Abstract
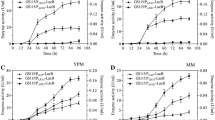
Controlling gene expression is often the foremost goal of most biological endeavors like the production of industrial enzymes and expression of heterologous metabolic pathway genes. The components of the entire “expression cassette” exert control on net protein output. This control is primarily achieved through altering the promoter driving expression and by changing the copy number of the gene. However, there are only a few recent studies on terminators. Terminators are essential components in expression cassettes that influence the 3′ end processing of mRNA, mRNA stability, and translational efficiency, which can modulate protein production. In Pichia pastoris (Komagataella phaffi), little attention has been paid to the selection of terminator regions in efforts to increase heterologous gene expression. To explore the potential application of the terminator regions on increased secretory production of Candida antarctica lipase B (CALB), we assessed the ability of three different classes of terminator regions: (1) terminator regions of methanol oxidation pathway genes of P. pastoris; (2) terminator regions of well-expressed and housekeeping genes of P. pastoris; and (3) terminators of other yeast genes like Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The terminator of dihydroxyacetone synthase (DHAS TT), a high expressing gene in the methanol utilization pathway, shows inducible CALB expression levels similar to the AOX1 terminator (AOX1 TT) under the control of AOX1 promoter and threefold higher in constitutive expression of CALB under the control of GAP promoter. The Calb transcript abundance was also found to correlate with protein expression. Furthermore, mRNA half-life determination showed a direct correlation between the stability of transcripts and increased transcription rate. Together, our results emphasize that enhancing transcript stability using the correct choice of transcription terminators (TT) will help in developing robust production strains suitable for scale-up.
Key points
• Influence of transcription terminators on Calb gene expression
• Modulation of gene expression by enhancing transcript stability







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
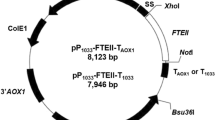
All sequence data related to the P. pastoris terminators used in this study are available in the KEGG database. The terminator sequences are provided in supplementary data.
References
Abe H, Aiba H (1996) Differential contributions of two elements of rho-independent terminator to transcription termination and mRNA stabilization. Biochimie. 78(11–12):1035–1042. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0300-9084(97)86727-2
Birse CE, Minvielle-Sebastia L, Lee BA, Keller W, Proudfoot NJ (1998) Coupling termination of transcription to messenger RNA maturation in yeast. Science. 280(5361):298–301. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.280.5361.298
Blazeck J, Alper HS (2013) Promoter engineering: recent advances in controlling transcription at the most fundamental level. Biotechnol J 8(1):46–58. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201200120
Coller J (2008) Methods to determine mRNA half-life in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol 448:267–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(08)02614-1
Curran KA, Karim AS, Gupta A, Alper HS (2013) Use of high capacity terminators in Saccharomyces cerevisiae to increase mRNA half-life and improve gene expression control for metabolic engineering applications. Metab Eng 19:88–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2013.07.001
Curran KA, Morse NJ, Markham KA, Wagman AM, Gupta A, Alper HS (2015) Short synthetic terminators for improved heterologous gene expression in yeast. ACS Synth Biol 4(7):824–832. https://doi.org/10.1021/sb5003357
Fan X, Moqtaderi X, Jin Y, Zhang Y, Liu XS, Struhl K (2010) Nucleosome depletion at yeast terminators is not intrinsic and can occur by a transcriptional mechanism linked to 3’-end formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(42):17945–17950. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1012674107
Geisberg JV, Moqtaderi Z, Fan X, Ozsolak F, Struhl K (2014) Global analysis of mRNA isoform half-lives reveals stabilizing and destabilizing elements in yeast. Cell 156(4):812–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.026
Guo Z, Sherman F (1996) 3’end-forming signals of yeast mRNA. Trends Biochem Sci 21(12):477–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0968-0004(96)10057-8
Guo Z, Russo P, Yun DF, Butler JS, Sherman F (1995) Redundant 3’ end-forming signals for the yeast CYC1 mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92(10):4211–4214. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.10.4211
Hammell CM, Gross S, Zenklusen D, Heath CV, Stutz F, Moore C, Cole CN (2002) Coupling of termination, 3’ processing, and mRNA export. Mol Cell Biol 22(18):6441–6457. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.22.18.6441-6457.2002
Ito Y, Yamanishi M, Ikeuchi A, Imamura C, Tokuhiro K, Kitagawa T, Matsuyama T (2013) Characterization of five terminator regions that increase the protein yield of a transgene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biotechnol 168(4):486–492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2013.09.024
Ito Y, Kitagawa T, Yamanishi M, Katahira S, Izawa S, Irie K, Seiki MF, Matsuyama T (2016) Enhancement of protein production via the strong DIT1 terminator and two RNA-binding proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Sci Rep 6:36997. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36997
Kuehner JN, Pearson EL, Moore C (2011) Unravelling the means to an end: RNA polymerase II transcription termination. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12(5):283–294. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3098
Leavitt JM, Alper HS (2015) Advances and current limitations in transcript-level control of gene expression. Curr Opin Biotechnol 34:98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2014.12.015
MacPherson M, Saka Y (2017) Short synthetic terminators for assembly of transcription units in vitro and stable chromosomal integration in Yeast S. cerevisiae. ACS Synth Biol 6(1):130–138. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.6b00165
Mapendano CK, Lykke-Andersen S, Kjems J, Bertrand E, Jensen TH (2010) Cross talk between mRNA3’ end processing and transcription initiation. Mol Cell 40:410–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2010.10.012
