical and molecular characterization of new keratinoytic protease from Actinomadura viridilutea DZ50. Int J Biol Macromol 92:299–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.07.009
Benkiar A, Nadia ZJ, Badis A, Rebzani F, Soraya BT, Rekik H, Naili B, Ferradji FZ, Bejar S, Jaouadi B (2013) Biochemical and molecular characterization of a thermo- and detergent-stable alkaline serine keratinolytic protease from Bacillus circulans strain DZ100 for detergent formulations and feather-biodegradation process. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 83:129–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.05.014
Bernal C, Cairó J, Coello N (2006) Purification and characterization of a novel exocellular keratinase from Kocuria rosea. Enzym Microb Technol 38(1–2):49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.02.021
Bohacz J (2017) Biodegradation of feather waste keratin by a keratinolytic soil fungus of the genus Chrysosporium and statistical optimization of feather mass loss. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2177-2
Boon L, Ugarte-berzal E, Vandooren J (2020) Protease propeptide structures, mechanisms of activation, and functions. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 55:1–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409238.2020.1742090
Bouacem K, Bouanane-Darenfed A, Zaraî JN, Joseph M, Hacene H, Ollivier B, Fardeau ML, Bejar S, Jaouadi B (2016) Novel serine keratinase from Caldicoprobacter algeriensis exhibiting outstanding hide dehairing abilities. Int J Biol Macromol 86:321–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.01.074
Burdette LA, Leach SA, Wong HT, Ercek DT (2018) Developing Gram-negative bacteria for the secretion of heterologous proteins. Microb Cell Factories 17:196. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-1041-5
Cai CG, Chen JS, Qi JJ, Yin Y, Zheng XD (2008) Purification and characterization of keratinase from a new Bacillus subtilis strain. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 9(9):713–720. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0820128
Cao H, Villatoro-Hernandez J, Weme RDO, Frenzel E, Kuipers OP (2018) Boosting heterologous protein production yield by adjusting global nitrogen and carbon metabolic regulatory networks in Bacillus subtilis. Metab Eng 49:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.08.001
Cheng J, Guan C, Cui W, Zhou L, Liu Z, Li W, Zhou Z (2016) Enhancement of a high efficient autoinducible expression system in Bacillus subtilis by promoter engineering. Protein Expr Purif 127:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2016.07.008
Danilova I, Sharipova M (2020) The practical potential of Bacilli and their enzymes for industrial production. Front Microbiol 11:1782. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01782
Darah I, Nur-Diyana A, Nurul-Husna S, Jain K, Lim SH (2013) Microsporum fulvum IBRL SD3: As novel isolate for chicken feathers degradation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 171(7):1900–1910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0496-4
Dedavid El Silva LA, Tirloni L, Loss-Morais G, Margis R, Da Silva VI, Macedo AJ, Termignoni C (2014) A recombinant subtilisin with keratinolytic and fibrin(ogen)olytic activity. Process Biochem 49(6):948–954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2014.03.017
Dong YZ, Chang WS, Chen PT (2017) Characterization and overexpression of a novel keratinase from Bacillus polyfermenticus B4 in recombinant Bacillus subtilis. Bioresour Bioprocess 4(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-017-0177-1
Duarte TR, Oliveira SS, Macrae A, Cedrola SML, Mazotto AM, Souza EP, Melo ACN, Vermelho AB (2011) Increased expression of keratinase and other peptidases by Candida parapsilosis mutants. Braz J Med Biol Res 44(3):212–216. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0100-879x2011007500011
El-Refai HA, AbdelNaby MA, Gaballa A, El-Araby MH, Abdel-Fattah AF (2005) Improvement of the newly isolated Bacillus pumilus FH9 keratinolytic activity. Process Biochem 40(7):2325–2332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2004.09.006
Fakhfakh-Zouari N, Haddar A, Hmidet N, Frikha F, Nasri M (2010) Application of statistical experimental design for optimization of keratinases production by Bacillus pumilus A1 grown on chicken feather and some biochemical properties. Process Biochem 45(5):617–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2009.12.007
Fang Z, Zhang J, Liu B, Jiang L, Du G, Chen J (2014) Cloning, heterologous expression and characterization of two keratinases from Stenotrophomonas maltophilia BBE11-1. Process Biochem 49(4):647–654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2014.01.009
Fang Z, Zhang J, Liu B, Du G, Chen J (2016) Enhancement of the catalytic efficiency and thermostability of Stenotrophomonas sp. keratinase KerSMD by domain exchange with KerSMF. Microb Biotechnol 9(1):35–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12300
