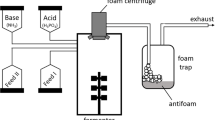
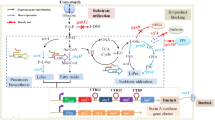
Abstract
As one of the most powerful biosurfactants, surfactin has extensive application prospects in numerous industrial fields. Bacillus subtilis 168 was genetically modified to produce surfactin by increasing the supply of the precursor fatty acyl-CoA by overexpressing 4′ phosphopantetheinyl transferase, medium-chain acyl-acyl carrier protein (ACP) thioesterase and fatty acyl CoA ligase (encoded by sfp, bte, and yhfL, respectively), and knocking out acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (encoded by fadE). The resulting recombinant strain BSFX022 produced 2203 mg/L surfactin with xylose as carbon source. The lower accumulation of organic acids with xylose as carbon source made it possible to maintain surfactin production in a non-buffered fermentation system, and the yield reached 2074 mg/L. Furthermore, to reduce the costs, waste biomass such as corncob hydrolysate and monosodium glutamate wastewater (MGW) were used, and 2032 mg/L of surfactin was produced in the optimal waste-based medium. To our best knowledge, this is the first report of surfactin production using genetically modified Bacillus subtilis 168 with xylose as carbon source.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Mawgoud AM, Aboulwafa MM, Hassouna NAH (2008) Optimization of surfactin production by Bacillus subtilis isolate BS5. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 150(3):305–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8155-x
Agnew DE, Stevermer AK, Youngquist JT, Pfleger BF (2012) Engineering Escherichia coli for production of C-12-C-14 polyhydroxyalkanoate from glucose. Metab Eng 14(6):705–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2012.08.003
Anagnostopoulos C, Spizizen J (1961) Requirements for transformation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 81(5):741–746
Arima K, Kakinuma A, Tamura G (1968) Surfactin, a crystalline peptidelipid surfactant produced by Bacillus subtilis: isolation, characterization and its inhibition of fibrin clot formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 31(3):488–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-291x(68)90503-2
Bose A, Pathan S, Pathak K, Keharia H (2014) Keratinolytic protease production by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens 6B using feather meal as substrate and application of feather hydrolysate as organic nitrogen input for agricultural soil. Waste Biomass Valoriz 5(4):595–605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-013-9272-5
Chen WC, Juang RS, Wei YH (2015) Applications of a lipopeptide biosurfactant, surfactin, produced by microorganisms. Biochem Eng J 103:158–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2015.07.009
Chen C, Lin JZ, Wang WD, Huang H, Li S (2019) Cost-effective production of surfactin from xylose-rich corncob hydrolysate using Bacillus subtilis BS-37. Waste Biomass Valoriz 10(2):341–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0052-5
Cosby WM, Vollenbroich D, Lee OH, Zuber P (1998) Altered srf expression in Bacillus subtilis resulting from changes in culture pH is dependent on the Spo0K oligopeptide permease and the ComQX system of extracellular control. J Bacteriol 180(6):1438–1445
Coutte F, Niehren J, Dhali D, John M, Versari C, Jacques P (2015) Modeling leucine's metabolic pathway and knockout prediction improving the production of surfactin, a biosurfactant from Bacillus subtilis. Biotechnol J 10(8):1216–1234. https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201400541
de Faria AF, Teodoro-Martinez DS, Barbosa GND, Vaz BG, Silva IS, Garcia JS, Totola MR, Eberlin MN, Grossman M, Alves OL, Durrant LR (2011) Production and structural characterization of surfactin (C-14/Leu(7)) produced by Bacillus subtilis isolate LSFM-05 grown on raw glycerol from the biodiesel industry. Process Biochem 46(10):1951–1957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2011.07.001
de Oliveira DWF, Franca IWL, Felix AKN, Martins JJL, Giro MEA, Melo VMM, Goncalves LRB (2013) Kinetic study of biosurfactant production by Bacillus subtilis LAMI005 grown in clarified cashew apple juice. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 101:34–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.06.011
Dong LM, Li YZ, Wang P, Feng ZH, Ding N (2018) Cleaner production of monosodium glutamate in China. J Clean Prod 190:452–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.098
Fahim S, Dimitrov K, Gancel F, Vauchel P, Jacques P, Nikov I (2012) Impact of energy supply and oxygen transfer on selective lipopeptide production by Bacillus subtilis BBG21. Bioresour Technol 126:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.09.019
Fujita Y, Matsuoka H, Hirooka K (2007) Regulation of fatty acid metabolism in bacteria. Mol Microbiol 66(4):829–839. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.05947.x
Geissler M, Kuhle I, Heravi KM, Altenbuchner J, Henkel M, Hausmann R (2019) Evaluation of surfactin synthesis in a genome reduced Bacillus subtilis strain. AMB Express 9:14–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13568-019-0806-5
