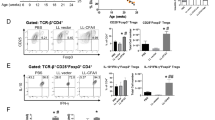
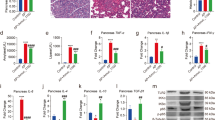
Abstract
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is an autoimmune disease characterized by the self-destruction of insulin-producing β cells. Recently, studies have revealed that neutrophils contribute to the early pathological injury to the pancreas, predominantly via the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). To determine whether early intervention targeting NETs with staphylococcal nuclease (SNase) can delay the onset of T1DM, non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice were orally administered recombinant Lactococcus lactis (L. lactis) expressing SNase. The results showed that NETs were effectively disrupted by SNase both in vivo and in vitro, leading to a significant decrease in neutrophil-derived circulating free DNA (cf-DNA/NETs), neutrophil elastase (NE), and protease 3 (PR3) in the serum compared with the controls. In addition, SNase effectively regulated the blood glucose levels of NOD mice, and the onset of diabetes was postponed with reduced mortality and morbidity. Recombinant L. lactis also ameliorated inflammation in NOD mice, as evidenced by the remarkable increase in IL-4 and reductions in TNF-α and CRP. Moreover, HE staining results showed that L. lactis expressing SNase exerted protective effects on pancreatic islets and relieved inflammation of the small intestine in NOD mice. Hence, the present study indicates that the oral delivery of SNase by L. lactis can effectively prevent T1DM, ameliorate inflammation, and contribute to immunomodulatory balance in NOD mice.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandraki KI, Piperi C, Ziakas PD, Apostolopoulos NV, Makrilakis K, Syriou V, Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Kaltsas G, Kalofoutis A (2008) Cytokine secretion in long-standing diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2: associations with low-grade systemic inflammation. J Clin Immunol 28(4):314–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-007-9164-1
Bahey-El-Din M, Gahan CGM, Griffin BT (2010) Lactococcus lactis as a cell factory for delivery of therapeutic proteins. Curr Gene Ther 10(1):34–45
Berends ETM, Horswill AR, Haste NM, Monestier M, Nizet V, von Kockritz-Blickwede M (2010) Nuclease expression by Staphylococcus aureus facilitates escape from neutrophil extracellular traps. J Innate Immun 2(6):576–586. https://doi.org/10.1159/000319909
Bosch X (2011) Systemic lupus erythematosus and the neutrophil. N Engl J Med 365(8):758–760
Cabrera SM, Henschel AM, Hessner MJ (2016) Innate inflammation in type 1 diabetes. Transl Res 167(1):214–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trsl.2015.04.011
Darrah E, Andrade F (2013) NETs: the missing link between cell death and systemic autoimmune diseases? Front Immunol 3:428. https://doi.org/10.3389/Fimmu.2012.00428
Devaraj S, Glaser N, Griffen S, Wang-Polagruto J, Miguelino E, Jialal I (2006) Increased monocytic activity and biomarkers of inflammation in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 55(3):774–779
Devaraj S, Cheung AT, Jialal I, Griffen SC, Nguyen D, Glaser N, Aoki T (2007) Evidence of increased inflammation and microcirculatory abnormalities in patients with type 1 diabetes and their role in microvascular complications. Diabetes 56(11):2790–2796. https://doi.org/10.2337/db07-0784
Diana J, Simoni Y, Furio L, Beaudoin L, Agerberth B, Barrat F, Lehuen A (2013) Crosstalk between neutrophils, B-1a cells and plasmacytoid dendritic cells initiates autoimmune diabetes. Nat Med 19(1):65–73. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3042
Farrera C, Fadeel B (2013) Macrophage clearance of neutrophil extracellular traps is a silent process. J Immunol 191(5):2647–2656. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1300436
Fuchs TA, Abed U, Goosmann C, Hurwitz R, Schulze I, Wahn V, Weinrauch Y, Brinkmann V, Zychlinsky A (2007) Novel cell death program leads to neutrophil extracellular traps. J Cell Biol 176(2):231–241. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200606027
Goldfine AB, Shoelson SE (2017) Therapeutic approaches targeting inflammation for diabetes and associated cardiovascular risk. J Clin Invest 127(1):83–93. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI88884