Fellahi S, Chibani A, Feuk-Lagerstedt E, Taherzadeh MJ (2016) Identification of two new keratinolytic proteases from a Bacillus pumilus strain using protein analysis and gene sequencing. AMB Express 6(42):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-016-0213-0
Freudl R (2018) Signal peptides for recombinant protein secretion in bacterial expression systems. Microb Cell Factories 17:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-018-0901-3
Giudice MC, Reis-Menezes AA, Rittner GMG, Mota AJ, Gambale W (2012) Isolation of Microsporum gypseum in soil samples from different geographical regions of Brazil, evaluation of the extracellular proteolytic enzymes activities (keratinase and elastase) and molecular sequencing of selected strains. Braz J Microbiol 43(3):895–902. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822012000300007
Gong J, Wang Y, Zhang D, Zhang R, Su C, Li H, Zhang X, Xu Z, Shi J (2015) Alkaline and surfactant-stable keratinase derived from a newly isolated actinomycete Streptomyces. RSC Adv 5:24691–24699. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA16423G
Gong JS, Ye JP, Tao LY, Su C, Qin J, Zhang YY, Li HH, Li HH, Xu ZH (2020) Shi JS (2020) Efficient keratinase expression via promoter engineering strategies for degradation of feather wastes. Enzym Microb Technol 137:109550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2020.109550
Gupta S, Tewatia P, Misri J, Singh R (2017) Molecular modeling of cloned Bacillus subtilis keratinase and its insinuation in psoriasis treatment using docking studies. Indian J Microbiol 57(4):485–491. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-004-2241-1485. 10.1007/s12088-017-0677-x
Gushterova A, Vasileva-Tonkova E, Dimova E, Nedkov P, Haertlé T (2005) Keratinase production by newly isolated Antarctic actinomycete strains. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:831–834. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-004-2241-1
Habbeche A, Saoudi B, Jaouadi B, Haberra S, Kerouaz B, Boudelaa M, Badis A, Ladjama A (2014) Purification and biochemical characterization of a detergent-stable keratinase from a newly thermophilic actinomycete Actinomadura keratinilytica strain Cpt29 isolated from poultry compost. J Biosci Bioeng 117(4):413–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2013.09.006
Hertel R, Meyerjürgens S, Voigt B, Liesegang H, Volland S (2017) Small RNA mediated repression of subtilisin production in Bacillus licheniformis. Sci Rep 7(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-05628-y
Herzog B, Overy DP, Haltli B, Kerr RG (2016) Discovery of keratinases using bacteria isolated from marine environments. Syst Appl Microbiol 39(1):49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.syapm.2015.10.004
Hu H, Gao J, He J, Yu B, Zheng P, Huang Z, Mao X, Yu J, Han G, Chen D (2013a) Codon optimization significantly improves the expression level of a keratinase gene in Pichia pastoris. PLoS One 8(3):e58393. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0058393
Hu H, He J, Yu B, Zheng P, Huang Z, Mao X, Yu J, Han G, Chen D (2013b) Expression of a keratinase (kerA) gene from Bacillus licheniformis in Escherichia coli and characterization of the recombinant enzymes. Biotechnol Lett 35(2):239–244. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1064-7
Joshi SG, Tejashwini MM, Revati N, Sridevi R, Roma D (2007) Isolation, identification and characterization of a feather degrading bacterium. Int J Poult Sci 6:689–693
Juturu V, Wu JC (2018) Heterologous protein expression in Pichia pastoris: latest research progress and applications. ChemBioChem 19:7–21. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201700460
Karbalaei M (2020) Pichia pastoris: a highly successful expression system for optimal synthesis of heterologous proteins. J Cell Physiol 2020:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29583
Khumalo M, Sithole B, Tesfaye T (2020) Valorisation of waste chicken feathers: optimisation of keratin extraction from waste chicken feathers by sodium bisulphite, sodium dodecyl sulphate and urea. J Environ Manag 262:110329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110329
Kumar AG, Swarnalatha S, Gayathri S, Nagesh N, Sekaran G (2008) Characterization of an alkaline active - thiol forming extracellular serine keratinase by the newly isolated Bacillus pumilus. J Appl Microbiol 104(2):411–419. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03564.x
Laba W, Rodziewicz A (2014) Biodegradation of hard keratins by two Bacillus strains. Jundishapur J Microbiol 7(2):e8896. https://doi.org/10.5812/jjm.8896
Lakshmi PJ, Kumari CCM, Lakshmi VV (2013) Efficient degradation of feather by keratinase producing Bacillus sp. Int J Microbiol, pp 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/608321