Gu Y, Xu XH, Wu YK, Niu TF, Liu YF, Li JH, Du GC, Liu L (2018) Advances and prospects of Bacillus subtilis cellular factories: from rational design to industrial applications. Metab Eng 50:109–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.05.006
Guo S, Tang JJ, Wei DZ, Wei W (2014) Construction of a shuttle vector for protein secretory expression in Bacillus subtilis and the application of the mannanase functional heterologous expression. J Microbiol Biotechnol 24(4):431–439. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1311.11009
Gurjar J, Sengupta B (2015) Production of surfactin from rice mill polishing residue by submerged fermentation using Bacillus subtilis MTCC 2423. Bioresour Technol 189:243–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.04.013
Hu FX, Liu YY, Li S (2019) Rational strain improvement for surfactin production: enhancing the yield and generating novel structures. Microb Cell Factories 18:13–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-019-1089-x
Jiang LQ, Pei HY, Hu WR, Ji Y, Han L, Ma GX (2015) The feasibility of using complex wastewater from a monosodium glutamate factory to cultivate Spirulina subsalsa and accumulate biochemical composition. Bioresour Technol 180:304–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.01.019
Jiao S, Li X, Yu HM, Yang H, Li X, Shen ZY (2017) In situ enhancement of surfactin biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis using novel artificial inducible promoters. Biotechnol Bioeng 114(4):832–842. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.26197
Jin P, Kang Z, Yuan PH, Du GC, Chen J (2016a) Production of specific-molecular-weight hyaluronan by metabolically engineered Bacillus subtilis 168. Metab Eng 35:21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2016.01.008
Jin P, Zhang LP, Yuan PH, Kang Z, Du GC, Chen J (2016b) Efficient biosynthesis of polysaccharides chondroitin and heparosan by metabolically engineered Bacillus subtilis. Carbohydr Polym 140:424–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.12.065
Kraas FI, Helmetag V, Wittmann M, Strieker M, Marahiel MA (2010) Functional dissection of surfactin synthetase initiation module reveals insights into the mechanism of lipoinitiation. Chem Biol 17(8):872–880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.06.015
Krispin O, Allmansberger R (1998) The Bacillus subtilis AraE protein displays a broad substrate specificity for several different sugars. J Bacteriol 180(12):3250–3252
Liu L, Liu YF, Shin HD, Chen RR, Wang NS, Li JH, Du GC, Chen J (2013) Developing Bacillus spp. as a cell factory for production of microbial enzymes and industrially important biochemicals in the context of systems and synthetic biology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(14):6113–6127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4960-4
Liu YF, Zhu YQ, Ma WL, Shin HD, Li JH, Liu L, Du GC, Chen J (2014) Spatial modulation of key pathway enzymes by DNA-guided scaffold system and respiration chain engineering for improved N-acetylglucosamine production by Bacillus subtilis. Metab Eng 24:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2014.04.004
Liu Q, Lin JZ, Wang WD, Huang H, Li S (2015) Production of surfactin isoforms by Bacillus subtilis BS-37 and its applicability to enhanced oil recovery under laboratory conditions. Biochem Eng J 93:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2014.08.023
Long XW, He N, He YK, Jiang JJ, Wu TY (2017) Biosurfactant surfactin with pH-regulated emulsification activity for efficient oil separation when used as emulsifier. Bioresour Technol 241:200–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.120
Ma WL, Liu YF, Shin HD, Li JH, Chen J, Du GC, Liu L (2018) Metabolic engineering of carbon overflow metabolism of Bacillus subtilis for improved N-acetyl-glucosamine production. Bioresour Technol 250:642–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.007
Meena KR, Kanwar SS (2015) Lipopeptides as the antifungal and antibacterial agents: applications in food safety and therapeutics. Biomed Res Int:9 doi:https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/473050
Merrick MJ, Edwards RA (1995) Nitrogen control in bacteria. Microbiol Rev 59(4):604–622. https://doi.org/10.0000/PMID8531888
Mootz HD, Marahiel MA (1997) Biosynthetic systems for nonribosomal peptide antibiotic assembly. Curr Opin Chem Biol 1(4):543–551. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1367-5931(97)80051-8
Nitschke M, Pastore GM (2006) Production and properties of a surfactant obtained from Bacillus subtilis grown on cassava wastewater. Bioresour Technol 97(2):336–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2005.02.044
Ramirez IM, Tsaousi K, Rudden M, Marchant R, Alameda EJ, Roman MG, Banat IM (2015) Rhamnolipid and surfactin production from olive oil mill waste as sole carbon source. Bioresour Technol 198:231–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.09.012
Ramirez IM, Vaz DA, Banat IM, Marchant R, Alameda EJ, Roman MG (2016) Hydrolysis of olive mill waste to enhance rhamnolipids and surfactin production. Bioresour Technol 205:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.016