Herder C (2016) Inflammation and cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction in patients with diabetes: update from the annual meeting of FID 2016 in Berne. Diabetes Stoffwechsel Und Herz 25(6):366–367
Hong L, Lang JC, He DM (2017) Studies on preparation and properties of staphylococcal nuclease [J]. J China Pharm Univ 48(2):214–219
Isa M, Amin M, Pranoto A, Mertaniasih NM (2013) The role of TLR-2, TNF-α, IL-4 in diabetes mellitus patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Respirology 18:63–63
Kenny EF, Herzig A, Kruger R, Muthu A, Mondal S, Thompson PR, Brinkman V, von Bernuth H, Zychlinsky A (2017) Diverse stimuli engage different neutrophil extracellular trap pathways. Elife 6:e24437. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.24437
Kessenbrock K, Krumbholz M, Schonermarck U, Back W, Gross WL, Werb Z, Grone HJ, Brinkmann V, Jenne DE (2009) Netting neutrophils in autoimmune small-vessel vasculitis. Nat Med 15(6):623–625. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.1959
Khandpur R, Carmona-Rivera C, Vivekanandan-Giri A, Gizinski A, Yalavarthi S, Knight JS, Friday S, Li S, Patel RM, Subramanian V, Thompson P, Chen P, Fox DA, Pennathur S, Kaplan MJ (2013) NETs are a source of citrullinated autoantigens and stimulate inflammatory responses in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Transl Med 5(178):178ra40. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3005580
Ko KS, Lee M, Koh JJ, Kim SW (2001) Combined administration of plasmids encoding IL-4 and IL-10 prevents the development of autoimmune diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. Mol Ther 4(4):313–316. https://doi.org/10.1006/mthe.2001.0459
Leslie RDG, Bradford C (2014) Autoimmune diabetes: caught in a NET. Diabetes 63(12):4018–4020. https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-1382
Liu F, Chen HY, Huang XR, Chung ACK, Zhou L, Fu P, Szalai AJ, Lan HY (2011) C-reactive protein promotes diabetic kidney disease in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 54(10):2713–2723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-011-2237-y
Liu W, Tan Z, Xue J, Luo W, Song H, Lv X, Zheng T, Xi T, Xing Y (2016a) Therapeutic efficacy of oral immunization with a non-genetically modified Lactococcus lactis-based vaccine CUE-GEM induces local immunity against helicobacter pylori infection. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100(14):6219–6229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7333-y
Liu KF, Liu XR, Li GL, Lu SP, Jin L, Wu J (2016b) Oral administration of Lactococcus lactis-expressing heat shock protein 65 and tandemly repeated IA2P2 prevents type 1 diabetes in NOD mice. Immunol Lett 174:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2016.04.008
Ma YJ, Liu JJ, Hou J, Dong YK, Lu Y, Jin L, Cao R, Li TM, Wu J (2014) Oral Administration of Recombinant Lactococcus lactis expressing HSP65 and tandemly repeated P277 reduces the incidence of type I diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice. PLoS One 9(8):e105701. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0105701
Margraf S, Logters T, Reipen J, Altrichter J, Scholz M, Windolf J (2008) Neutrophil-derived circulating free DNA (cf-DNA/NETs): a potential prognostic marker for posttraumatic development of inflammatory second hit and sepsis. Shock 30(4):352–358. https://doi.org/10.1097/ SHK.0b013e31 816a 6bb1
Maugeri N, Rovere-Querini P, Manfredi AA (2016) Disruption of a regulatory network consisting of neutrophils and platelets fosters persisting inflammation in rheumatic diseases. Front Immunol 7:182. https://doi.org/10.3389/Fimmu.2016.00182
Mejia-Leon ME, Barca AM (2015) Diet, microbiota and immune system in type 1 diabetes development and evolution. Nutrients 7(11):9171–9184. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7115461
Menegazzo L, Ciciliot S, Poncina N, Mazzucato M, Persano M, Bonora B, Albiero M, de Kreutzenberg SV, Avogaro A, Fadini GP (2015) NETosis is induced by high glucose and associated with type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol 52(3):497–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-014-0676-x