Lange L, Huang Y, Busk PK (2016) Microbial decomposition of keratin in nature—a new hypothesis of industrial relevance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(5):2083–2096. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7262-1
Lateef A, Adelere IA, Gueguim-Kana EB (2015) Bacillus safensis LAU 13: a new source of keratinase and its multi-functional biocatalytic applications. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 29:54–63. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2014.986360
Li Q (2019) Progress in microbial degradation of feather waste. Front Microbiol 10:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02717
Li ZW, Liang S, Ke Y, Deng JJ, Zhang MS, Lu DL, Li JZ, Luo XC (2020) The feather degradation mechanisms of a new Streptomyces sp. isolate SCUT-3. Commun Biol 3(191):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-0918-0
Lin X, Lee CG, Casale ES, Shih JCH (1992) Purification and characterization of a keratinase from a feather-degrading Bacillus licheniformis strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 58(10):3271–3275. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.58.10.3271-3275.1992
Lin X, Wong SL, Miller ES, Shin JCH (1997) Expression of the Bacillus licheniformis PWD-1 keratinase gene in B. subtilis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 19(2):134–138. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.2900440
Lin HH, Yin LJ, Jiang ST (2009a) Cloning, expression, and purification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratinase in Escherichia coli AD494(DE3)pLysS expression system. J Agric Food Chem 57(9):3506–3511. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf803752j
Lin HH, Yin LJ, Jiang ST (2009b) Functional expression and characterization of keratinase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Pichia pastoris. J Agric Food Chem 57(12):5321–5325. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf900417t
Lin HH, Yin LJ, Jiang ST (2009c) Expression and purification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratinase in Bacillus subtilis DB104 expression system. J Agric Food Chem 57(17):7779–7784. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf901903p
Liu B, Zhang J, Fang Z, Du G, Chen J, Liao X (2014a) Functional analysis of the C-terminal propeptide of keratinase from Bacillus licheniformis BBE11-1 and its effect on the production of keratinase in Bacillus subtilis. Process Biochem 49(9):1538–1542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2014.04.021
Liu B, Zhang J, Gu L, Du G (2014b) Comparative analysis of bacterial expression systems for keratinase production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 173:1222–1235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-0925-z
Mabrouk MEM (2008) Feather degradation by a new keratinolytic Streptomyces sp. MS-2. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24(10):2331–2338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9748-9
Macedo AJ, Da Silva WOB, Gava R, Driemeier D, Henriques JAP, Termignoni C (2005) Novel keratinase from Bacillus subtilis S14 exhibiting remarkable dehairing capabilities. Appl Environ Biotechnol 71(1):594–596. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.1.594-596.2005
Macedo AJ, Da Silva WOB, Termignoni C (2008) Properties of a non collagen-degrading Bacillus subtilis keratinase. Can J Microbiol 54(3):180–188. https://doi.org/10.1139/w07-124
Marciniak BC, Trip H, van-der Veek PJ, Kuipers OP (2012) Comparative transcriptional analysis of Bacillus subtilis cells overproducing either secreted proteins, lipoproteins or membrane proteins. Microb Cell Factories 11:66. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-11-66
Mazotto AM, Coelho RRR, Cedrola SML, De Lima MF, Couri S, De Souza EP, Vermelho AB (2011) Keratinase production by three Bacillus spp. using feather meal and whole feather as substrate in a submerged fermentation. Enzyme Res 2011(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/523780
Mohamad N, Phang LY, Abd-Aziz S (2017) Optimization of metallo-keratinase production by Pseudomonas sp. LM19 as a potential enzyme for feather waste conversion. Biocatal Biotransform 35(1):41–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/10242422.2017.1280031
Mukherjee AK, Rai SK, Bordoloi NK (2011) Biodegradation of waste chicken-feathers by an alkaline β-keratinase (Mukartinase) purified from a mutant Brevibacillus sp. strain AS-S10-II. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 65(8):1229–1237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2011.09.007
Nagal S, Jain PC (2010) Feather degradation by strains of Bacillus isolated from decomposing feathers. Braz J Microbiol 41(1):196–200. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-83822010000100028
Navone L, Speight R (2018) Understanding the dynamics of keratin weakening and hydrolysis by proteases. PLoS One 13(8):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0202608