Mischo HE, Proudfoot NJ (2013) Disengaging polymerase: terminating RNA polymerase II transcription in budding yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta 1829(1):174–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.10.003
Morse NJ, Gopal MR, Wagner JM, Alper HS (2017) Yeast terminator function can be modulated and designed on the basis of predictions of nucleosome occupancy. ACS Synth Biol 6(11):2086–2095. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.7b00138
Munchel SE, Shultzaberger RK, Takizawa N, Weis K (2011) Dynamic profiling of mRNA turnover reveals gene-specific and system-wide regulation of mRNA decay. Mol Biol Cell 22:2787–2795. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E11-01-0028
Nolan T, Hands R, Bustin S (2006) Quantification of mRNA using real-time RT-PCR. Nat Protoc 1:1559–1582. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.236
O’Sullivan JM, Tan-Wong SM, Morillon A, Lee B, Coles J, Mellor J, Proudfoot NJ (2004) Gene loops juxtapose promoters and terminators in yeast. Nat Genet 36:1014–1018. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1411
Overton TW (2014) Recombinant protein production in bacterial host. Drug Discov Today 19(5):590–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2013.11.008
Richard P, Manley JL (2009) Transcription termination by nuclear RNA polymerases. Genes Dev 23(11):1247–1269. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1792809
Scorer CA, Clare JJ, McCombie WR, Romanos MA, Sreekrishna K (1994) Rapid selection using G418 of high copy number transformants of Pichia pastoris for high-level foreign gene expression. Biotechnology (N Y) 12(2):181–184. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0294-181
Shalem O, Sharon E, Lubliner S, Regev I, Lotan-Pompan M, Yakhini Z, Segal E (2015) Systematic dissection of the sequence determinants of gene 3’ end mediated expression control. PLoS Genet 11(4):e1005147. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005147
Shalgi R, Lapidot M, Shamir R, Pilpel Y (2005) A catalog of stability-associated sequence elements in 3’ UTRs of yeast mRNAs. Genome Biol 6:R86. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2005-6-10-r86
Shao Z, Zhao H, Zhao H (2009) DNA assembler, an in vivo genetic method for rapid construction of biochemical pathways. Nucleic Acids Res 37(2):e16. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn991
Steinmetz EJ, Ng SB, Cloute JP, Brow DA (2006) cis- and trans-acting determinants of transcription termination by yeast RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol 26(7):2688–2696. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.26.7.2688-2696.2006
Uwimana N, Collin P, Jeronimo C, Haibe-Kains B, Robert F (2017) Bidirectional terminators in Saccharomyces cerevisiae prevent cryptic transcription from invading neighboring genes. Nucleic Acids Res 45(11):6417–6426. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx242
Vadhana AK, Samuel P, Berin RM, Krishna J, Kamatchi K, Meenakshisundaram S (2013) Improved secretion of Candida antarctica lipase B with its native signal peptide in Pichia pastoris. Enzym Microb Technol 52(3):177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2013.01.001
Vogl T, Glieder A (2013) Regulation of Pichia pastoris promoters and its consequences for protein production. New Biotechnol 30(4):385–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2012.11.010
Vogl T, Sturmberger L, Kickenweiz T, Wasmayer R, Schmid C, Hatzl AM, Gerstmann MA, Pitzer J, Wagner M, Thallinger GG, Geier M, Glieder A (2016) A toolbox of diverse promoters related to methanol utilization: functionally verified parts for heterologous pathway expression in Pichia pastoris. ACS Synth Biol 5:172–186. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.5b00199
Vogl T, Kickenweiz T, Pitzer J, Sturmberger L, Weninger A, Biggs BW, Köhler EM, Baumschlager A, Fischer JE, Hyden P, Wagner M, Baumann M, Borth N, Geier M, Ajikumar PK, Glieder A (2018) Engineered bidirectional promoters enable rapid multi-gene co-expression optimization. Nat Commun 9:3589. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05915-w
West S, Proudfoot NJ (2009) Transcriptional termination enhances protein expression in human cells. Mol Cell 33(3):354–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2009.01.008
Yamada T, Nagahama M & Akimitsu N (2018). Interplay between transcription and RNA degradation. Fumiaki Uchimi (ed) Gene expression and regulation in mammalian cells – transcription from general aspects, 6th chapter https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.71862
Yamanishi M, Katahira S, Matsuyama T (2011) TPS1 terminator increases mRNA and protein yield in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 75(11):2234–2236. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.110246
Yamanishi M, Ito Y, Kintaka R, Imamura C, Katahira S, Ikeuchi A, Moriya H, Matsuyama T (2013) Genome-wide activity assessment of terminator regions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae provides a “terminatome” toolbox. ACS Synth Biol 2(6):337–347. https://doi.org/10.1021/sb300116y
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the support from the DBT-BUILDER programme for providing infrastructure facility (BT/PR12153/INF/22/200/2014). The authors acknowledge the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) for granting Senior Research Fellowship to Kamatchi Ramakrishnan and Ministry of Human Resources and Development Undertaking project under the Centre of Excellence in Biomedical Applications, India, for granting fellowship to Mahesh Prattipati. The authors also wish to thank Dr. Nikhil Sangith, Chief Scientific Officer, Xact Diagnotek Pvt. Limited, Chennai, and Dr. Charumathi Jayachandran for reviewing this manuscript.
Funding
This work is funded by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) - Human Resource Development Group (CSIR award number: 38(1413)/16/EMR-II).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, project administration, and supervision by M.S and K.R conceived, designed, and performed research and analysis of data. K.R wrote the paper. M.P. contributed to designing experiments and analyzing data. P.S. contributed to designing the promoter sequence.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 122 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramakrishnan, K., Prattipati, M., Samuel, P. et al. Transcriptional control of gene expression in Pichia pastoris by manipulation of terminators. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 7841–7851 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10785-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10785-8