Meyer-Hoffert U, Wiedow O (2011) Neutrophil serine proteases: mediators of innate immune responses. Curr Opin Hematol 18(1):19–24. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOH.0b013e32834115d1
Mocsai A (2013) Diverse novel functions of neutrophils in immunity, inflammation, and beyond. J Exp Med 210(7):1283–1299. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20122220
Murri M, Leiva I, Gomez-Zumaquero JM, Tinahones FJ, Cardona F, Soriguer F, Queipo-Ortuno MI (2013) Gut microbiota in children with type 1 diabetes differs from that in healthy children: a case-control study. BMC Med 11:46. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7015-11-46
Pham CTN (2008) Neutrophil serine proteases fine-tune the inflammatory response. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40(6–7):1317–1333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2007.11.008
Rao XQ, Zhong JX, Sun QH (2014) The heterogenic properties of monocytes/macrophages and neutrophils in inflammatory response in diabetes. Life Sci 116(2):59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.lfs. 2014.09.015
Robert S, Gysemans C, Takiishi T, Korf H, Spagnuolo I, Sebastiani G, Van Huynegem K, Steidler L, Caluwaerts S, Demetter P, Wasserfall CH, Atkinson MA, Dotta F, Rottiers P, Van Belle TL, Mathieu C (2014) Oral delivery of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD)-65 and IL10 by Lactococcus lactis reverses diabetes in recent-onset NOD mice. Diabetes 63(8):2876–2887. https://doi.org/10.2337/db13-1236
Roth Flach RJ, Czech MP (2015) NETs and traps delay wound healing in diabetes. Trends Endocrinol Metab 26(9):451–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2015.07.004
Thammavongsa V, Missiakas DM, Schneewind O (2013) Staphylococcus aureus degrades neutrophil extracellular traps to promote immune cell death. Science 342(6160):863–866. https://doi.org/10.1126/ science.1242255
Thomas GM, Carbo C, Curtis BR, Martinod K, Mazo IB, Schatzberg D, Cifuni SM, Fuchs TA, von Andrian UH, Hartwig JH, Aster RH, Wagner DD (2012) Extracellular DNA traps are associated with the pathogenesis of TRALI in humans and mice. Blood 119(26):6335–6343. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-01-405183
Wang Y, Xiao Y, Zhong L, Ye D, Zhang J, Tu Y, Bornstein SR, Zhou Z, Lam KS, Xu A (2014) Increased neutrophil elastase and proteinase 3 and augmented NETosis are closely associated with beta-cell autoimmunity in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 63(12):4239–4248. https://doi.org/10.2337/db14-0480
Wiedow O, Meyer-Hoffert U (2005) Neutrophil serine proteases: potential key regulators of cell signalling during inflammation. J Intern Med 257(4):319–328
Wong SL, Demers M, Martinod K, Gallant M, Wang YM, Goldfine AB, Kahn CR, Wagner DD (2015) Diabetes primes neutrophils to undergo NETosis, which impairs wound healing. Nat Med 21(7):815. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.3887
Wright TK, Gibson PG, Simpson JL, McDonald VM, Wood LG, Baines KJ (2016) Neutrophil extracellular traps are associated with inflammation in chronic airway disease. Respirology 21(3):467–475. https://doi.org/10.1111/resp.12730
Wu J, Lang JC, Liu KF(2016) Recombinant lactococcus lactis and SNase in the development of drugs for prevention and treatment of T1DM. CN Patent 201610353343.5
Acknowledgements
L. lactis strains were kindly provided by Professor Shuhua Tan, School of Life Science and Technology, China Pharmaceutical University. The English language of this article was edited by American Journal Experts.
Funding
This work was supported by the China National Natural Science Fund Committee (Grant Nos. 81172973 and 81673340), the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, No. 2015AA020314), the Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. BK20161462), and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lang, J., Wang, X., Liu, K. et al. Oral delivery of staphylococcal nuclease by Lactococcus lactis prevents type 1 diabetes mellitus in NOD mice. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 7653–7662 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8480-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8480-5