Ningthoujam DS, Mukherjee S, Devi LJ, Singh ES, Tamreihao K, Khunjamayum R, Banerjee S, Mukhopadhyay D (2019) In vitro degradation of β-amyloid fibrils by microbial keratinase. Alzheimers Dement 16(5):154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trci.2019.03.003
Nnolim NE, Nwodo UU (2021) Microbial keratinase and the bio-economy: a three-decade meta-analysis of research exploit. AMB Express 11:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-020-01155-8
Nnolim NE, Udenigwe CC, Okoh AI, Nwodo UU (2020) Microbial keratinase: next generation green catalyst and prospective applications. Front Microbiol 11:580164. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.580164
Oncel SS, Vardar-sukan F (2015) An optimization approach to scale up keratinase production by Streptomyces sp. 2M21 by utilizing chicken feather. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 103:134–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.04.025
Paul T, Das A, Mandal A, Halder SK, Jana A, Maity C, Dasmohapatra PK, Pati BR, Mondal KC (2014) An efficient cloth cleaning properties of a crude keratinase combined with detergent: towards industrial viewpoint. J Clean Prod 66:672–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.10.054
Phan TTP, Nguyen HD, Schumann W (2012) Development of a strong intracellular expression system for Bacillus subtilis by optimizing promoter elements. J Biotechnol 157(1):167–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.10.006
Porres JM, Benito MJ, Lei XG (2002) Functional expression of keratinase (kerA) gene from Bacillus licheniformis in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnol Lett 24(8):631–636. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015083007746
Radha S, Gunasekaran P (2007) Cloning and expression of keratinase gene in Bacillus megaterium and optimization of fermentation conditions for the production of keratinase by recombinant strain. J Appl Microbiol 103(4):1301–1310. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03372.x
Radha S, Gunasekaran P (2008) Sustained expression of keratinase gene under PxylA and PamyL promoters in the recombinant Bacillus megaterium MS941. Bioresour Technol 99:5528–5537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007.10.052
Radha S, Gunasekaran P (2009) Purification and characterization of keratinase from recombinant Pichia and Bacillus strains. Protein Expr Purif 64(1):24–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pep.2008.10.008
Rahayu S, Syah D, Suhartono MT (2012) Degradation of keratin by keratinase and disulfide reductase from Bacillus sp. MTS of Indonesian origin. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 1(2):152–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2012.02.001
Rajput R, Gupta R (2013) Thermostable keratinase from Bacillus pumilus KS12: production, chitin crosslinking and degradation of Sup35NM aggregates. Bioresour Technol 133:118–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.01.091
Rajput R, Tiwary E, Sharma R, Gupta R (2012) Swapping of pro-sequences between keratinases of Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus pumilus: altered substrate specificity and thermostability. Enzym Microb Technol 51(3):131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2012.04.010
Reddy MR, Reddy KS, Chouhan YR, Bee H, Reddy G (2017) Effective feather degradation and keratinase production by Bacillus pumilus GRK for its application as bio-detergent additive. Bioresour Technol 243:254–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.067
Rekik H, Badis A, Trabelsi S, Belhoul M, Zaraı N, Yahiaoui B, Aicha HB, Toumi A, Bejar S, Jaouadi B (2013) Biochemical and molecular characterization of a serine keratinase from Brevibacillus brevis US575 with promising keratin-biodegradation and hide-dehairing activities. PLoS One 8(10):e76722. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076722
Riffel A, Brandelli A, Bellato CM, Souza GHMF, Eberlin MN, Tavares FCA (2007) Purification and characterization of a keratinolytic metalloprotease from Chryseobacterium sp. kr6. J Biotechnol 128(3):693–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2006.11.007
Sangali S, Brandelli A (2000) Feather keratin hydrolysis by a Vibrio sp. strain kr2. J Appl Microbiol 89(5):735–743. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2672.2000.01173.x
Schwarzhans JP, Wibberg D, Winkler A, Luttermann T, Kalinowski J, Friehs K (2016) Integration event induced changes in recombinant protein productivity in Pichia pastoris discovered by whole genome sequencing and derived vector optimization. Microb Cell Factories 15:84. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-016-0486-7
Sharma S, Gupta A (2016) Sustainable management of keratin waste biomass: applications and future perspectives. Braz Arch Biol Technol 59:1–15 https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4324-2016150684