Rehm BHA, Steinbuchel A (2001) Heterologous expression of the acyl-acyl carrier protein thioesterase gene from the plant Umbellularia californica mediates polyhydroxyalkanoate biosynthesis in recombinant Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 55(2):205–209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530000541
Reuter K, Mofid MR, Marahiel MA, Ficner R (1999) Crystal structure of the surfactin synthetase-activating enzyme Sfp: a prototype of the 4 '-phosphopantetheinyl transferase superfamily. EMBO J 18(23):6823–6831. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.23.6823
Schmiedel D, Hillen W (1996) A Bacillus subtilis 168 mutant with increased xylose uptake can utilize xylose as sole carbon source. FEMS Microbiol Lett 135(2–3):175–178
Seydlova G, Svobodova J (2008) Review of surfactin chemical properties and the potential biomedical applications. Cent Eur J Med 3(2):123–133. https://doi.org/10.2478/s11536-008-0002-5
Slivinski CT, Mallmann E, de Araujo JM, Mitchell DA, Krieger N (2012) Production of surfactin by Bacillus pumilus UFPEDA 448 in solid-state fermentation using a medium based on okara with sugarcane bagasse as a bulking agent. Process Biochem 47(12):1848–1855. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2012.06.014
Wang GS, Lee JW, Zhu JY, Jeffries TW (2011) Dilute acid pretreatment of corncob for efficient sugar production. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 163(5):658–668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-010-9071-4
Wang MM, Yu HM, Shen ZY (2019) Antisense RNA-based strategy for enhancing surfactin production in Bacillus subtilis TS1726 via overexpression of the unconventional biotin carboxylase II to enhance ACCase activity. ACS Synth Biol 8(2):251–256. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.8b00459
Wemhoff S, Meinhardt F (2013) Generation of biologically contained, readily transformable, and genetically manageable mutants of the biotechnologically important Bacillus pumilus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(17):7805–7819. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4935-5
Wu Q, Zhi Y, Xu Y (2019) Systematically engineering the biosynthesis of a green biosurfactant surfactin by Bacillus subtilis 168. Metab Eng 52:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2018.11.004
Xu HY, Wang HJ, Jia WH, Ren SL, Wang JQ (2019) Application of Bacillus subtilis strain for microbial-enhanced oil recovery. Int J Green Energy 16(7):530–539. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2019.1598416
Yao XW, Xu KL, Li Y (2016) Physicochemical properties and possible applications of waste corncob fly ash from biomass gasification industries of China. BioResources 11(2):3783–3798
Yaseen Y, Gancel F, Bechet M, Drider D, Jacques P (2017) Study of the correlation between fengycin promoter expression and its production by Bacillus subtilis under different culture conditions and the impact on surfactin production. Arch Microbiol 199(10):1371–1382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-017-1406-x
Yeh MS, Wei YH, Chang JS (2006) Bioreactor design for enhanced carrier-assisted surfactin production with Bacillus subtilis. Process Biochem 41(8):1799–1805. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2006.03.027
Yi GB, Liu Q, Lin JZ, Wang WD, Huang H, Li S (2017) Repeated batch fermentation for surfactin production with immobilized Bacillus subtilis BS-37: two-stage pH control and foam fractionation. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 92(3):520–525. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.5028
Zhi Y, Wu Q, Xu Y (2017a) Genome and transcriptome analysis of surfactin biosynthesis in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MT45. Sci Rep 7:13–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40976
Zhi Y, Wu Q, Xu Y (2017b) Production of surfactin from waste distillers' grains by co-culture fermentation of two Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strains. Bioresour Technol 235:96–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.090
Zhou CY, Shi LL, Ye B, Feng HC, Zhang J, Zhang RF, Yan X (2017) pheS (*) , an effective host-genotype-independent counter-selectable marker for marker-free chromosome deletion in Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101(1):217–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7906-9
Zhou D, Hu F, Lin J, Wang W, Li S (2019) Genome and transcriptome analysis of Bacillus velezensis BS-37, an efficient surfactin producer from glycerol, in response to d−/l-leucine. Microbiol Open:e794 doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.794
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21576133) and the Jiangsu Synergetic Innovation Center for Advanced Bio-Manufacture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 187 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, F., Liu, Y., Lin, J. et al. Efficient production of surfactin from xylose-rich corncob hydrolysate using genetically modified Bacillus subtilis 168. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104, 4017–4026 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10528-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10528-9