Sharma A, Chandra S, Sharma M (2012) Difference in keratinase activity of dermatophytes at different environmental conditions is an attribute of adaptation to parasitism. Mycoses 55(5):410–415. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0507.2011.02133.x
Sharma R, Verma VV, Gupta R (2013) Functional characterization of an extracellular keratinolytic protease, Ker AP from Pseudomonas aeruginosa KS-1: a putative aminopeptidase with PA domain. Mol. Catal. B Enzym 91:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2013.01.021
Shu M, Shen W, Yang S, Wang X, Wang F, Wang Y, Ma L (2016) High-level expression and characterization of a novel serine protease in Pichia pastoris by multi-copy integration. Enzym Microb Technol 92:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2016.06.007
Silveira ST, Jaeger MK, Brandelli A (2009) Kinetic data and substrate specificity of a keratinase from Chryseobacterium sp. strain kr6. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84(3):361–366. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2048
Suh HJ, Lee HK (2001) Characterization of a Keratinolytic Serine Protease from Bacillus subtilis KS-1. J Protein Chem 20:165–169. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011075707553
Thi D, Tran M, Thi T, Phan P, Thi T, Doan N (2020) Integrative expression vectors with Pgrac promoters for inducer-free overproduction of recombinant proteins in Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol Rep 28:e00540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2020.e00540
Verma A, Singh H, Anwar MS, Kumar S, Ansari MW, Agrawal S (2016) Production of thermostable organic solvent tolerant keratinolytic protease from Thermoactinomyces sp. RM4: IAA production and plant growth promotion. Front Microbiol 7:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01189
Vidmar B, Vodovnik M (2018) Microbial keratinases: enzymes with promising biotechnological applications. Food Technol Biotechnol 56(3):312–328. 10.17113/ftb.56.03.18.5658
Wang L, Cheng G, Ren Y, Dai Z, Zhao ZS, Liu F, Li S, Wei Y, Xiong J, Tang XF, Tang B (2015) Degradation of intact chicken feathers by Thermoactinomyces sp. CDF and characterization of its keratinolytic protease. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(9):3949–3959. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-6207-4
Wang L, Zhou Y, Huang Y, Wei Q, Huang H, Guo C (2019) Cloning and expression of a thermostable keratinase gene from Thermoactinomyces sp. YT06 in Escherichia coli and characterization of purified recombinant enzymes. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35(135):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2710-1
Wu WL, Chen MY, Tu IF, Lin YC, Eswarkumar N, Chen MY, Ho MC, Wu SH (2017) The discovery of novel heat-stable keratinases from Meiothermus taiwanensis WR-220 and other extremophiles. Sci Rep 7(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04723-4
Yang L, Wang H, Lv Y, Bai Y, Luo H, Shi P, Huang H, Yao B (2016) Construction of a rapid feather-degrading bacterium by overexpression of a highly efficient alkaline keratinase in its parent strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens K11. J Agric Food Chem 64(1):78–84. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b04747
Yong B, Fei X, Shao H, Xu P, Hu Y, Ni W, Xiao Q, Tao X, He X (2020) Recombinant expression and biochemical characterization of a novel keratinase BsKER71 from feather degrading bacterium Bacillus subtilis S1-4. AMB Express 10(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-019-0939-6
Yusuf I, Ahmad SA, Phang LY, Syed MA, Shamaan NA, Abdul Khalil K, Dahalan FA, Shukor MY (2016) Keratinase production and biodegradation of polluted secondary chicken feather wastes by a newly isolated multi heavy metal tolerant bacterium-Alcaligenes sp. AQ05-001. J Environ Manag 183:182–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.08.059
Zhang K, Duan X, Wu J (2016) Multigene disruption in undomesticated Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6051a using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Sci Rep 6:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27943
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Universiti Putra Malaysia—Putra Graduate Initiative grant (GP-IPS/2021/9696100). RSRY was sponsored by a Graduate Research Fellowship from Universiti Putra Malaysia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RSRY and SS drafted the content, analyzed the subjects, and wrote the manuscript. NMY, LYP, JOA, and SAA gave critical insights on the subjects and reviewed and improved the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies involving human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yahaya, R.S.R., Normi, Y.M., Phang, L.Y. et al. Molecular strategies to increase keratinase production in heterologous expression systems for industrial applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 3955–3969 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11321-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11321-y